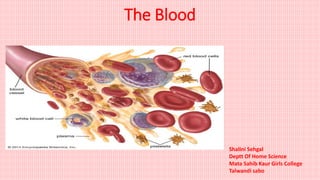
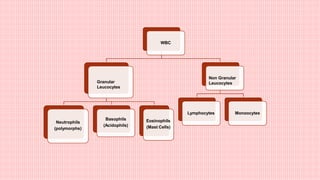
This document summarizes the components of blood - plasma and blood cells. Plasma contains water, salts, proteins, antibodies, hormones, nutrients, waste products, blood clotting substances and enzymes. The three main types of blood cells are red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells carry oxygen and carbon dioxide using hemoglobin. White blood cells help fight infections. Platelets help form blood clots to stop bleeding.