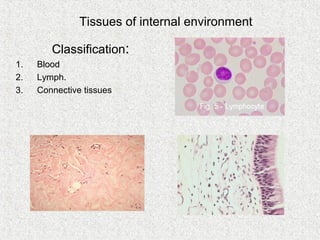
1. The document discusses the tissues of the internal environment, including blood, lymph, and connective tissues.
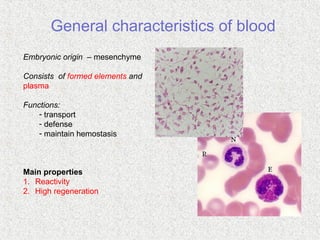
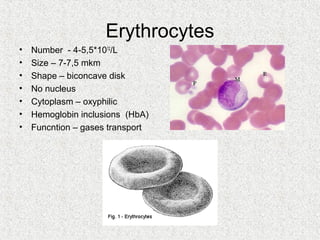
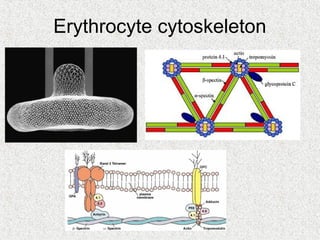
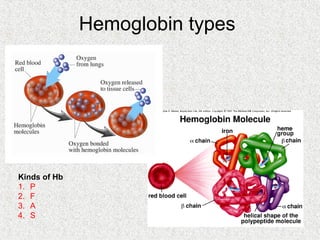
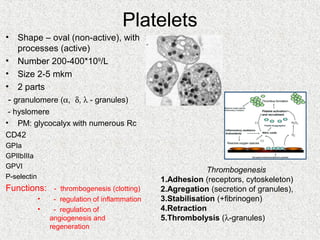
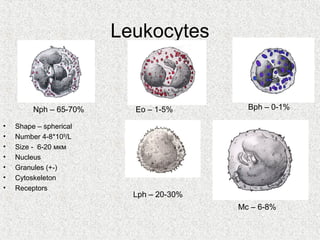
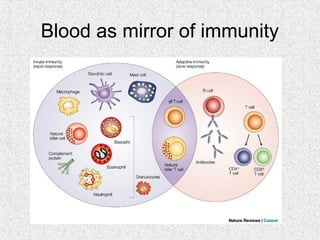
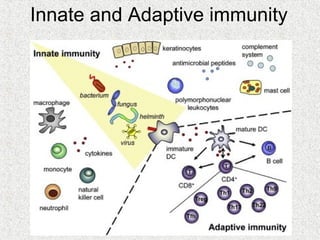
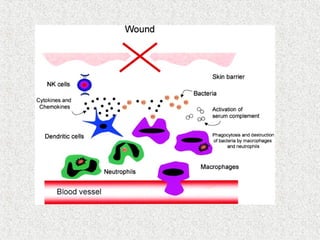
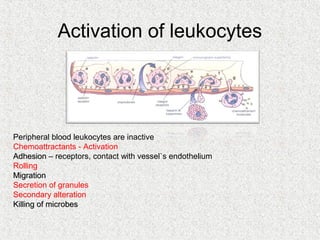
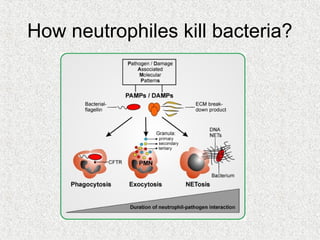
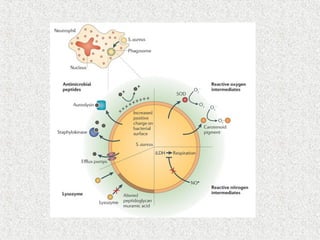
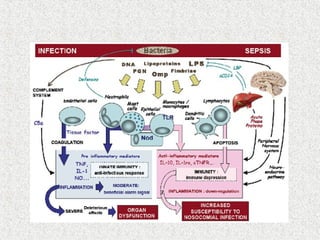
2. Blood consists of formed elements and plasma, and functions include transport, defense, and maintaining hemostasis. It contains erythrocytes, platelets, and leukocytes.
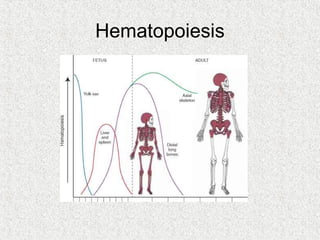
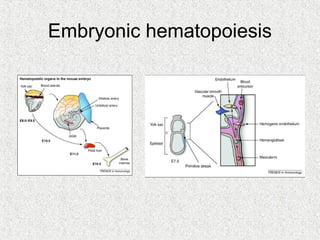
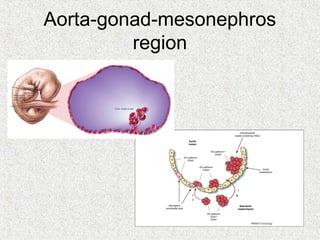
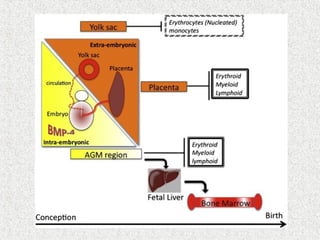
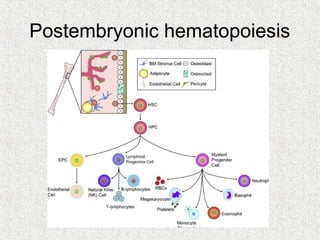
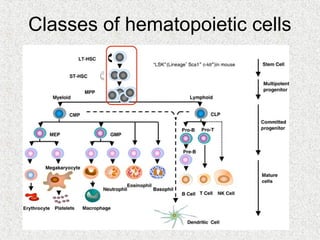
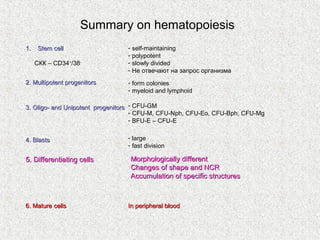
3. Hematopoiesis is the process by which blood cells are formed from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow through determination of multipotent progenitors into oligo- and unipotent progenitors and then mature blood cell types.