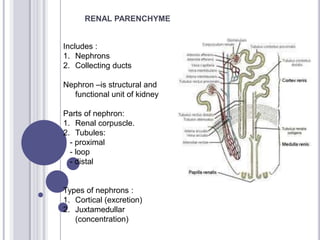
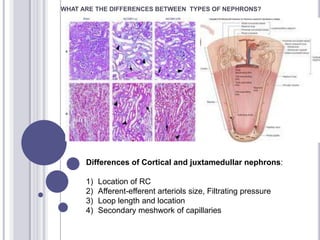
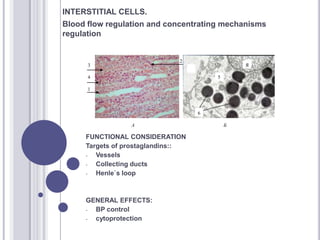
The urinary system consists of the kidneys and urinary tract. The kidneys contain nephrons, which are the functional filtering units. Nephrons contain a renal corpuscle with a glomerulus for blood filtration and tubules for reabsorption and secretion. There are cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons. The kidneys filter blood and produce urine, which drains through the ureters into the urinary bladder and exits through the urethra.