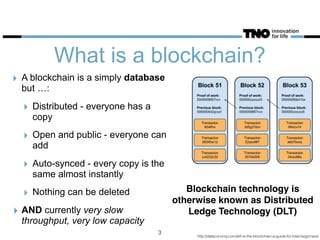
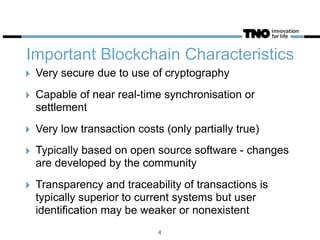
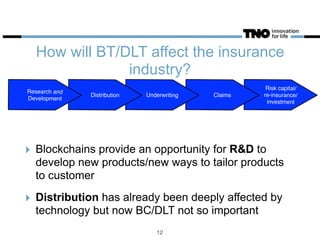
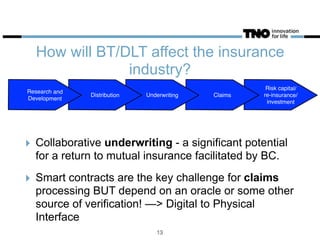
This document discusses opportunities and challenges for blockchain technology in the insurance industry. It begins by explaining what blockchains and bitcoin are, highlighting key characteristics like security, transparency, and low transaction costs. Blockchains could reduce insurance fraud by providing permanent ledgers and could enable smart contracts to automate certain insurance processes. However, smart contracts still require an "oracle" to verify events in the physical world. The document examines how blockchains could impact different parts of the insurance value chain and considers several real-world blockchain insurance projects and examples.