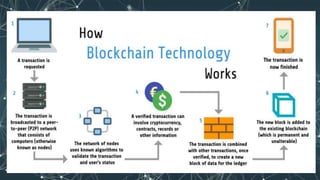
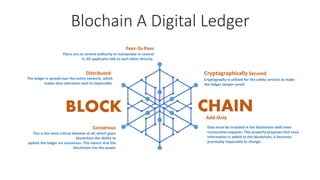
The document discusses the history and evolution of Bitcoin and blockchain technology, highlighting key milestones from its inception in 2008 to its growth in value and acceptance. It explains the fundamental characteristics of blockchain as a decentralized, secure, and tamper-proof digital ledger that operates through consensus among participants. Additionally, the document emphasizes the benefits of blockchain technology, including improved security, increased efficiency, and the elimination of intermediaries.