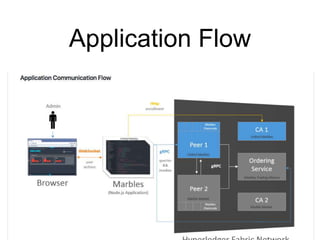
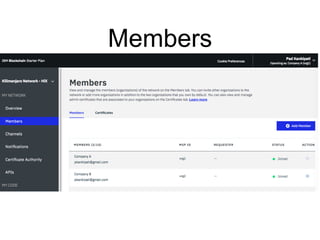
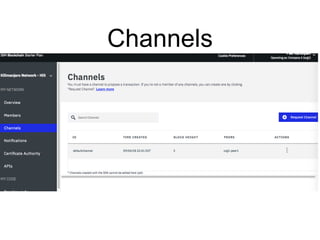
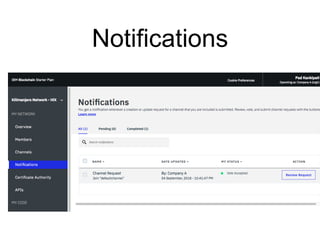
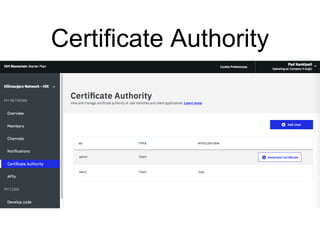
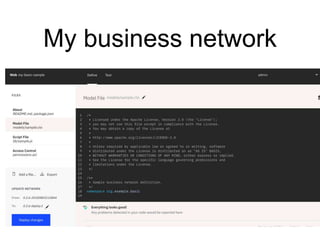
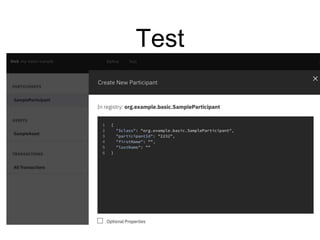
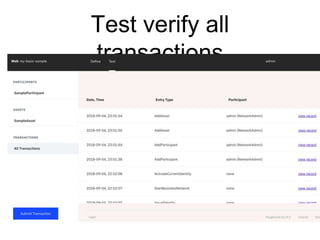
Hyperledger Fabric is an open-source blockchain framework that allows for the creation of permissioned distributed ledgers through the use of smart contracts and pluggable consensus mechanisms. It uses a modular architecture including ordering services, membership services, peer-to-peer gossip, and smart contracts to validate transactions. Permissioned blockchains like Hyperledger Fabric provide identity management that allows known participants to securely conduct transactions while permissionless blockchains are open for anyone to participate anonymously.