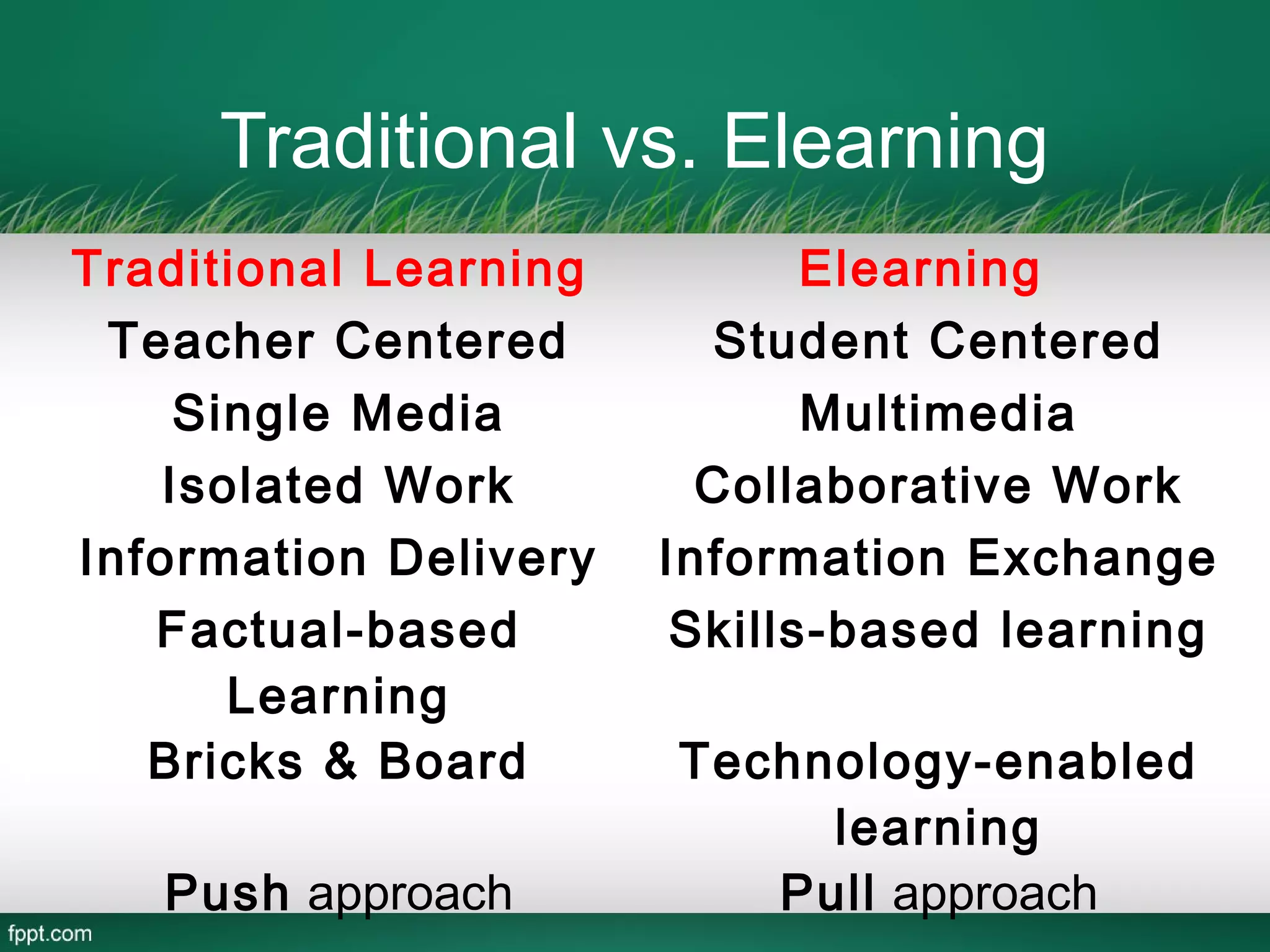
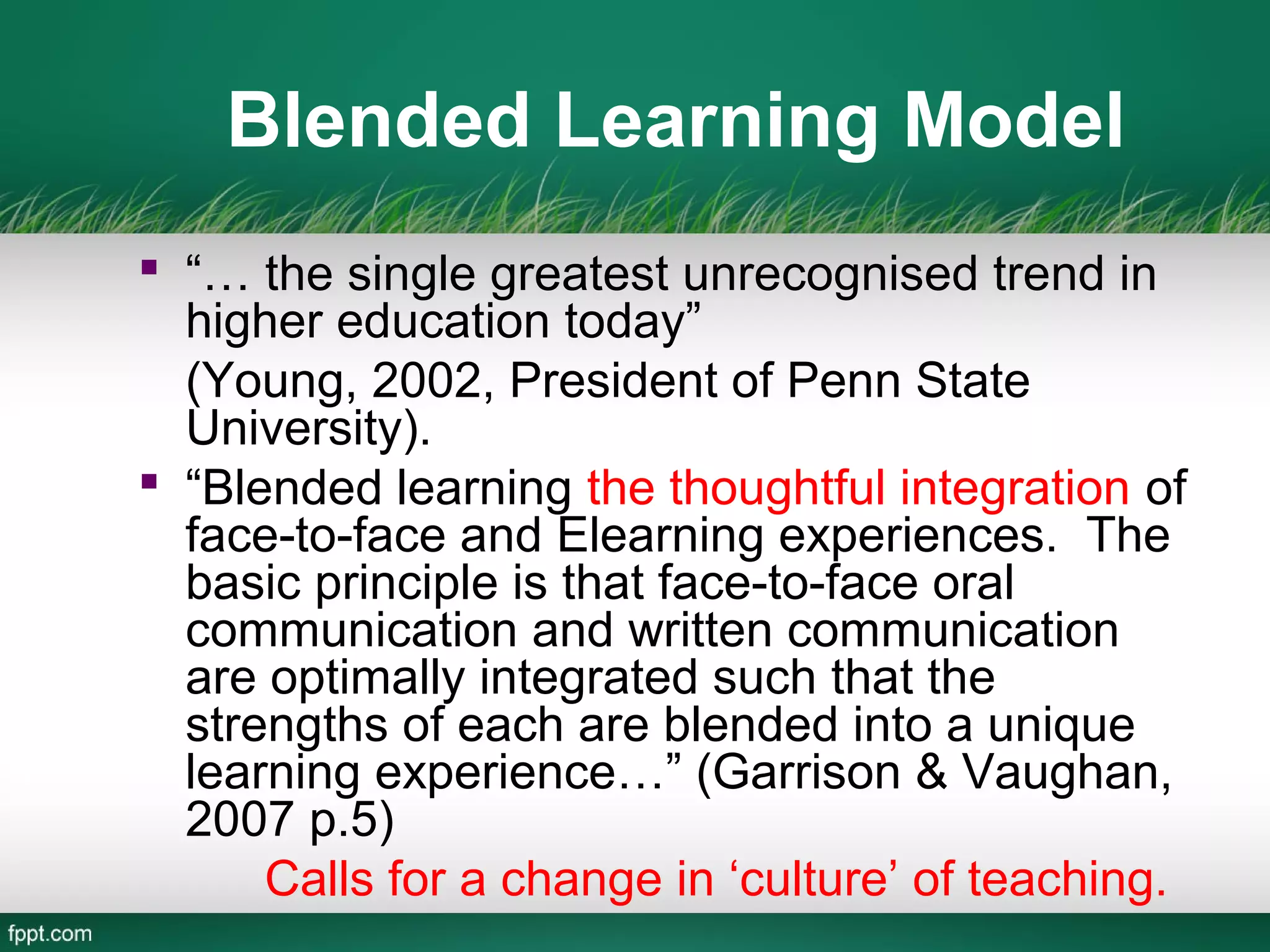
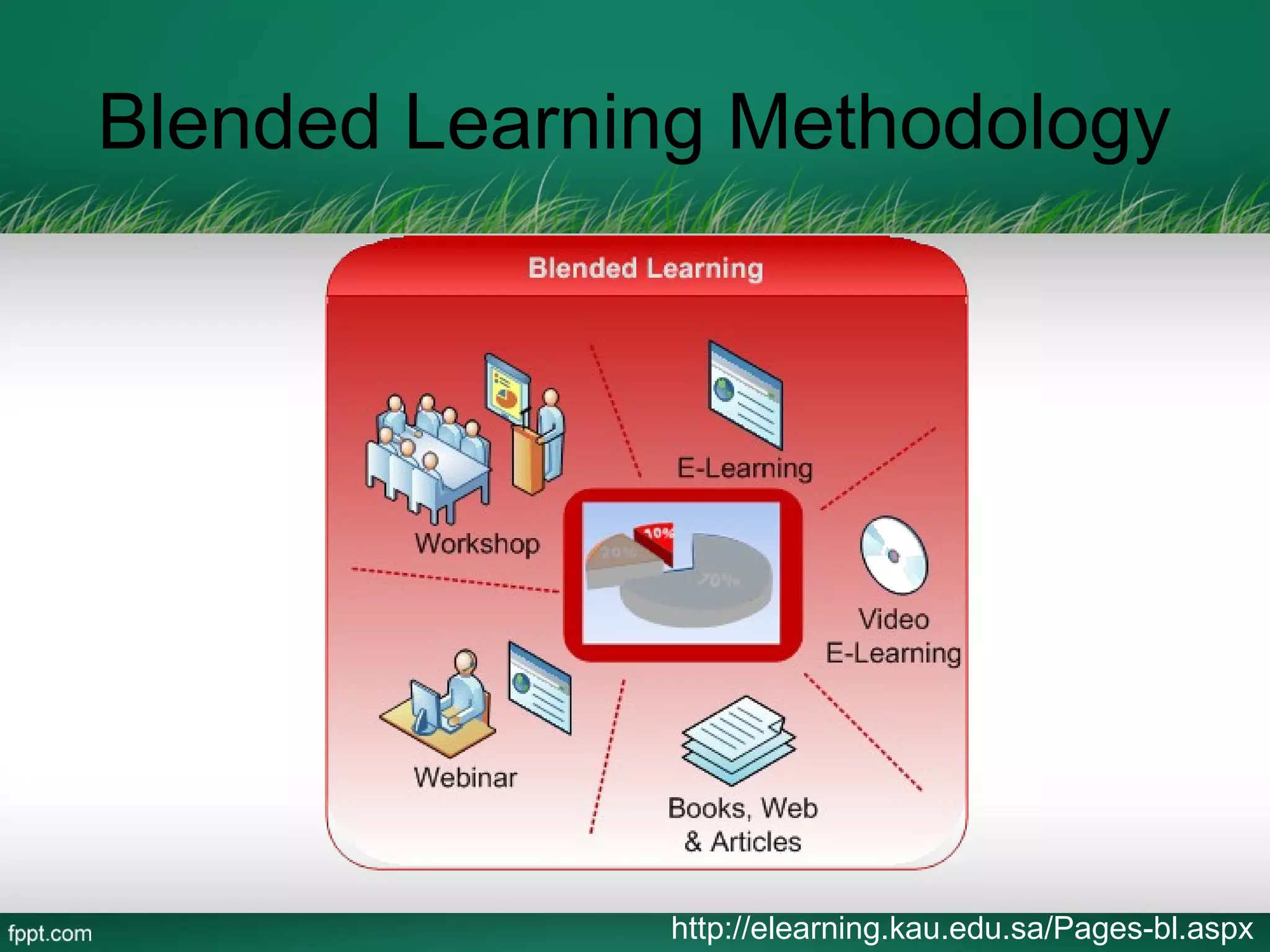
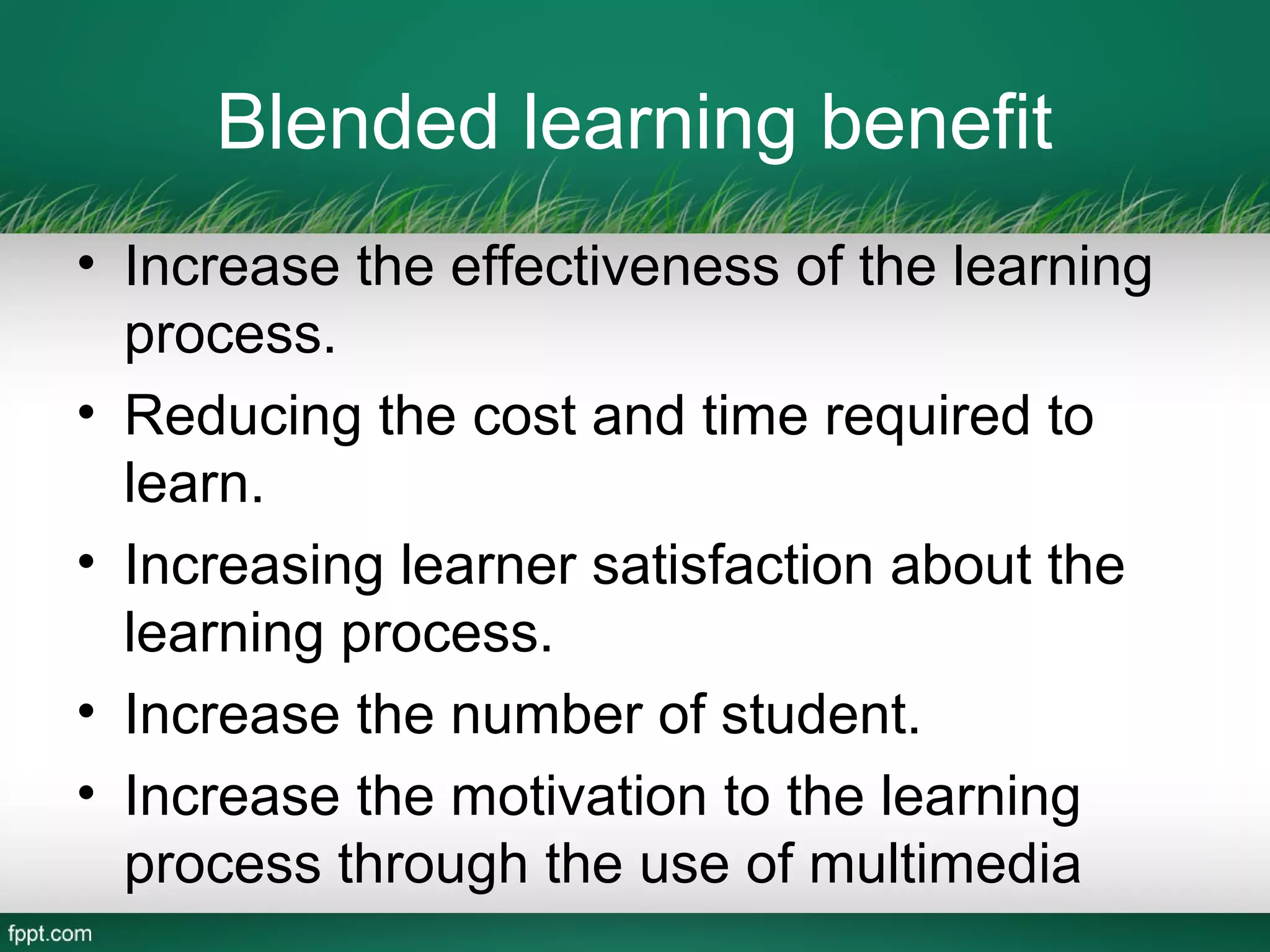
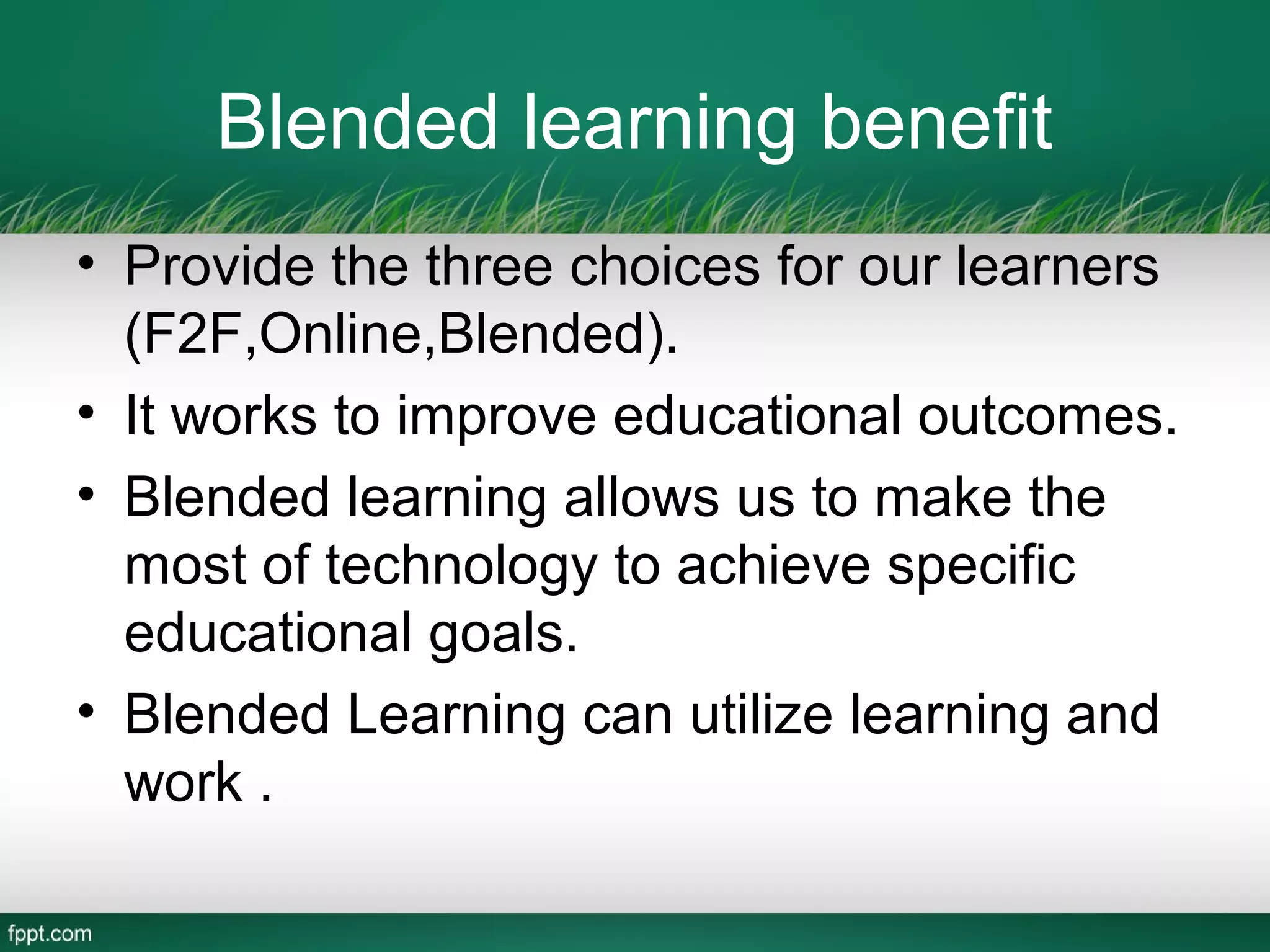
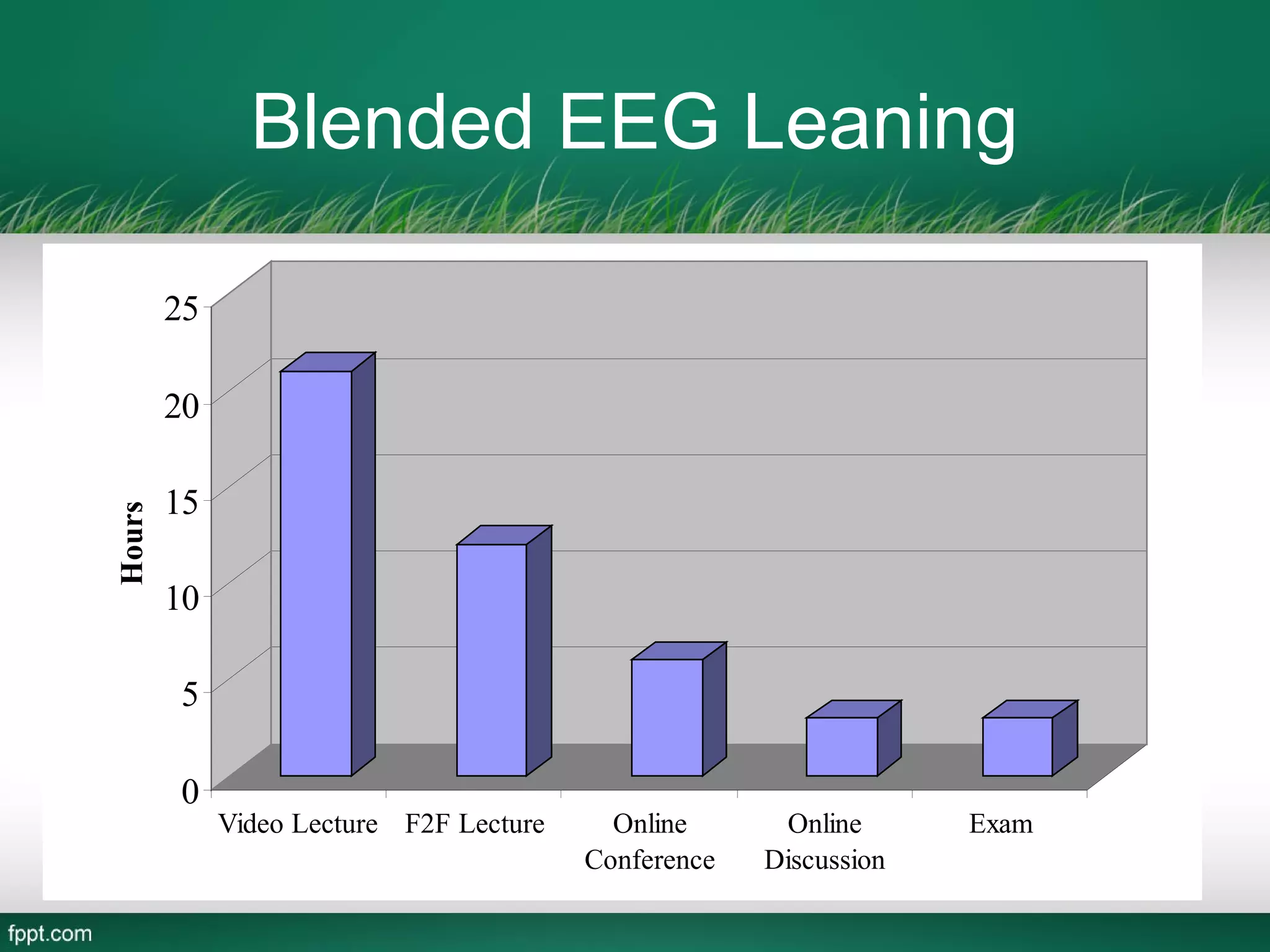
This document outlines a blended learning model for a master's course in engineering and environmental geology at the Asian Institute of Technology in Vietnam. It begins by describing traditional and e-learning models and their advantages and disadvantages. It then introduces a blended learning model that combines face-to-face instruction, online video lectures, online discussions, and international expert conferences. The document provides details of an environmental engineering geology course schedule using this blended approach, mixing online and in-person activities over several weeks. The goal is to increase learning effectiveness, reduce costs and time, and boost student satisfaction and numbers by integrating online and classroom experiences.