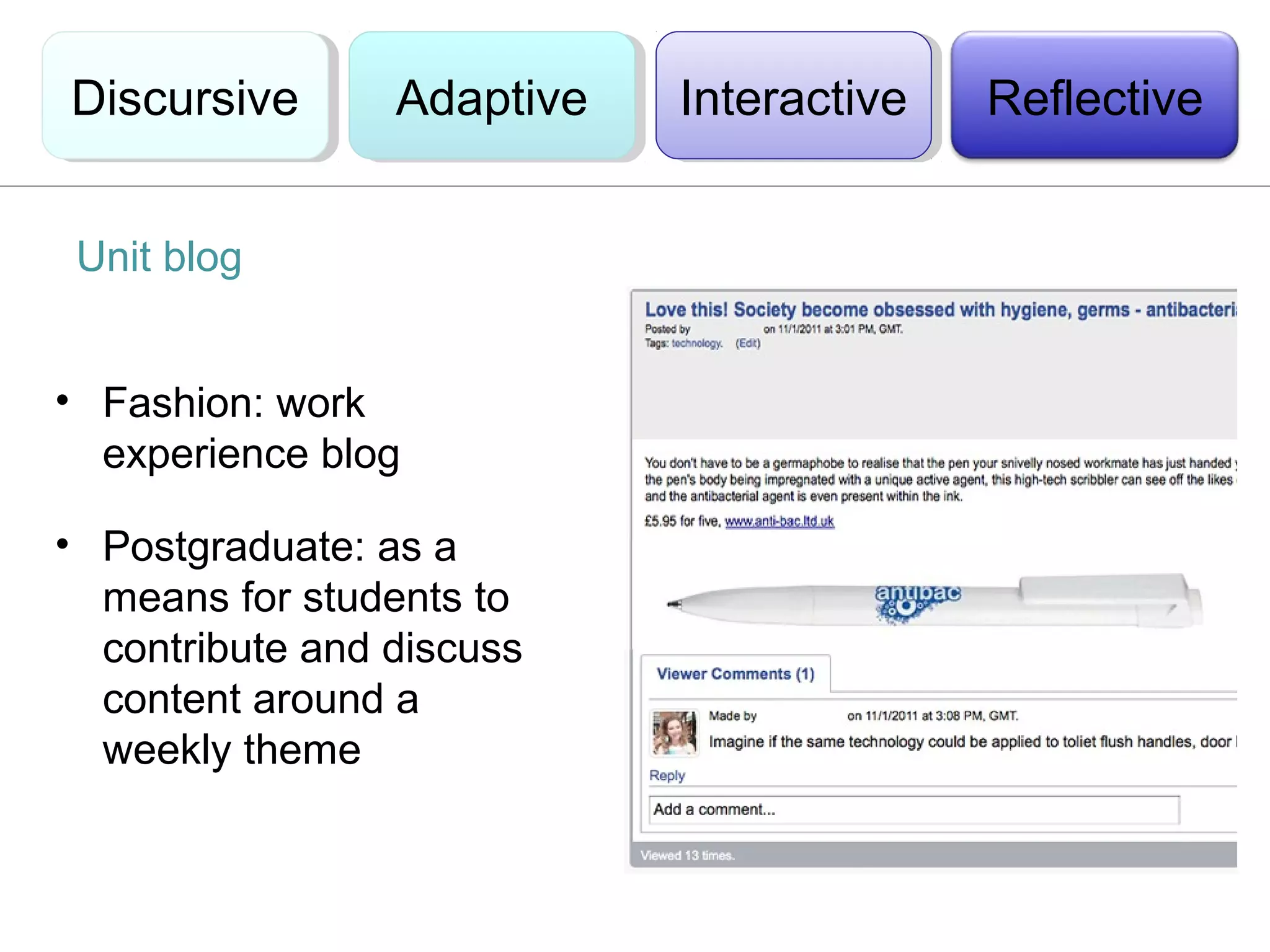
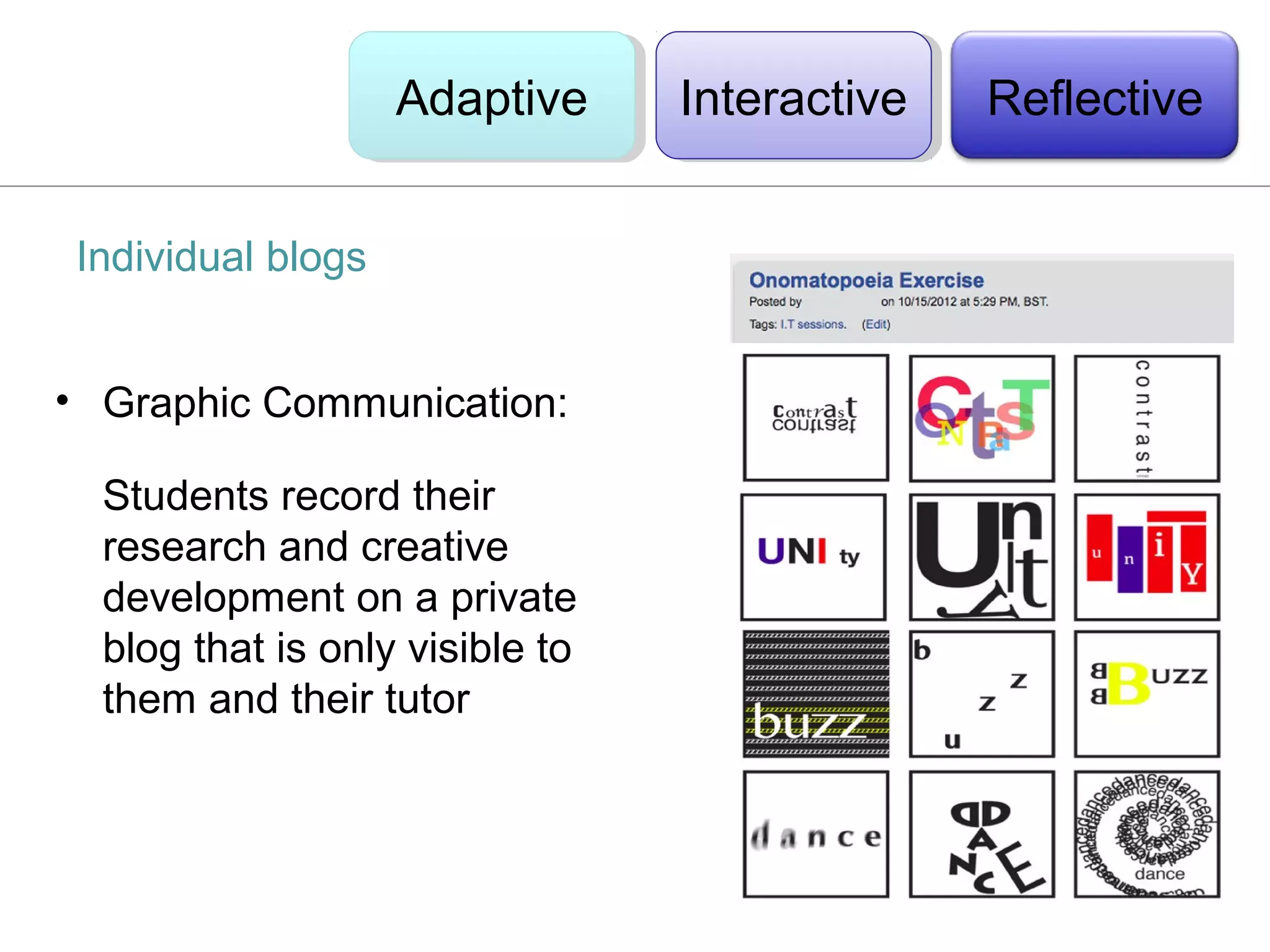
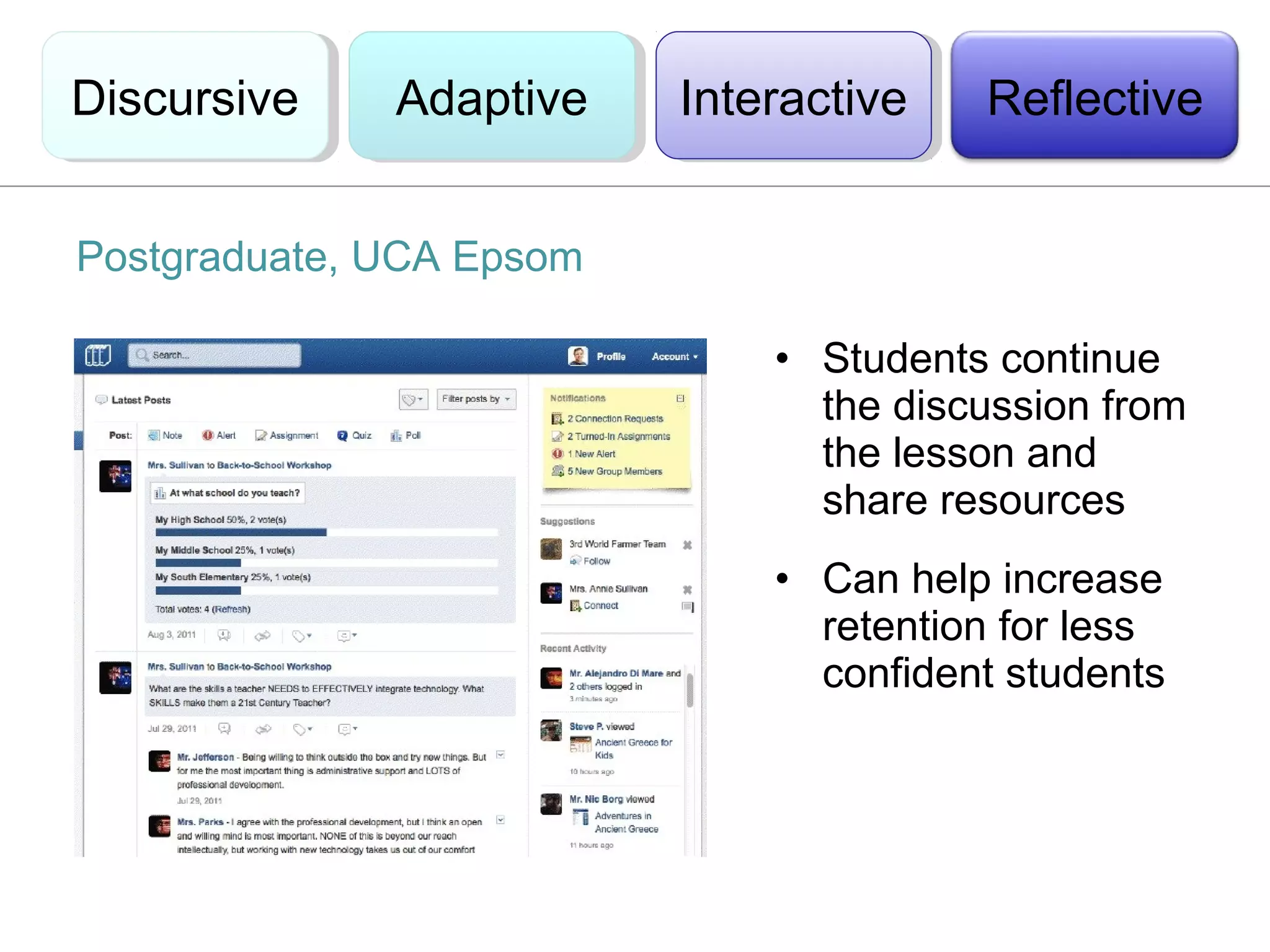
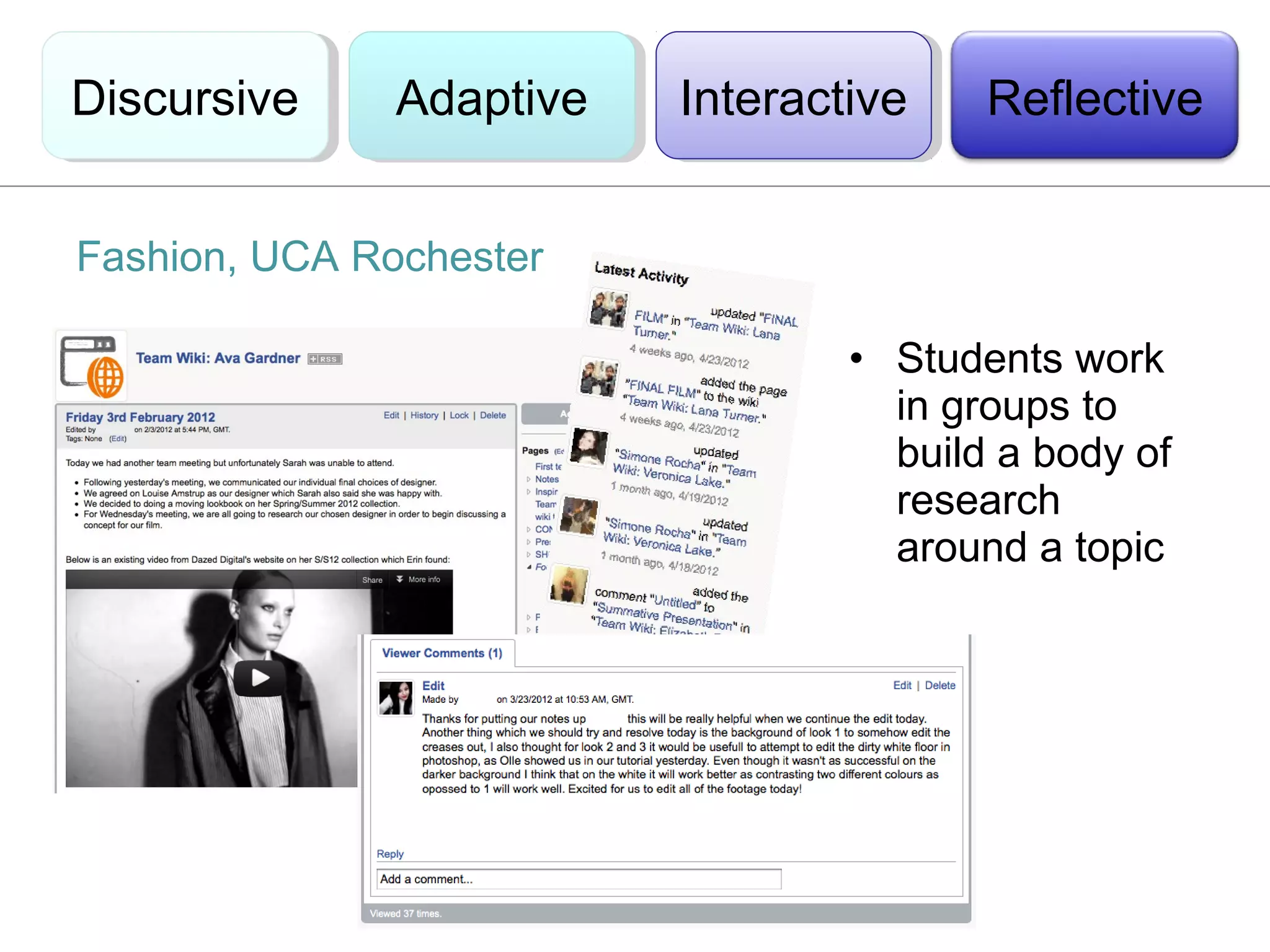
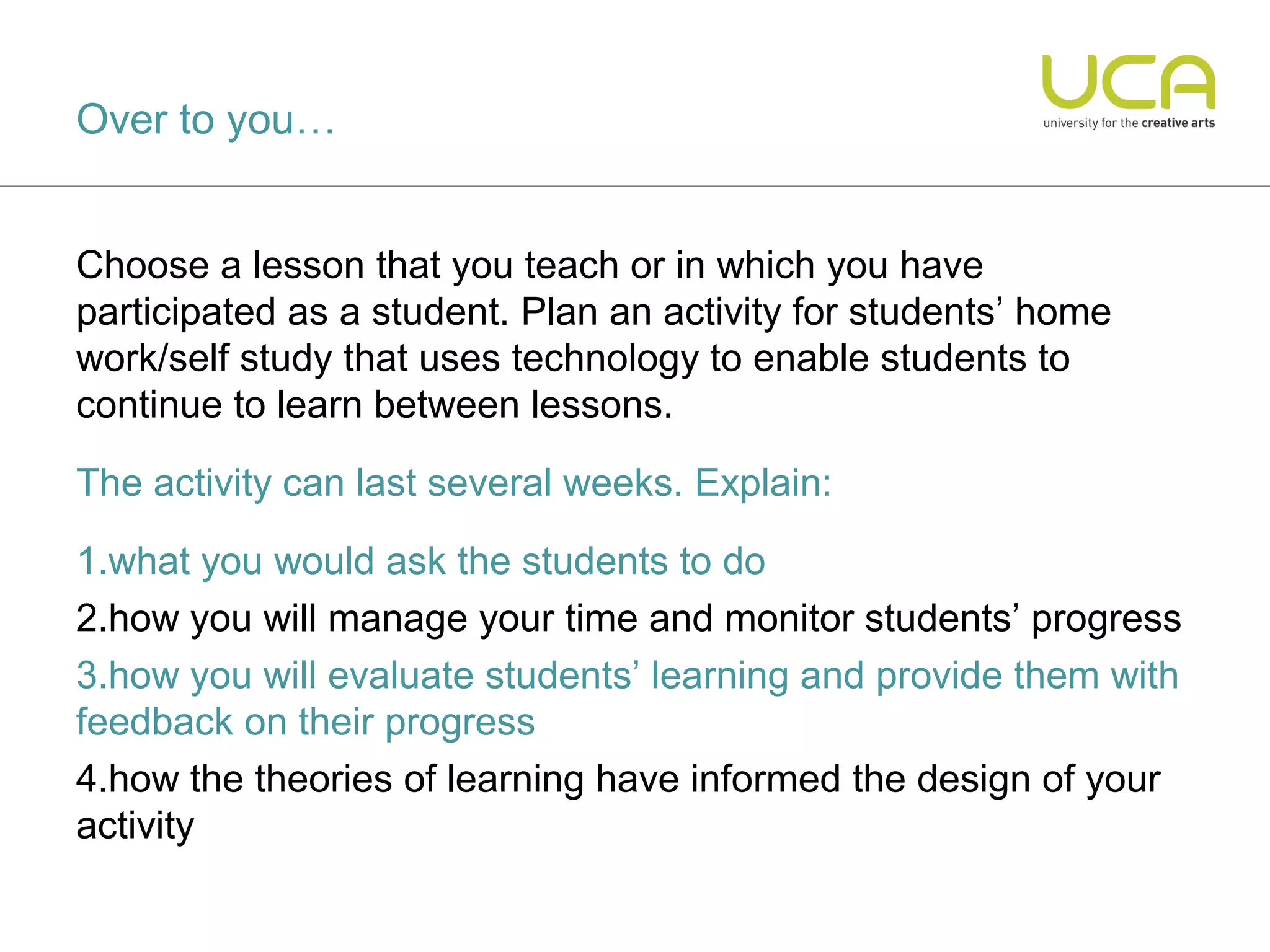
This document discusses the integration of technology in education through blended learning and e-environments, emphasizing methods to enhance inclusive online activities. It reviews various learning theories, including behaviorism, cognitivism, and constructivism, and their implications for teaching practices with technology. The text also outlines practical approaches and examples of technology use in various educational settings to support student learning and interaction.




![Some theories of learning
Deep / surface learning (Marton & Saljo, 1979)
understanding (deep) memorising (surface)
making sense (deep) strategic (surface)
A deep learner: articulate, autonomous but collaborative with high
meta-cognitive control and the generic skills of learning…they
have developed a certain kind of learner identity (Simms, 2006)
“In learning with and through [technology], young people are also
learning how to learn” (Buckingham 2008: 17)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pgc1-3blendedlearninge-environments-121023121700-phpapp01/75/PGC1-3-Blended-Learning-e-Environments-5-2048.jpg)