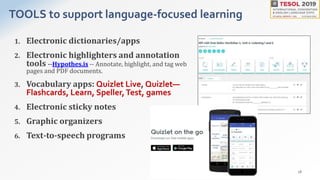
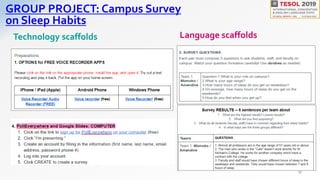
Christine Bauer-Ramazani presented best practices for integrating technology into an intensive English program through blended learning. She discussed using learning management systems and flipped learning to extend classroom learning outside of class time. The presentation outlined how to implement the four strands of language teaching - meaning-focused input, meaning-focused output, language-focused learning, and fluency development - using various digital tools. Examples of tools that can be used to support the different strands included learning management systems, vocabulary apps, voice recording tools, and collaborative writing platforms. The goal of blended learning is to take full advantage of digital platforms in order to design effective learning experiences and scaffold assignments with technology.