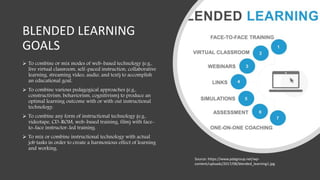
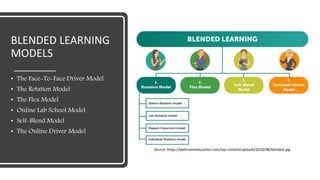
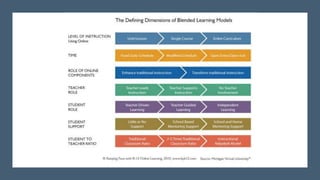
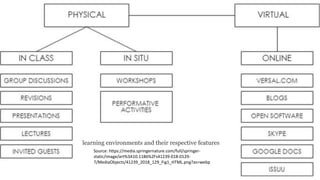
Blended learning combines traditional in-person classroom methods with online and digital learning. It allows incorporating different teaching methods and technologies to optimize learning. Blended learning mixes self-paced online learning with live virtual or in-person classroom sessions, allowing a gradual transition from traditional to online. When used for architecture education, blended learning transforms the design studio into a collaborative online and in-person space where students work on project-based learning and receive feedback from peers and instructors in various formats.