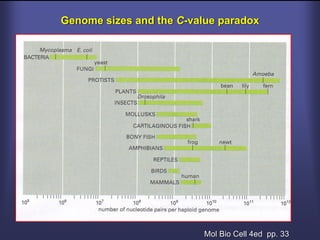
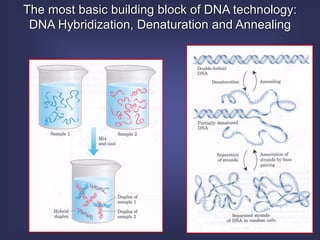
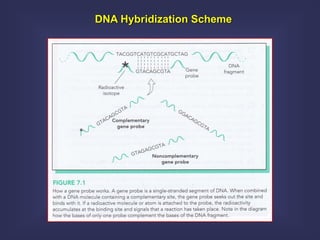
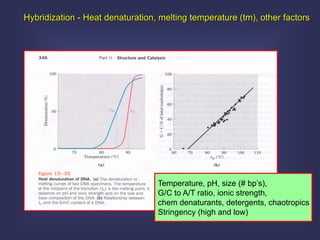
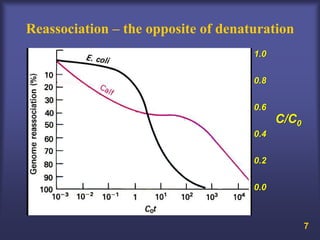
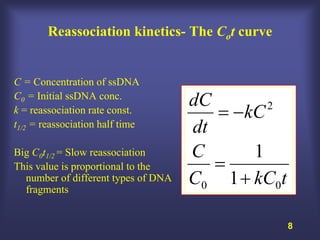
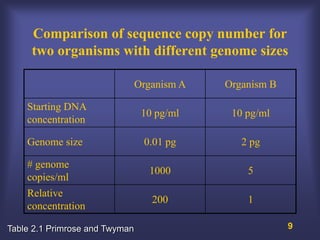
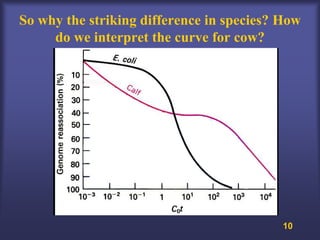
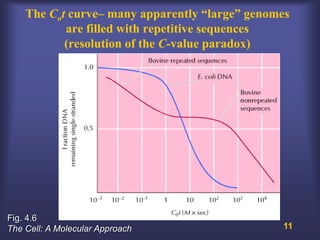
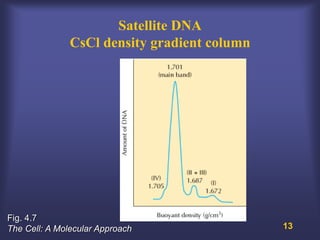
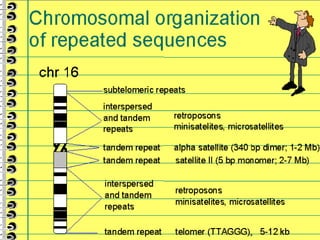
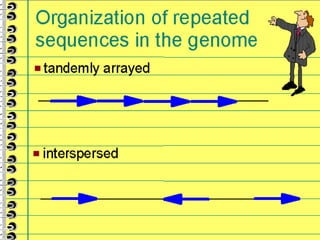
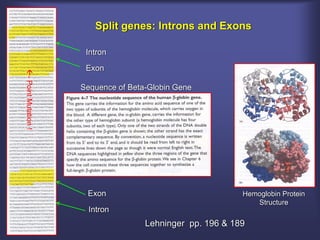
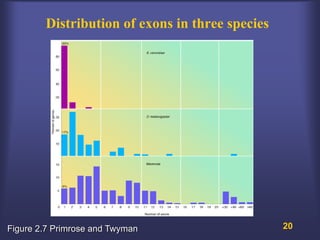
This lecture discusses genome organization and structure. It covers topics like genome size, DNA hybridization, Cot curves, repeated sequences, introns and exons. Cot curves show that apparently large genomes are filled with repetitive sequences, resolving the C-value paradox. There are two types of repeated sequences - tandem repeats like satellites and interspersed repeats like retrotransposons and SINEs. Genome structure includes features like linear/circular chromosomes, centromeres, telomeres, GC content distributions. Genes contain exons and introns, and detecting open reading frames is a way to predict genes, though it works better in prokaryotes than eukaryotes due to intron sizes.