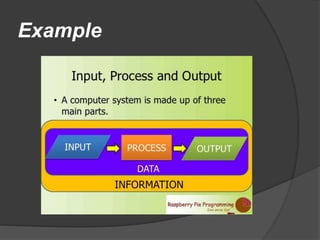
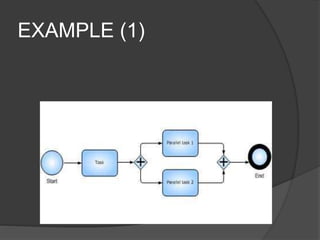
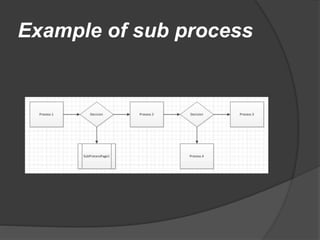
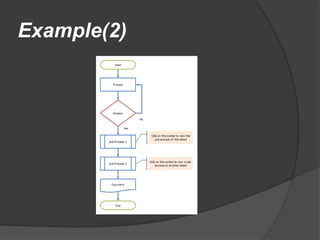
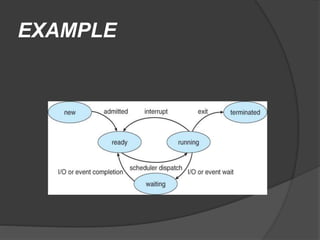
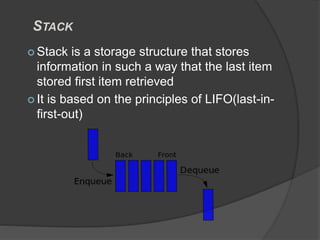
The document discusses BIOS, the boot process, processes, and stacks. It begins by explaining that BIOS initializes hardware and loads the boot loader. It describes cold booting when powering on and warm booting for restarting the OS after a crash. A process is an executing computer program containing code and activity. Processes can create child processes and have various states like running and waiting. A stack uses LIFO to temporarily store information for program execution using a stack pointer to track the top address.