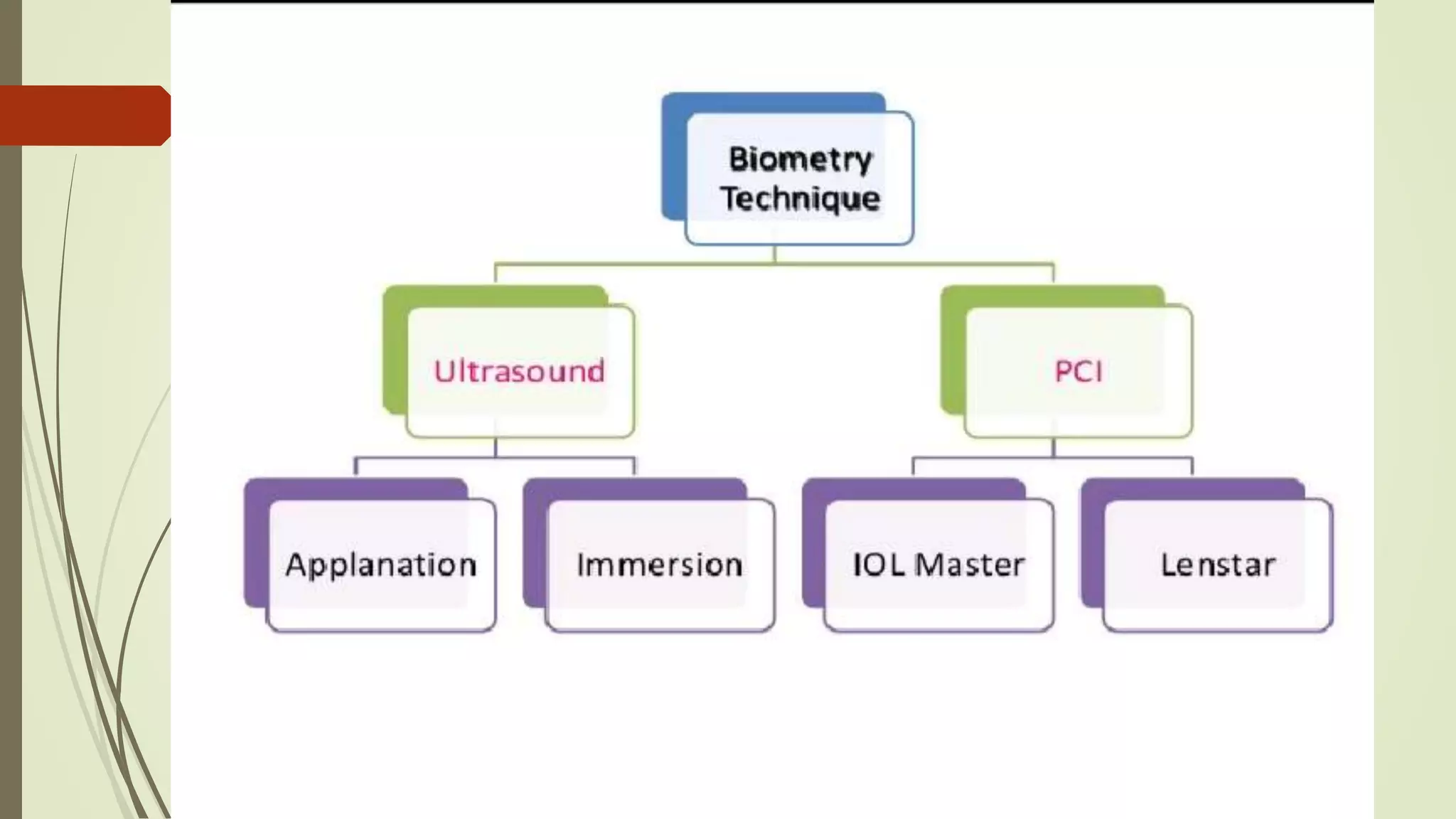
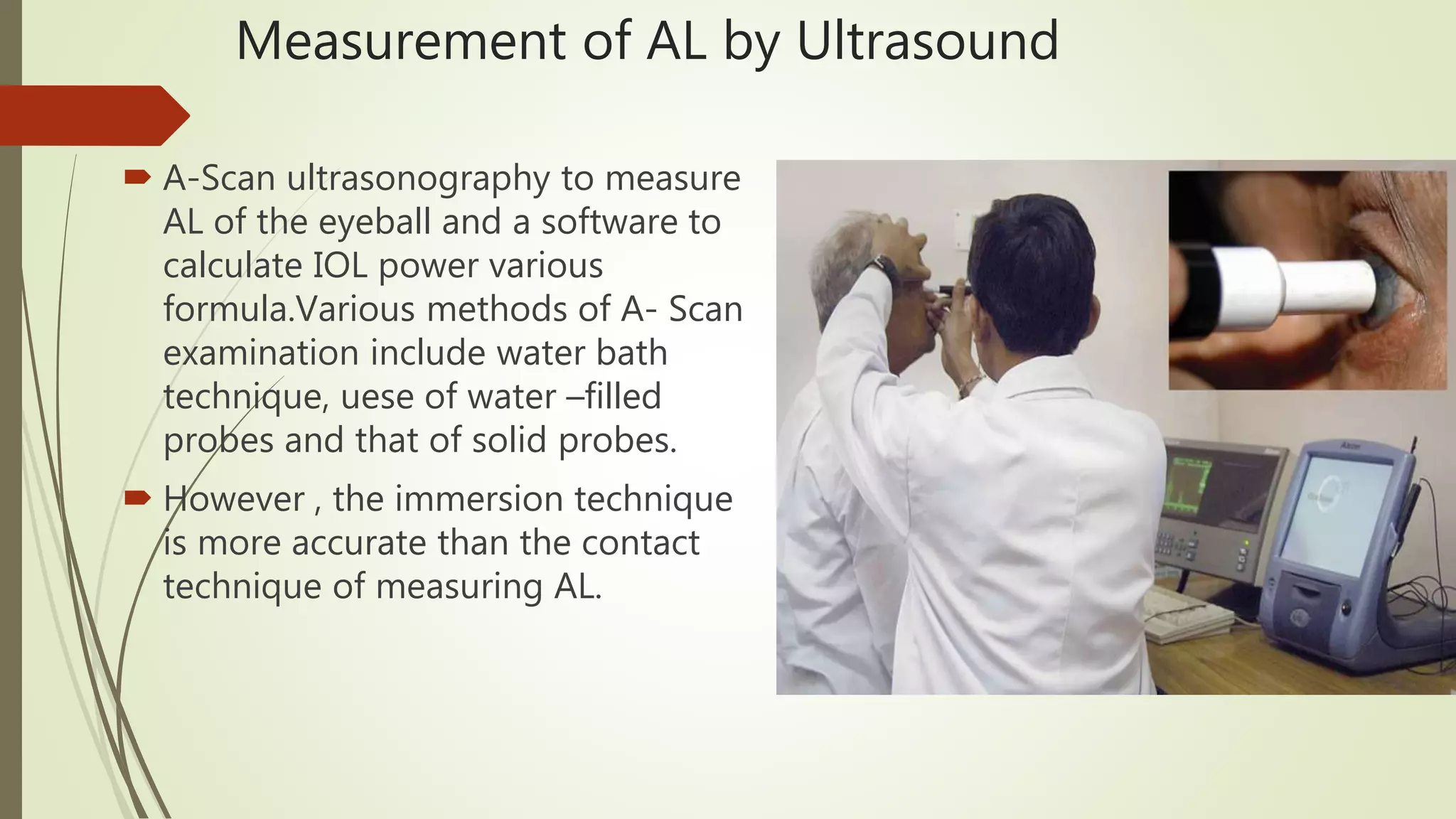
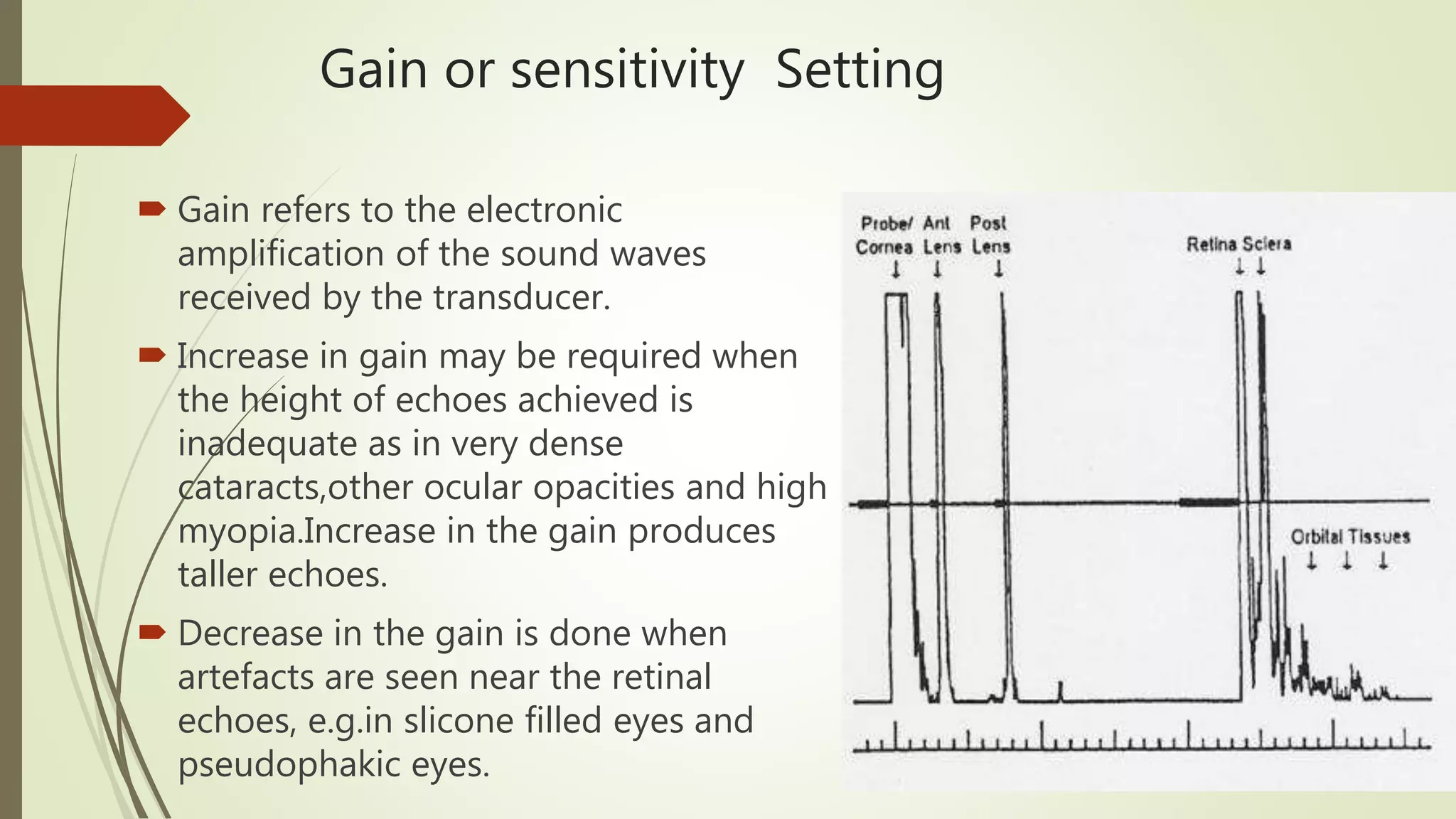
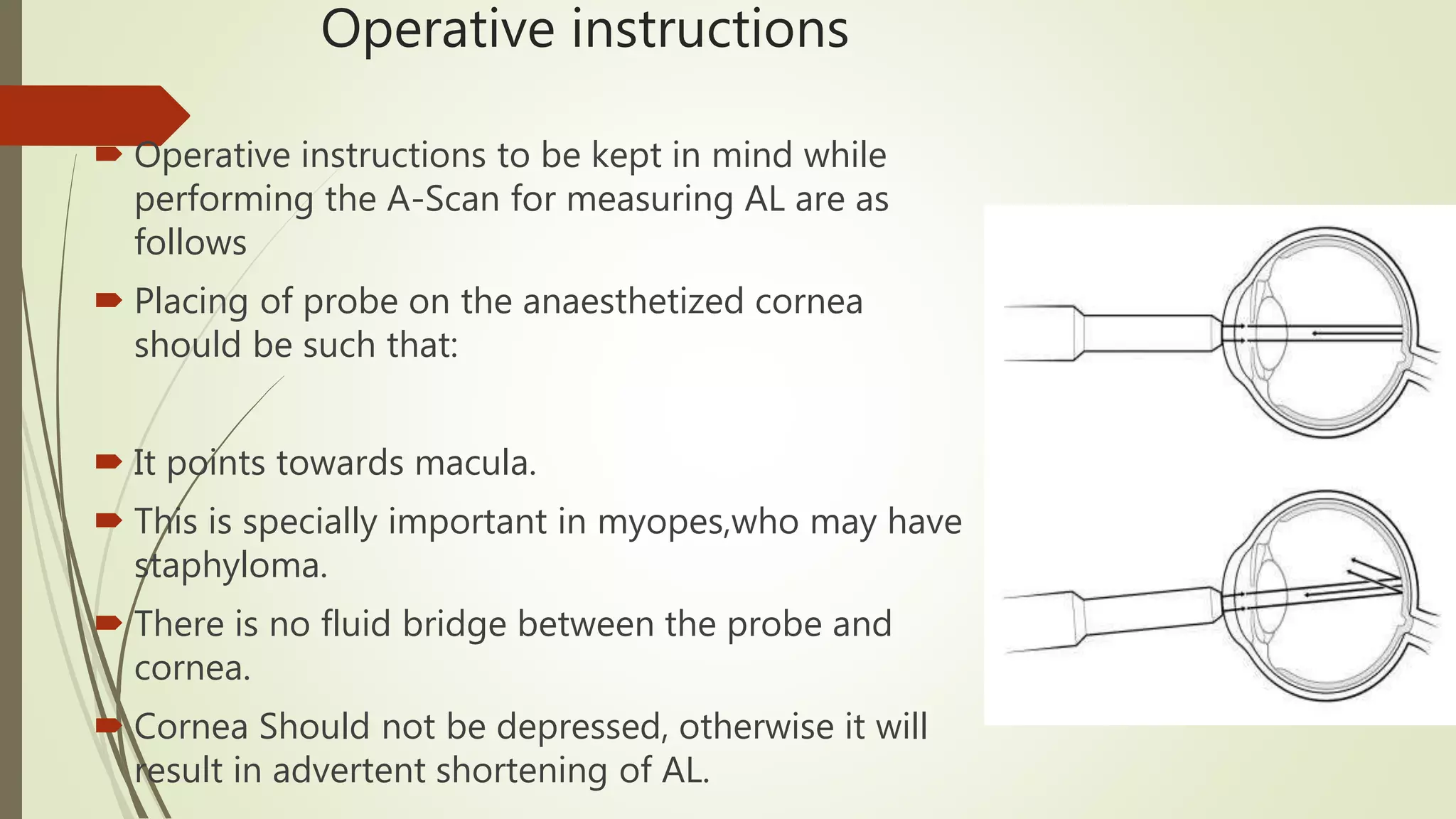
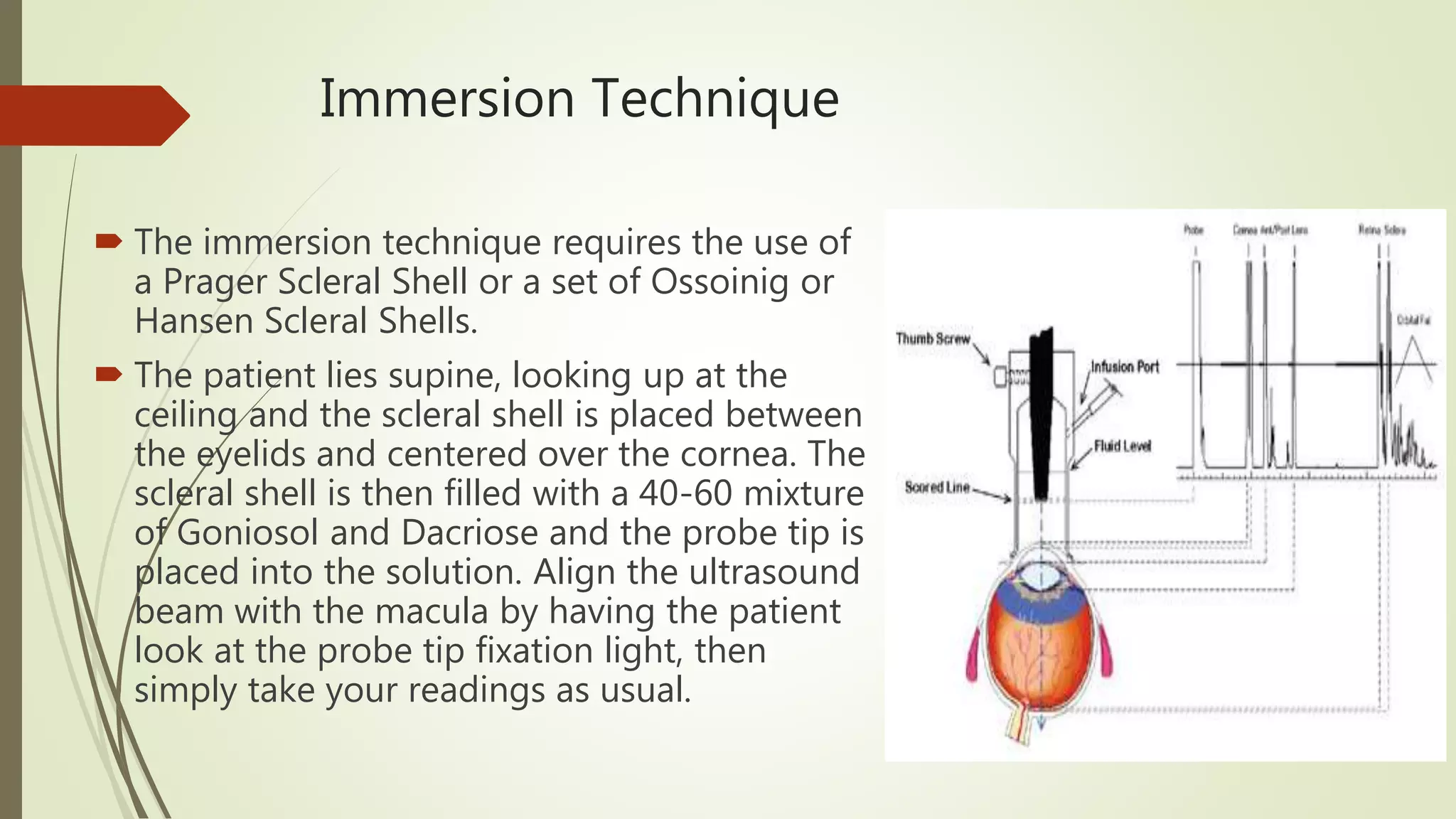
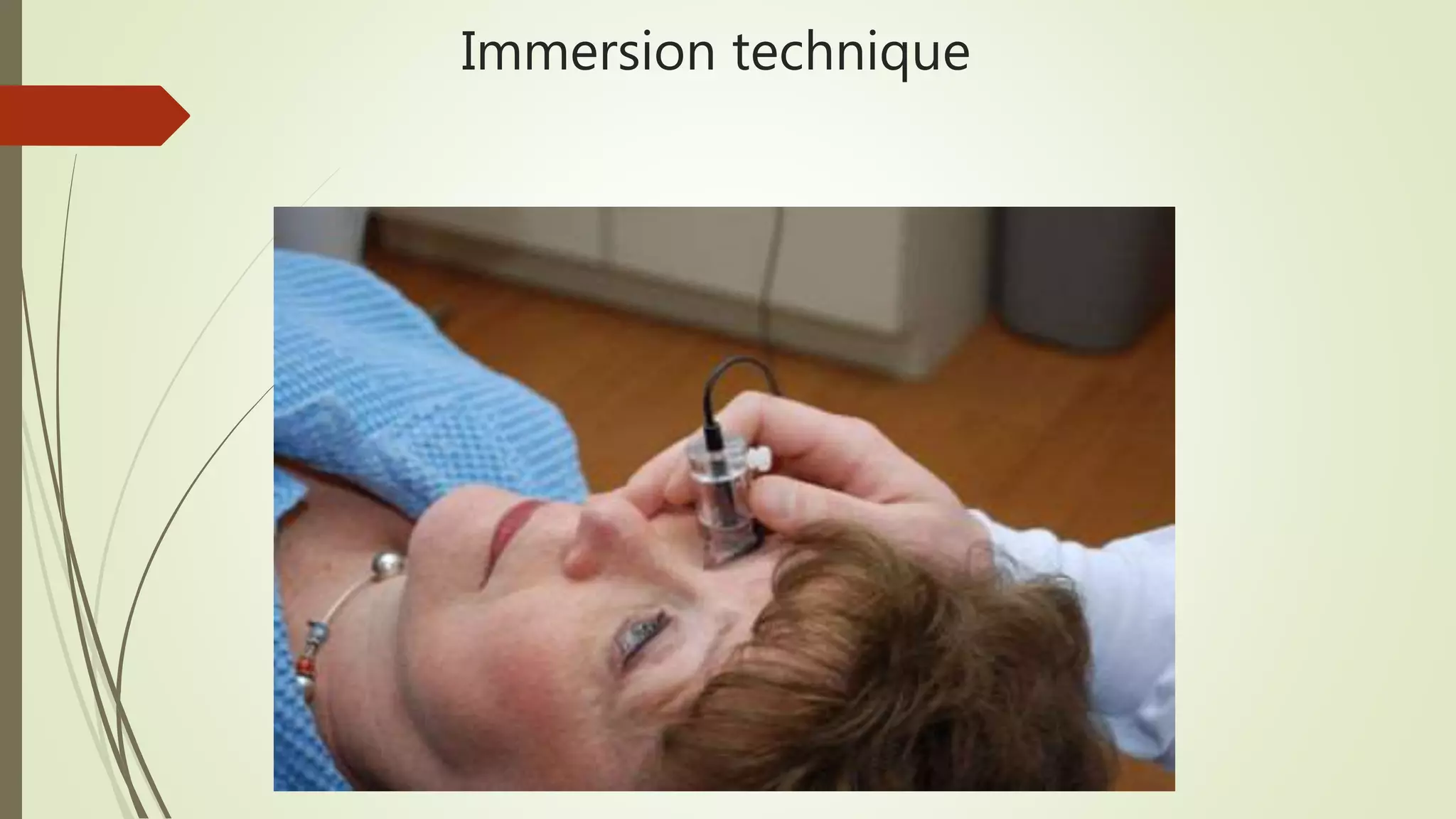
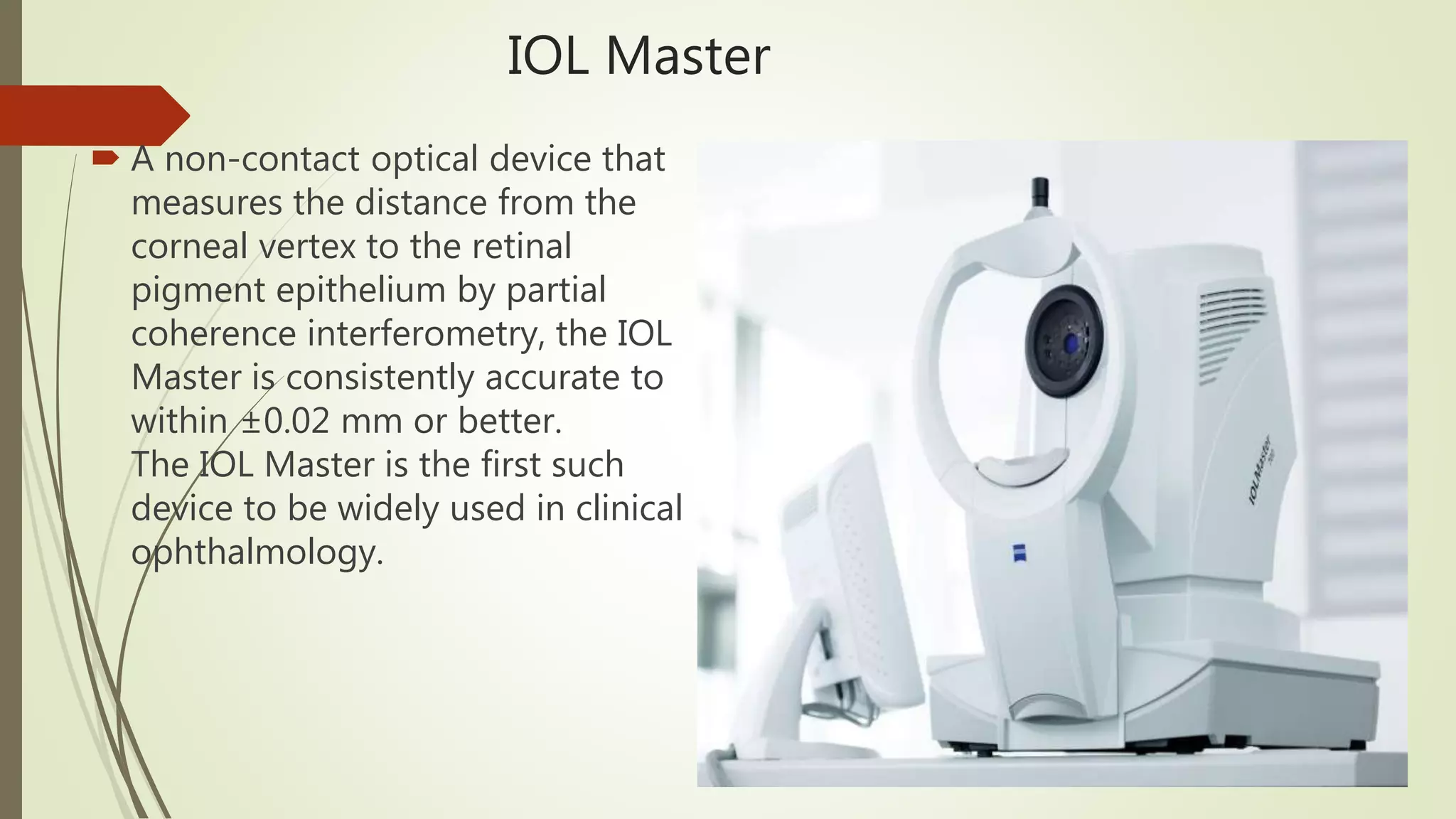
Biometry uses ultrasound A-scans to measure the eye's dimensions, which are used to calculate the ideal intraocular lens power for cataract surgery. The A-scan procedure involves taking a patient history, preparing the patient, and using ultrasound to measure the axial length of the eye. Accurate measurements require using the proper gain and sound velocity settings for each patient's eye condition, and ensuring the probe is correctly positioned on the cornea pointing towards the macula. The immersion technique, where the probe is submerged in fluid coupled to the eye, provides more precise measurements than the contact technique.