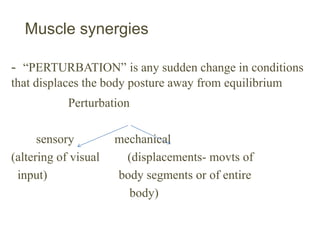
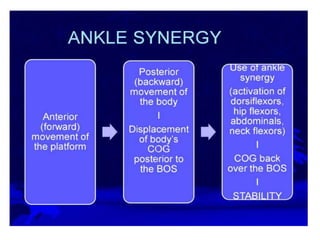
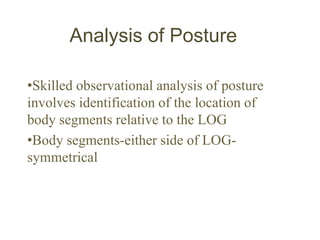
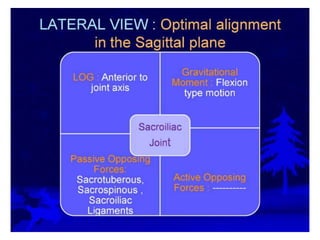
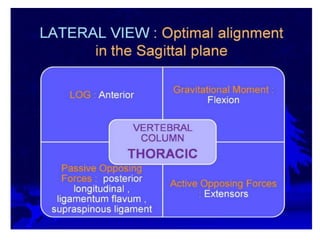
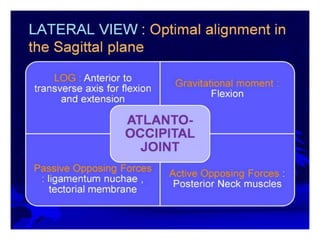
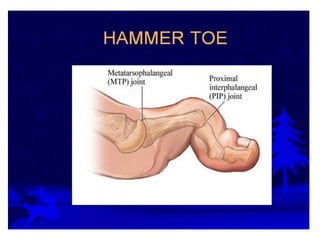
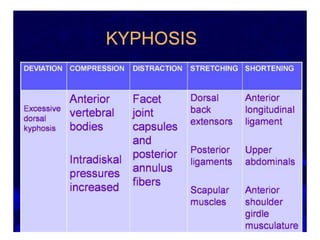
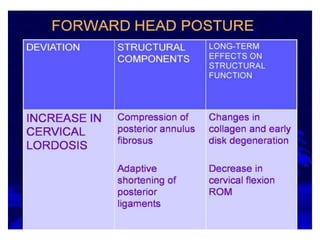
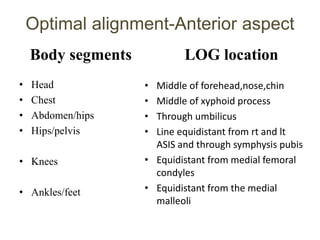
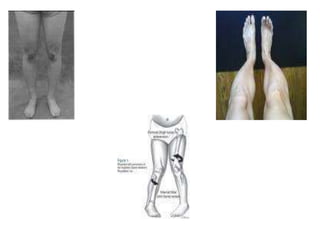
This document provides an overview of biomechanics of posture. It defines static and dynamic posture and describes the major goals and elements of postural control, including maintaining the body's center of gravity over its base of support and stabilizing the head vertically. It discusses perturbations that can disrupt posture and the fixed and change-in-support synergies used to regain equilibrium. Key aspects of posture such as external forces, ground reaction forces, and optimal alignment are summarized. Common postural deviations are also outlined.