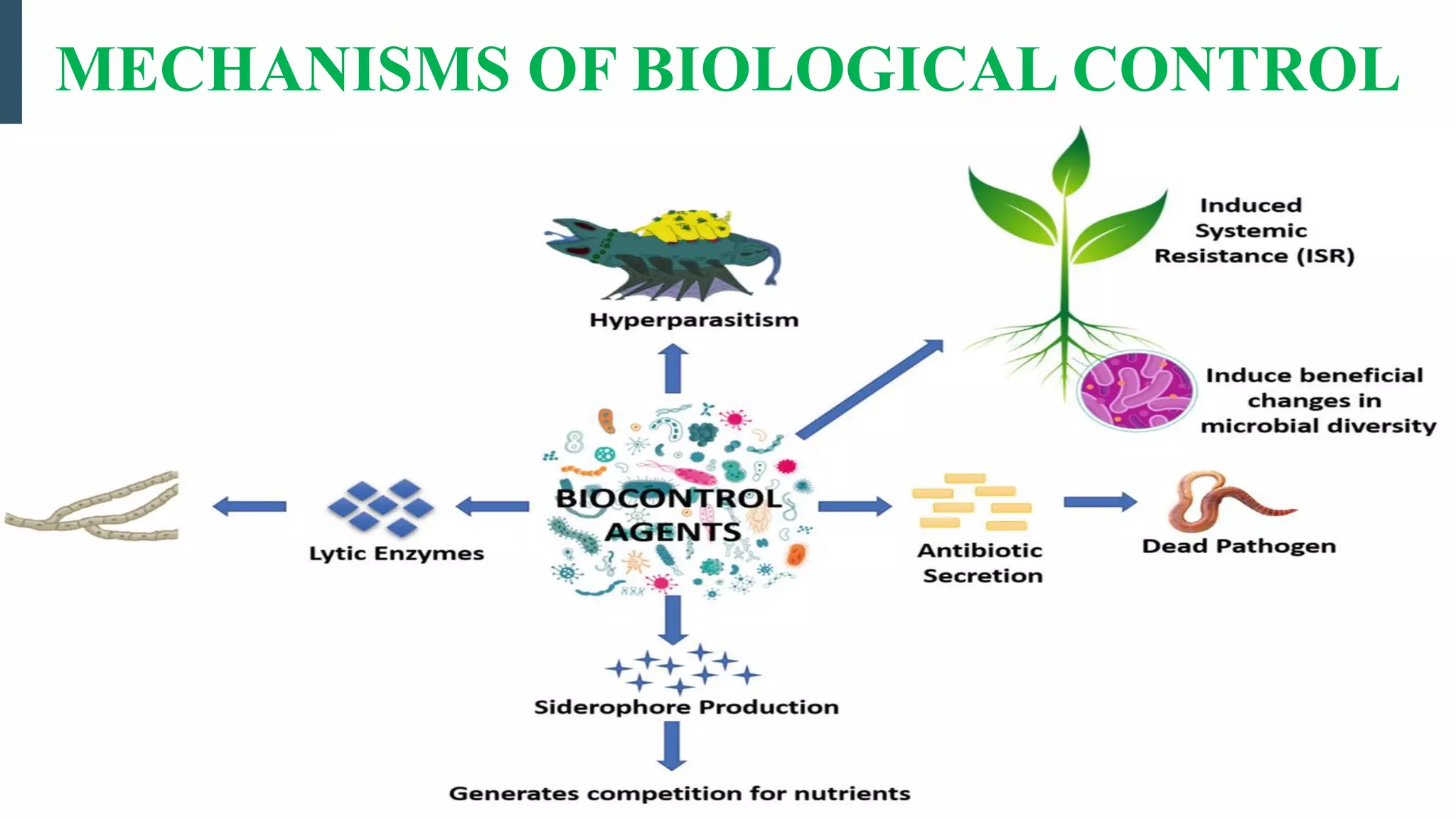
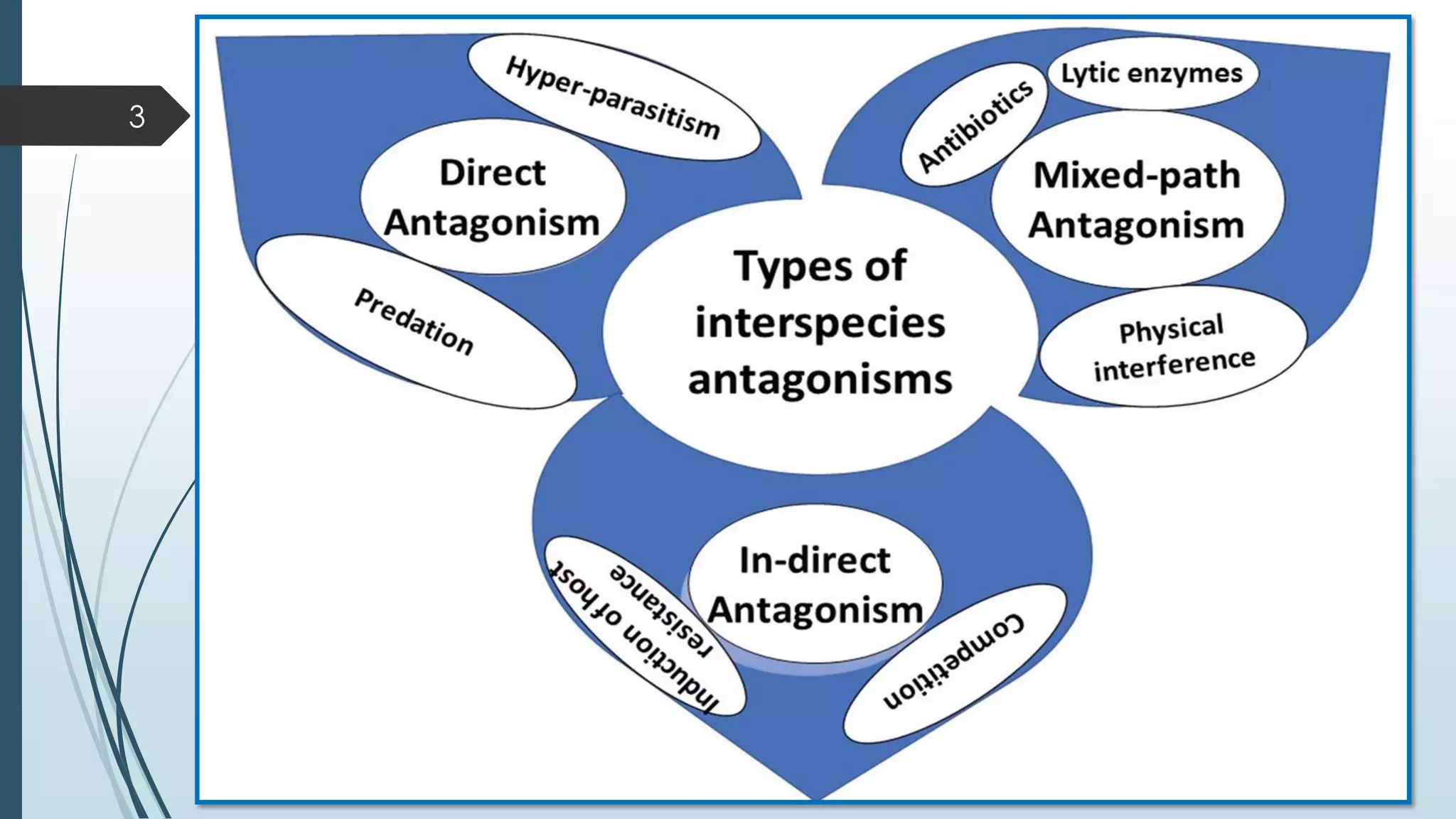
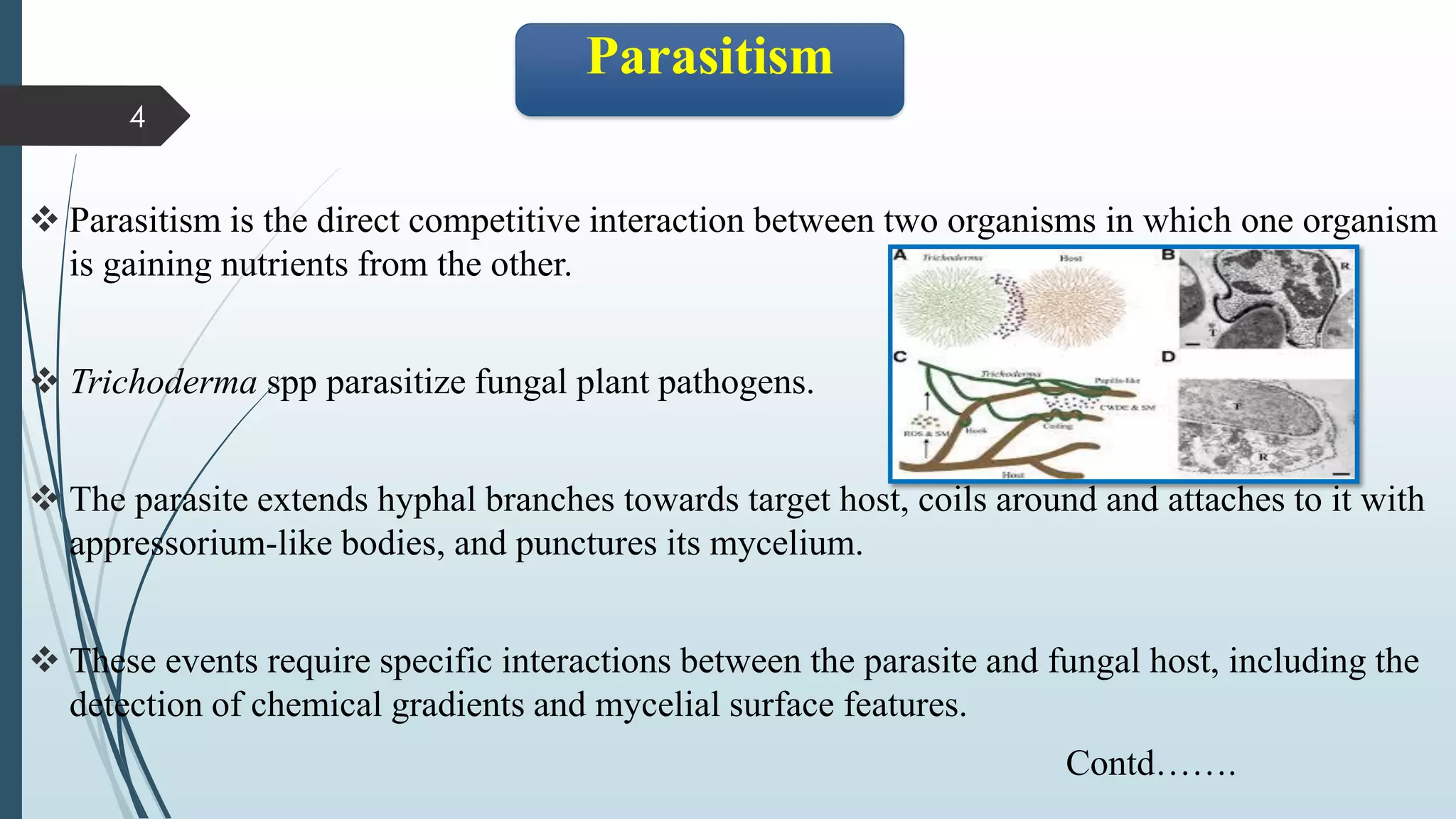
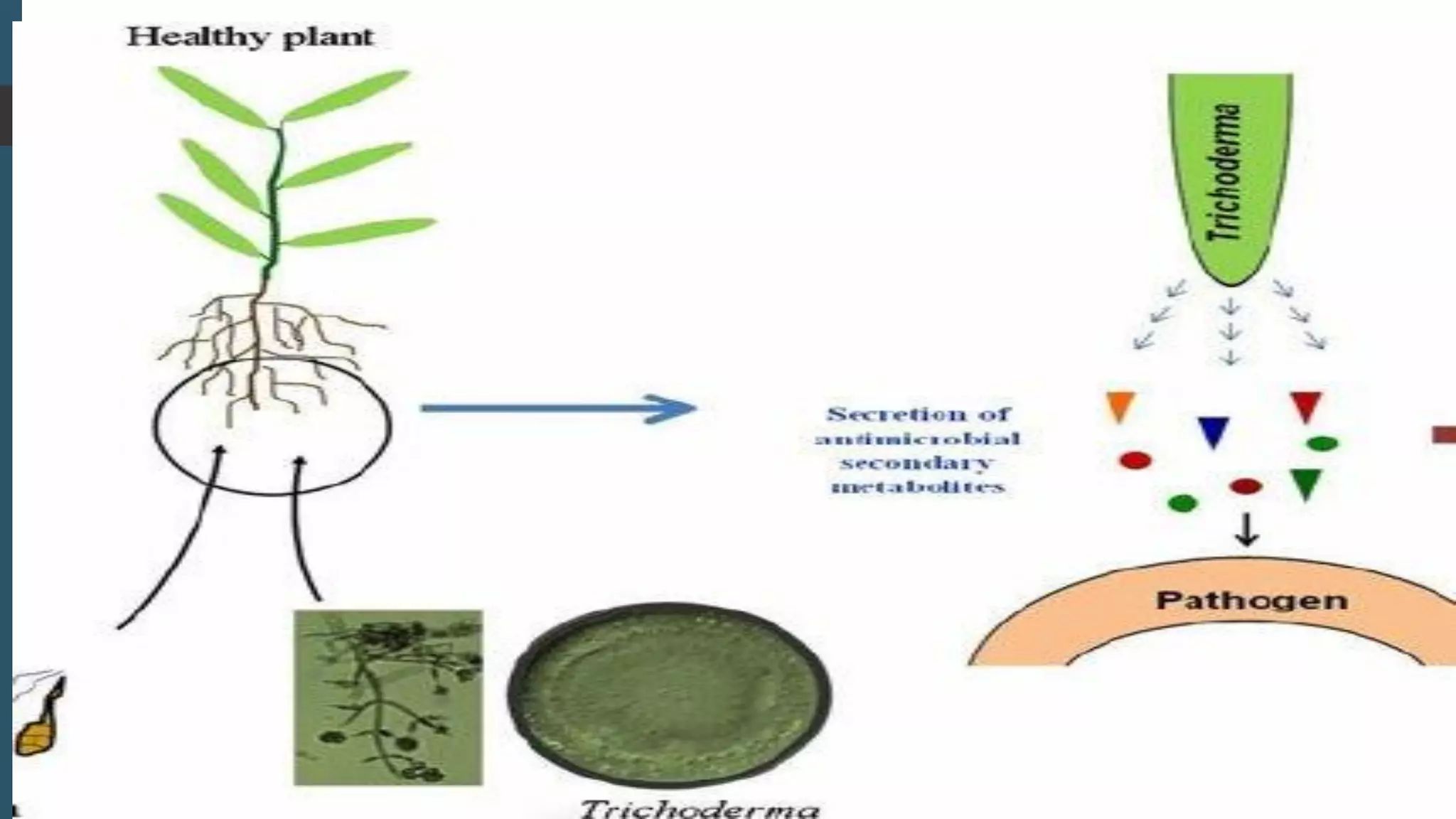
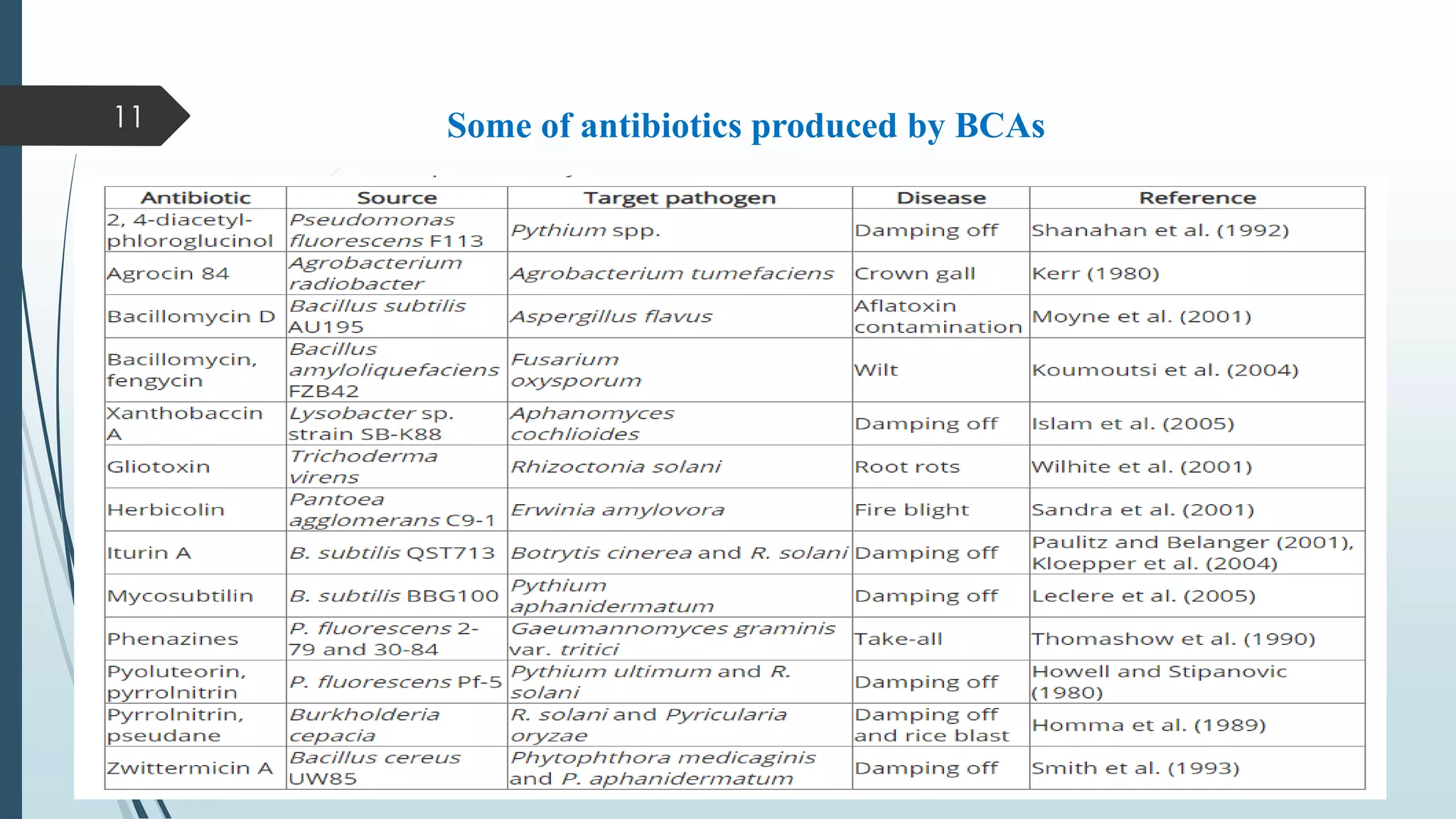
The document discusses various biological control mechanisms such as antagonism, parasitism, hyperparasitism, and antibiotic-mediated suppression. It highlights the roles of specific organisms like Trichoderma spp., Pseudomonas, and Bacillus cereus in suppressing plant pathogens through competitive interactions, enzyme production, and antibiotic secretion. Additionally, it explains the significance of specificity in interactions and the effectiveness of these biological control strategies in agricultural contexts.