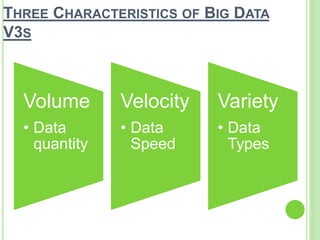
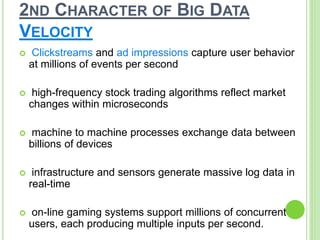
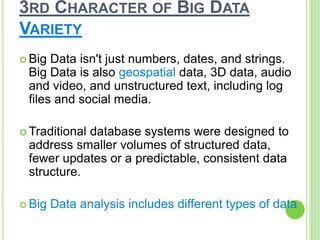
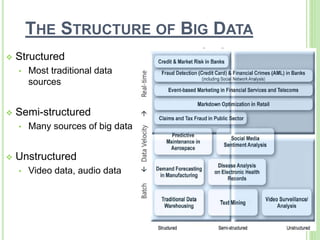
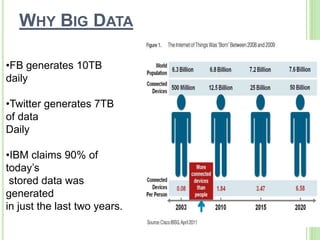
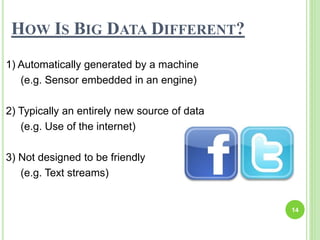
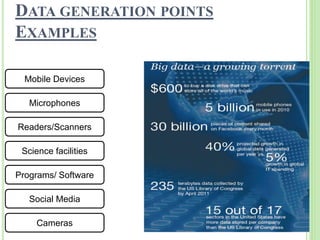
This document provides an overview of big data. It begins by defining big data and noting that it first emerged in the early 2000s among online companies like Google and Facebook. It then discusses the three key characteristics of big data: volume, velocity, and variety. The document outlines the large quantities of data generated daily by companies and sensors. It also discusses how big data is stored and processed using tools like Hadoop and MapReduce. Examples are given of how big data analytics can be applied across different industries. Finally, the document briefly discusses some risks and benefits of big data, as well as its impact on IT jobs.