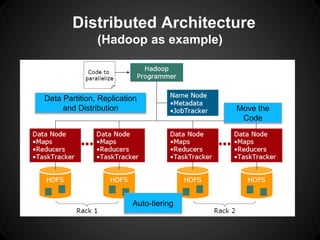
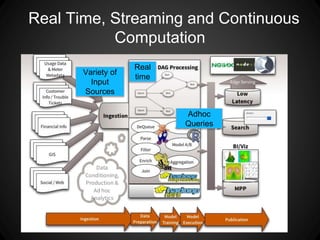
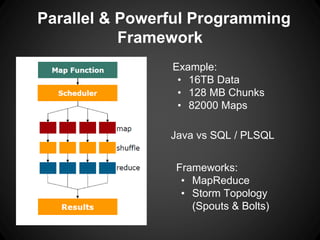
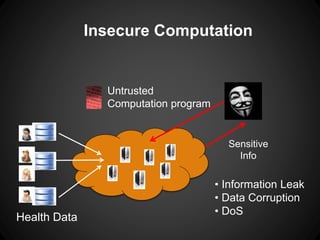
The document outlines key insights and security risks associated with big data architecture, such as insecure computation, inadequate access controls, and privacy concerns. It emphasizes best practices to mitigate these risks, including securing computation code, implementing granular access controls, and conducting privacy-preserving analytics. Additionally, it highlights the importance of continuous evaluation and validation of data handling processes to ensure security.