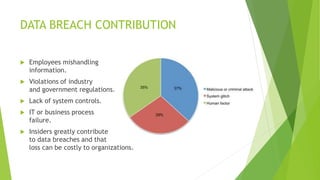
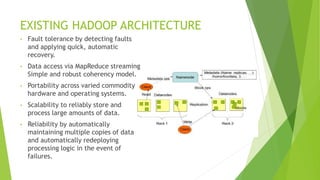
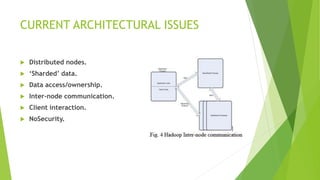
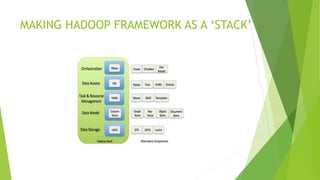
This document discusses security measures for Hadoop environments. It outlines existing issues with Hadoop's architecture like distributed nodes and lack of security. It proposes solutions like using Kerberos and encryption. It also discusses how some corporate security solutions like IBM and Solera Networks use big data analytics to detect abnormalities and insider threats in real-time. The conclusion states that traditional security solutions are insufficient for big data and real-time analytics is needed to derive actionable security intelligence from data streams.