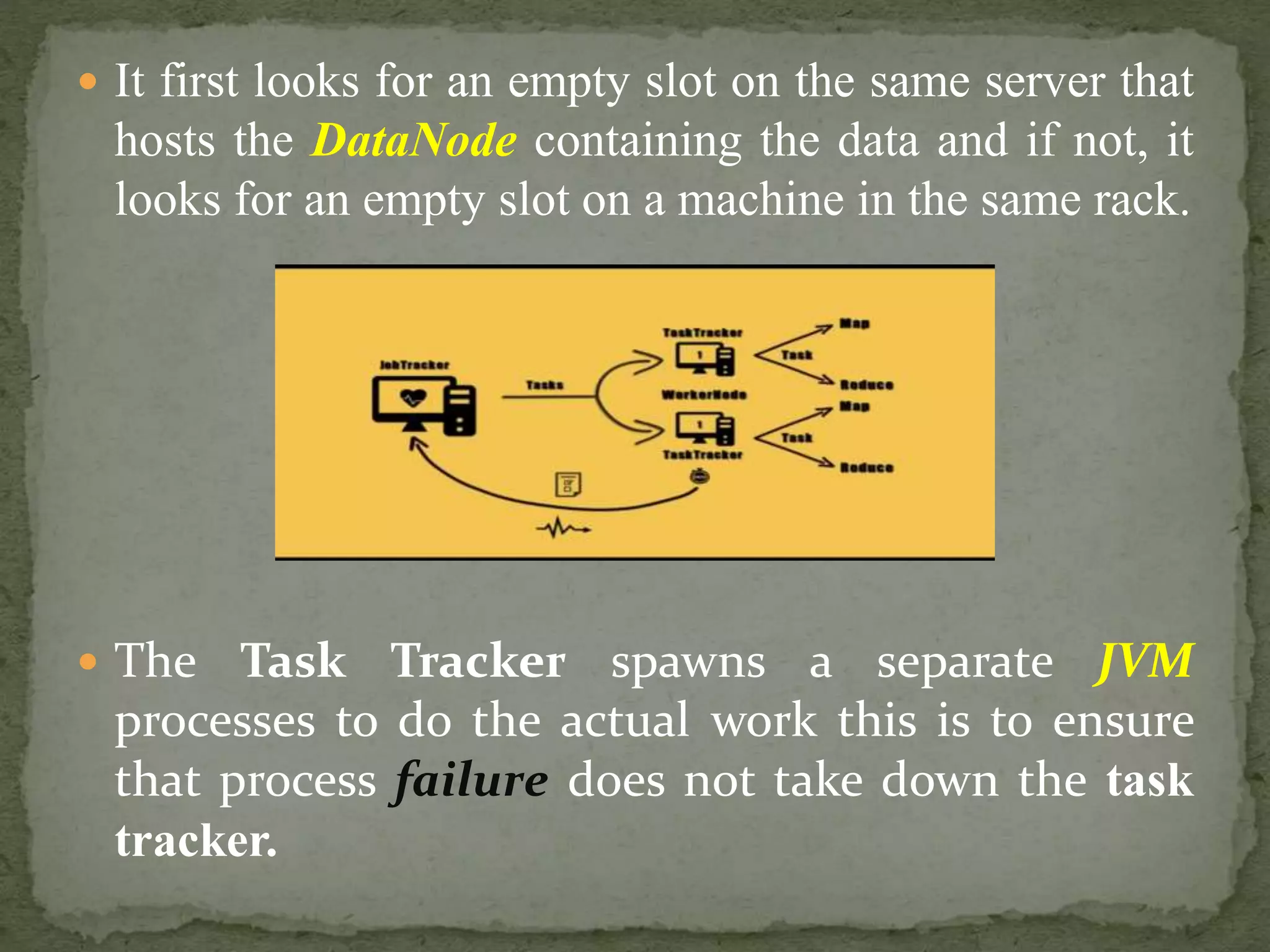
MapReduce is a distributed processing technique and programming model used for big data. It uses map and reduce tasks, where map tasks break down data into smaller chunks that are processed independently, and reduce tasks combine the outputs of the maps into a final set of results. MapReduce relies on job trackers to assign tasks to task trackers, which are nodes that execute the tasks, monitor their completion, and provide status updates back to the job trackers.