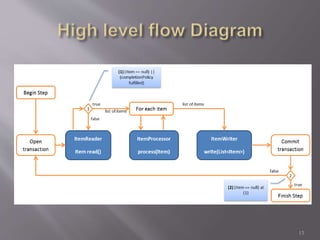
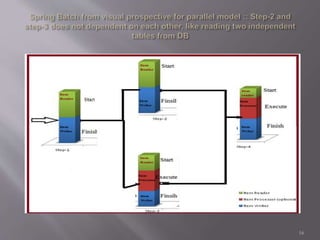
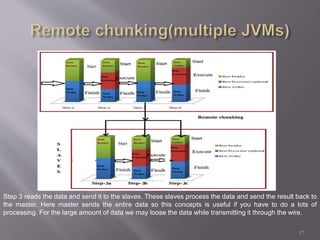
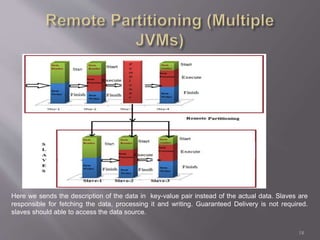
Spring Batch is a highly scalable and customizable batch processing framework developed as a collaboration between Accenture and Spring Source. It enables the processing of large datasets without human intervention, utilizing periodic commits for optimization, and supports a wide range of functionalities including job control, multithreading, and remote processing. The framework separates application logic from batch logic, allowing developers to focus on business needs while efficiently managing data processing tasks.