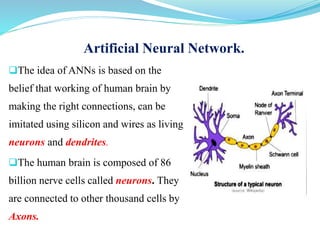
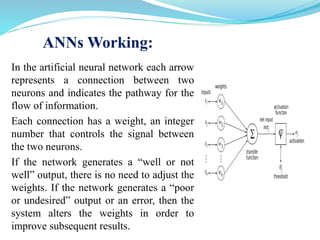
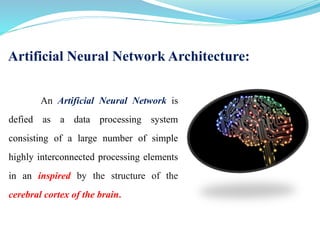
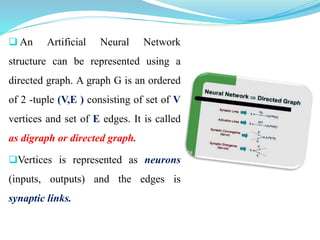
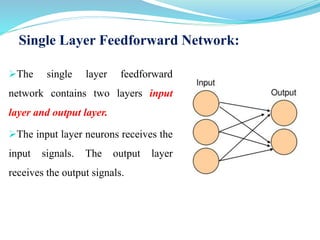
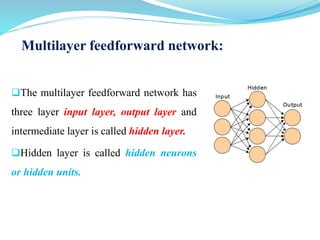
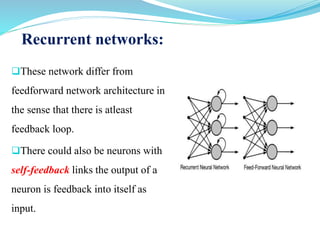
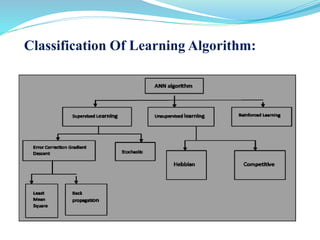
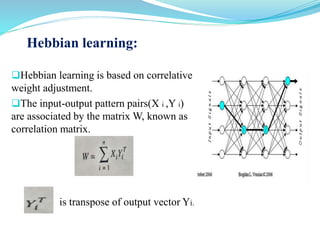
This document introduces artificial neural networks and their relationship to biological neural networks. It discusses the basic components and functioning of artificial neural networks, including nodes, links, weights, and learning. Different network architectures are described, including single layer feedforward networks and multilayer feedforward networks. Supervised, unsupervised, and reinforced learning methods are also summarized. Applications of artificial neural networks include areas like airline security, investment management, and sales forecasting.