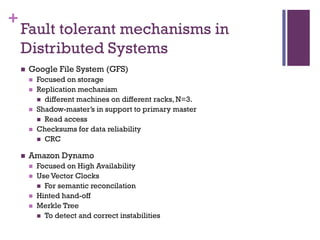
The document discusses the importance of fault-tolerant mechanisms in big data, highlighting various distributed systems such as Google File System, Amazon Dynamo, and Facebook's Cassandra, each implementing unique strategies for ensuring reliability and availability. It introduces existing models for cloud computing fault tolerance and proposes a new model that incorporates features like master nodes and probabilistic failure detection. Future work aims to develop a more robust fault-tolerant model using these identified features.