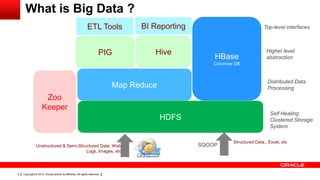
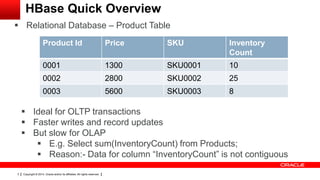
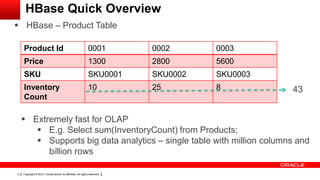
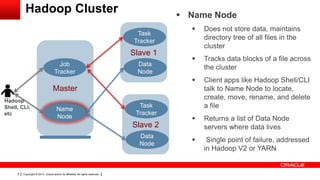
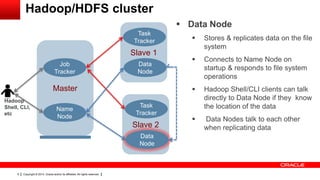
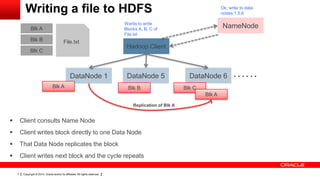
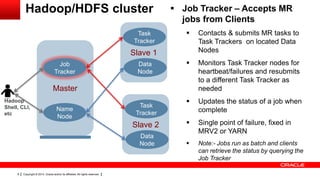
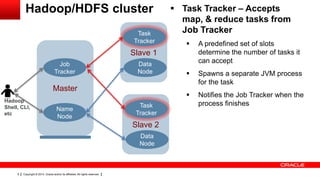
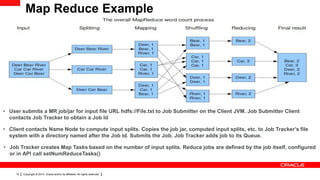
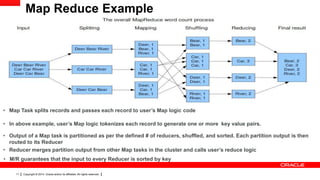
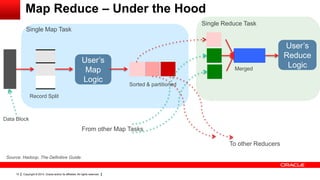
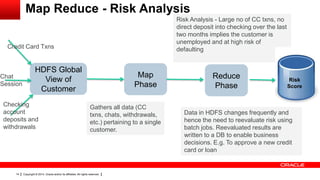
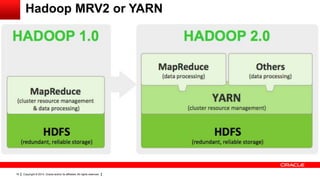
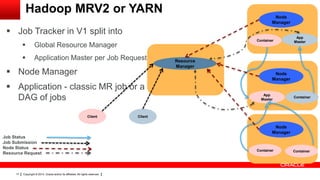
This document provides an overview of big data concepts including HDFS, MapReduce, HBase, Pig, Hive and Hadoop clusters. It describes how HBase is better suited than a relational database for large-scale analytics due to its columnar data structure. It also summarizes how MapReduce programming works, with the map phase organizing data and the reduce phase aggregating it. Finally, it outlines limitations of the original Hadoop 1.0 and how YARN improved cluster resource management and scheduling in Hadoop 2.0.