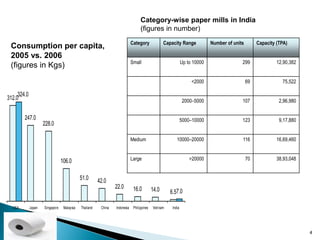
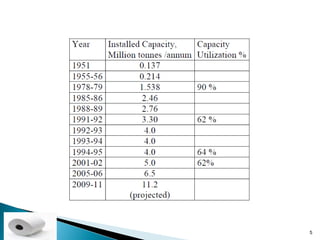
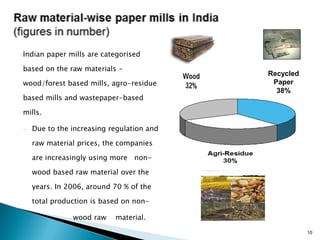
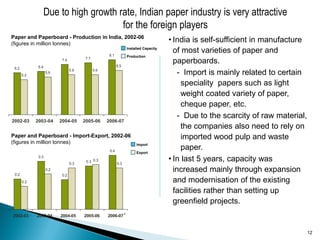
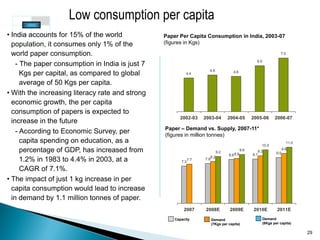
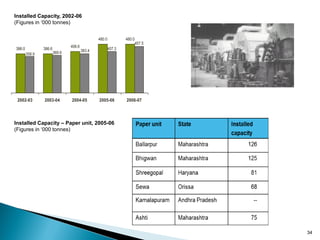
The document provides an overview of the Indian paper industry. It notes that India is the 15th largest paper producer in the world, with the industry employing nearly 1.5 million people. Per capita paper consumption in India is estimated to be 7 kg in 2006, much lower than global and Asian averages. The industry is expected to face challenges in meeting growing demand due to constraints on raw material availability. Projections estimate paper demand in India could double by 2015 and reach 21 million tonnes by 2020.