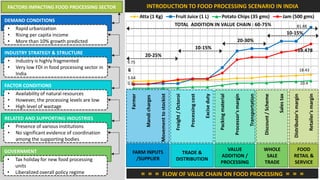
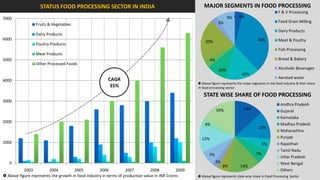
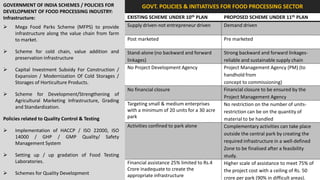
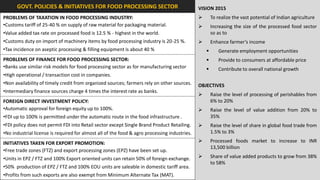
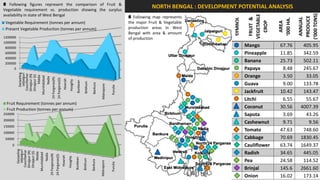
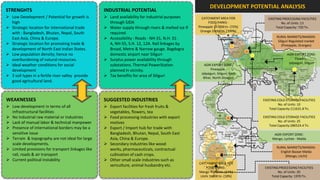
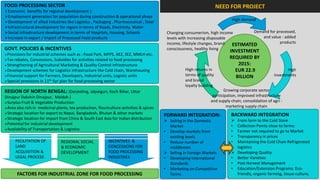
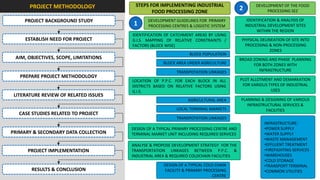
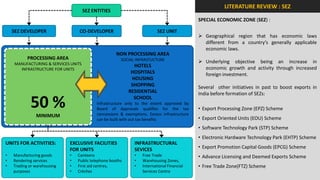
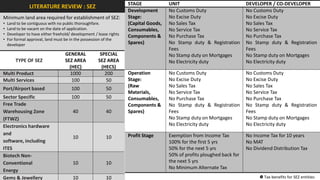
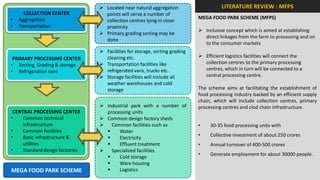
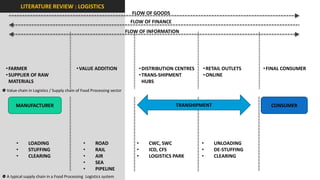
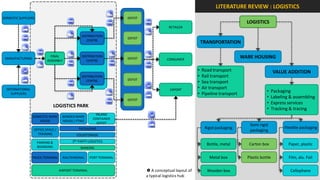
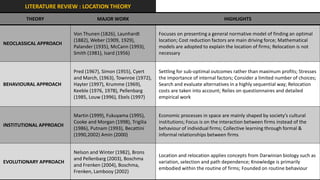
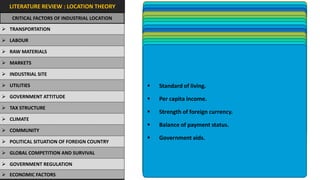
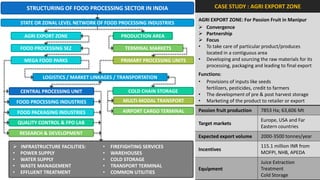
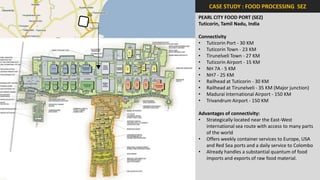
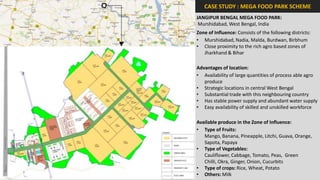
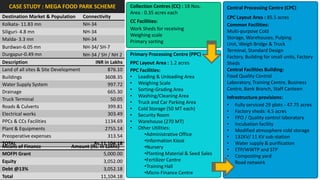
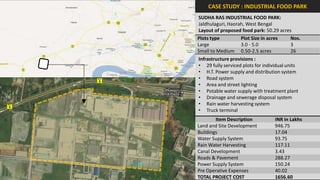
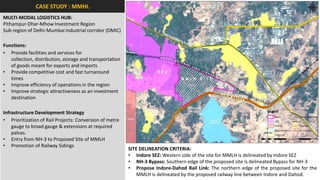
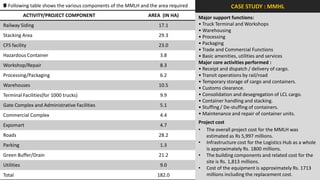
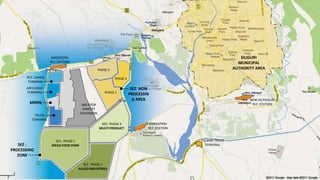
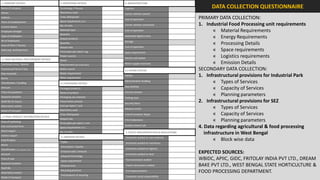
The document analyzes the development potential of the food processing sector in North Bengal, India, highlighting current government policies, initiatives, and the existing infrastructure for food processing. It emphasizes the need for improved industrial zones to enhance the supply chain, reduce waste, and meet growing consumer demand for processed foods. Additionally, it discusses the challenges faced by the industry, including low foreign direct investment, taxation issues, and regional instability, while outlining strategies for increasing production and processing levels.