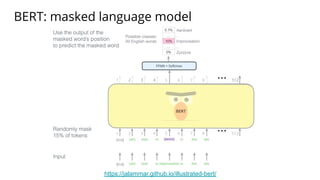
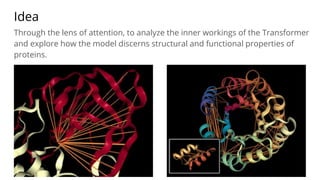
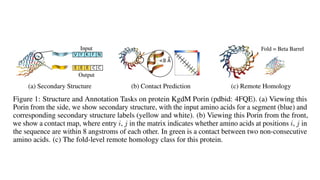
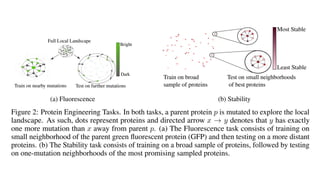
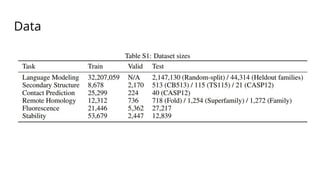
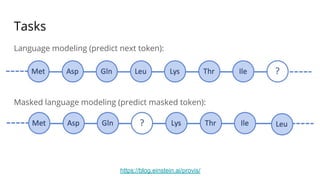
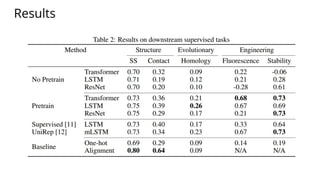
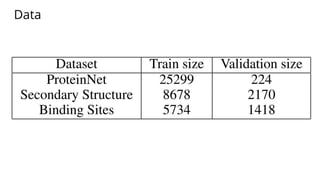
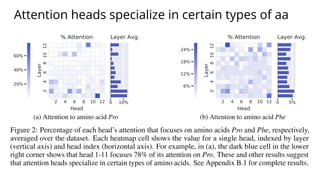
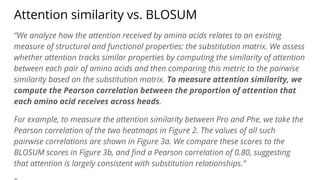
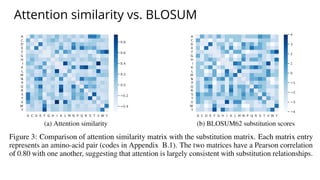
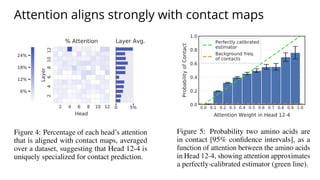
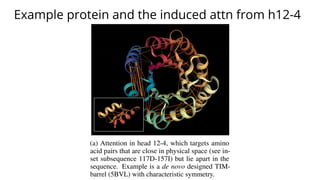
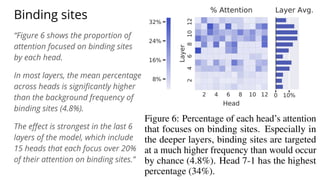
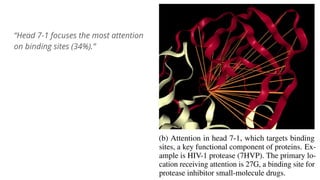
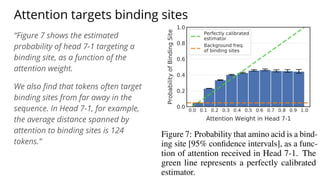
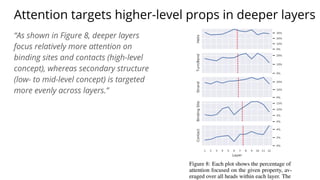
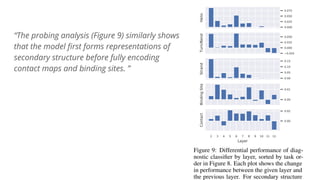
The document discusses the application of BERT representations to protein language models, focusing on how attention mechanisms can interpret structural and functional properties of proteins. It evaluates the performance of protein embeddings using datasets and various tasks, concluding that certain attention heads specialize in particular amino acids and align with functional structures like contact maps and binding sites. The findings highlight the relevance of transformer models in understanding protein interactions, despite challenges in using attention weights as explanations for model behavior.