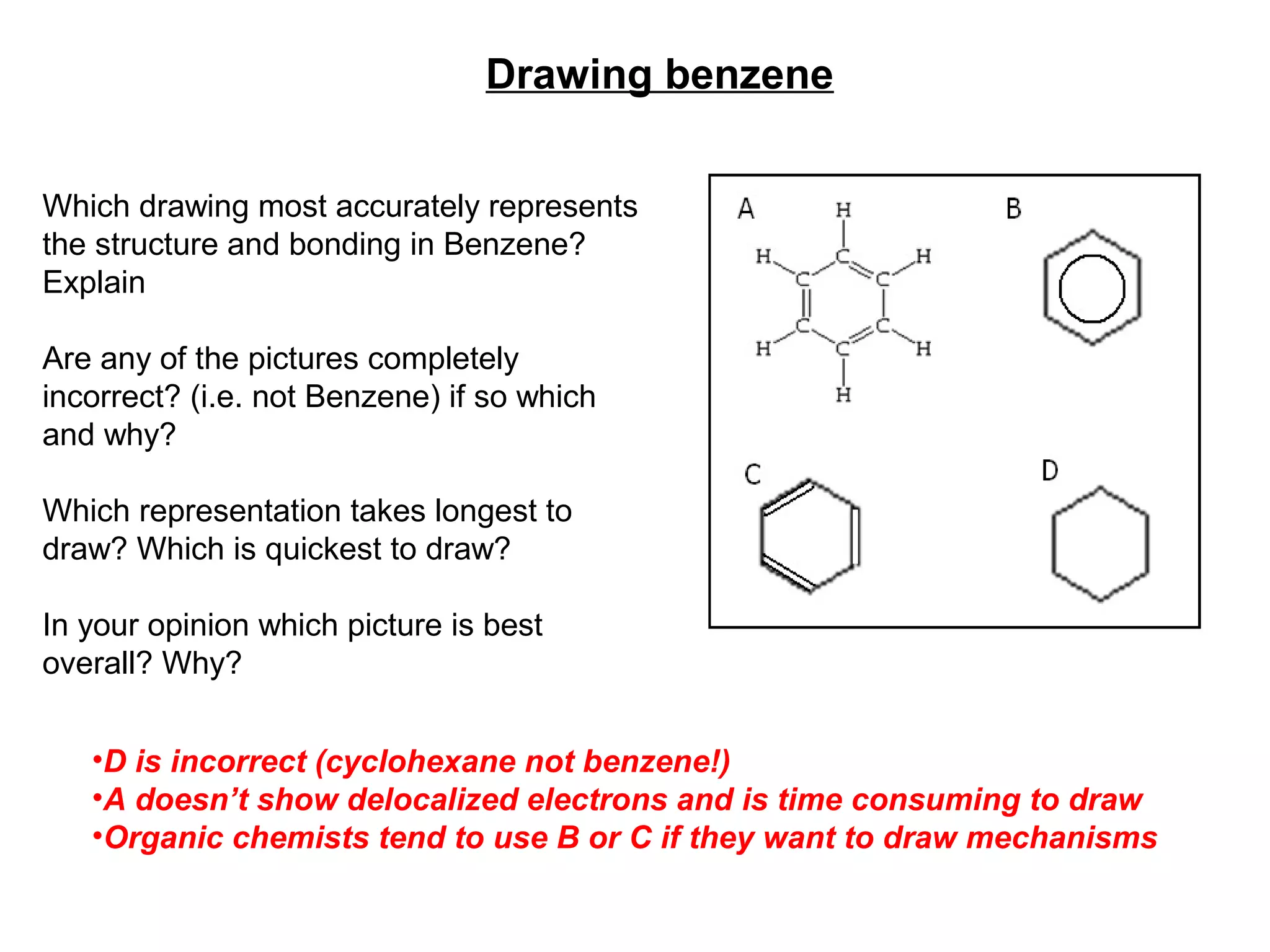
Here are 3 key problems scientists faced in explaining the structure and bonding of benzene:
1. Benzene did not react like a typical alkene as expected based on its molecular formula.
2. The thermodynamic stability of benzene was greater than predicted if it contained alternating double and single bonds.
3. The carbon-carbon bond lengths in benzene were equal in length, inconsistent with alternating double and single bonds.
Through continued experimentation using new techniques like STM and theoretical developments like valence bond theory, the current understanding of benzene emerged. Scientists now recognize that benzene's electrons are delocalized through conjugation into a ring above and below the nuclei. This explains benzene's extra stability and