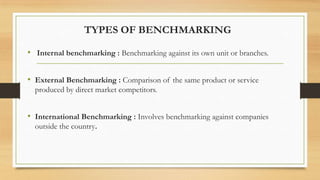
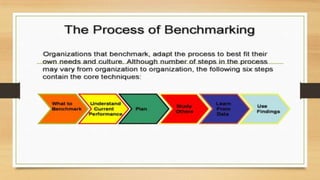
Benchmarking is comparing business processes and performance metrics to best practices from other companies or industries in order to improve. Xerox used benchmarking in the 1980s after losing market share, comparing itself to competitors like Canon and IBM. Xerox benchmarked all aspects of its business from supplier management and inventory to marketing and quality. This led to significant improvements in defects, costs, productivity and reliability, allowing Xerox to become the market leader again. Benchmarking involved planning, analysis, implementation and continuous improvement.