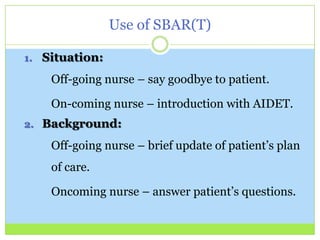
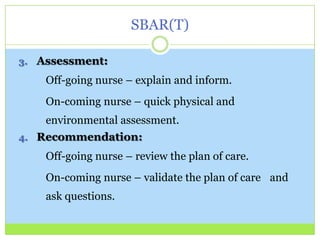
Bedside report involves the off-going nurse handing off report to the on-coming nurse at the patient's bedside. Research shows this provides safer patient care by improving identification accuracy and communication among caregivers while also increasing patient satisfaction and involvement in their own care. Bedside report meets three National Patient Safety Goals. Advantages include building teamwork, ownership, brief assessments, and allowing patient involvement and questions. Obstacles can be overcome through techniques like role playing and using SBAR(T) communication structure.