Shared governance in nursing is a collaborative model aimed at improving nurses' work conditions, job satisfaction, and patient care through shared decision-making principles like partnership, equity, accountability, and ownership. This framework empowers nurses and healthcare professionals to engage actively in decision-making processes, fostering a sense of responsibility and enhancing care outcomes. The article explores the theoretical foundations, practical applications, benefits, and challenges of shared governance in nursing practice.









![Decentralized decision-making is most successful when responsibility, authority,
and accountability are clearly delineated and assigned.
• Responsibility: the clear and specific allocation of duties to achieve desired results.
• Authority: the right to act and make decisions in the areas where one is given and accepts
responsibility.
1. Data gathering
2. Data gathering + recommendations
3. Data gathering + recommendations [pause] + act
4. Act and inform/update
• Accountability: begins when one reviews and reflects upon his or her own actions and decisions,
and culminates with a personal assessment that helps determine the best actions to take in the
future.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lorielenepowerpointpresentation-200614202045/85/Shared-Governance-in-Nursing-11-320.jpg)
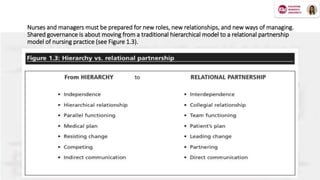
![Shared governance and relational partnerships
“The best [leader] is the one who has sense enough to pick good [people] to do what he/she wants done, and
self-restraint enough to keep from meddling with them while they do it.” —Theodore Roosevelt
Professional nurses long ago identified shared governance as a key
indicator of excellence in nursing practice. Porter-O’Grady (2001)
described shared governance as a process model that provides a
structure for organizing nursing work within organizational settings. It
empowers nurses to express and manage their practice with a greater
degree of professional autonomy.
Today’s transformational relationship-based healthcare, which is driven
by technology, creates a new paradigm with different goals and
objectives in an organizational learning environment. Leaders,
administrators, and employees are learning and implementing new
ways of providing care, new technologies, and new ways of thinking
and working.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lorielenepowerpointpresentation-200614202045/85/Shared-Governance-in-Nursing-12-320.jpg)