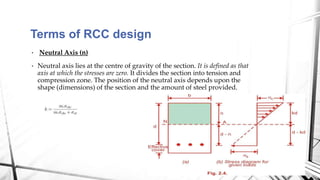
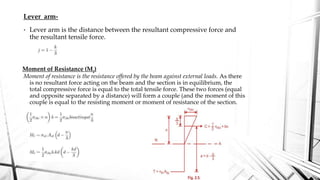
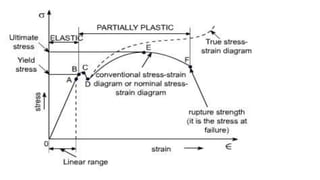
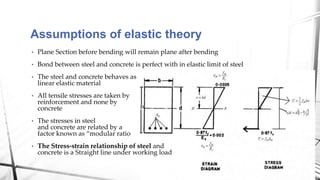
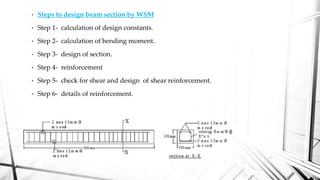
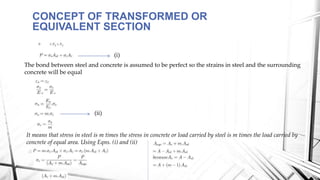
This document discusses the working stress method for designing reinforced concrete structures. It defines key terms like neutral axis, lever arm, and moment of resistance. It describes the assumptions and steps of the working stress method, including designing for under-reinforced, balanced, and over-reinforced beam sections. The document also discusses limitations of the working stress method and introduces the limit state method as a more modern approach.