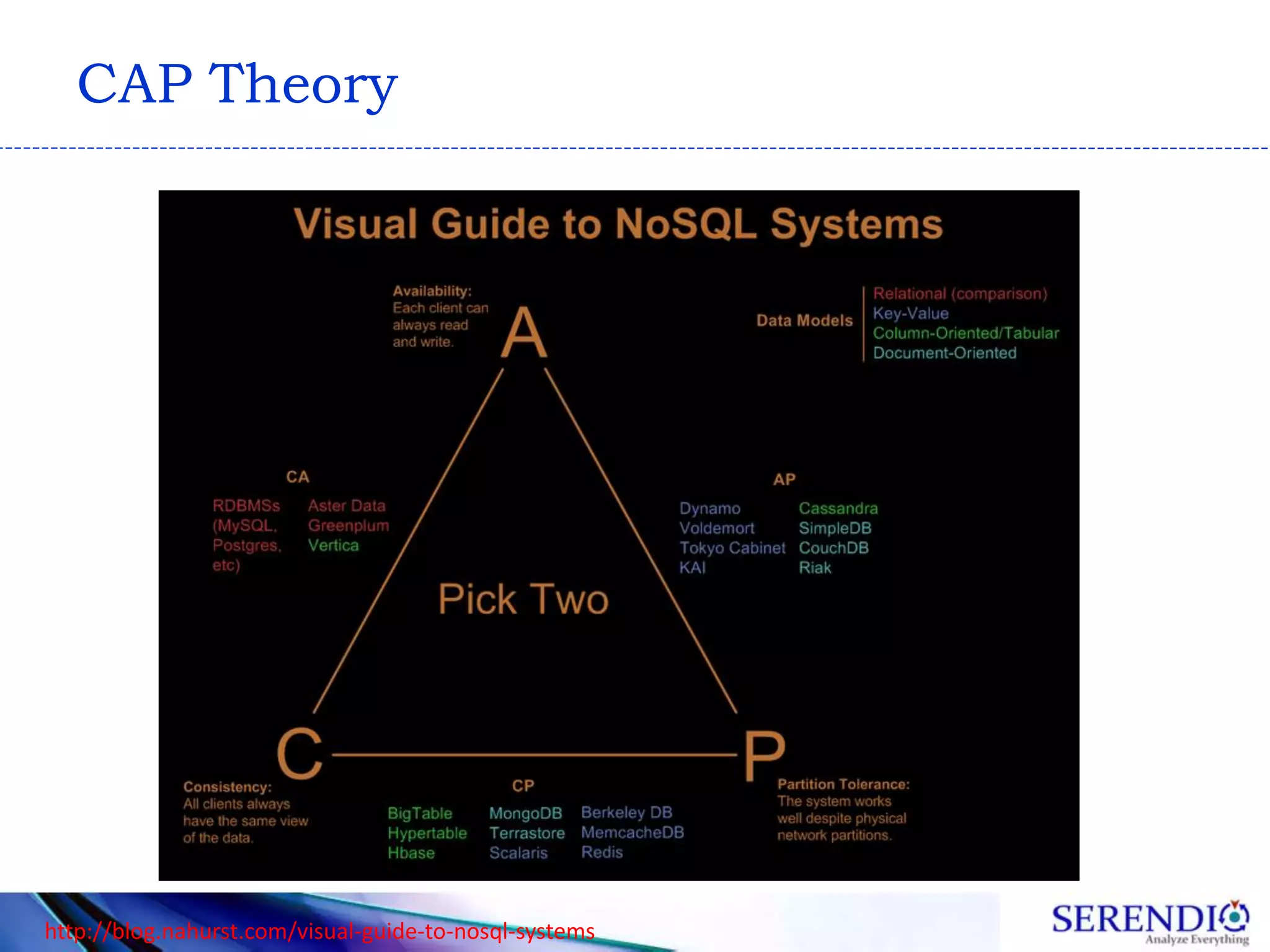
This document provides an introduction to big data, including definitions of big data and why it is important. It discusses characteristics of big data like volume, velocity, variety and veracity. It provides examples of big data applications in various industries like GE, Boeing, social media, finance, CERN, journalism, politics and more. It also introduces NoSQL and the CAP theorem, and concludes that big data is changing business and technology by enabling new insights from data to reduce costs and optimize operations.