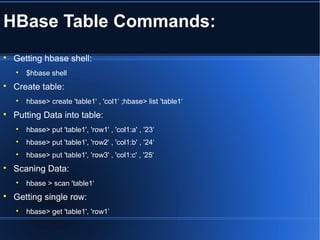
This document provides an agenda for a Big Data summer training session presented by Amrit Chhetri. The agenda includes modules on Big Data analytics with Apache Hadoop, installing Apache Hadoop on Ubuntu, using HBase, advanced Python techniques, and performing ETL with tools like Sqoop and Talend. Amrit introduces himself and his background before delving into the topics to be covered in the training.

![About Me :
Me:
I’m Amrit Chhetri from Bara Mangwa, West Bengal, India, a beautiful Village/Place in Darjeeling.
I am CSCU, CEH, CHFI,CPT, CAD, CPD, IOT & BigData Analyst( University of California), Information
Security Specialist(Open University, UK) and Machine Learning Enthusiast ( University of
California[USA] and Open University[UK]), Certified Cyber Physical System Exert( Open
University[UK]) and Certified Smart City Expert.
Current Position:
Principal IT Security Consultant/Instructor, Principal Forensics Investigator and Principal Techno-
Functional Consultant/Instructor
BigData Consultant to KnowledgeLab
Experiences:
I was J2EE Developer and BI System Architect/Designer of DSS for APL and Disney World
I have played the role of BI Evangelist and Pre-Sales Head for BI System* from OST
I have worked as Business Intelligence Consultant for national and multi-national companies including
HSBC, APL, Disney, Fidedality , LG(India) , Fidelity, BOR( currently ICICI), Reliance Power. * Top 5
Indian BI System ( by NASSCOM)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdataanalytics-hadoopecosystem-160723111411/85/BigData-Analytics-with-Hadoop-and-BIRT-2-320.jpg)


![Apache Hadoop on Ubuntu 15.10 or
15.04:
Platforms tested and finalized:
Ubuntu :15.10 or 15.04
JDK: 1.8
Hadoop: 2.7.2
Eclipse : Mars R1/R2
MySQL : 5.x
Two ways to have Apache Hadoop:
Pre-configured
Self-configured ( steps are given)
SSH installation requires Ubuntu’s updates using $sudo [<http_proxy>] apt-get update
sudo [<http_proxy>] apt-get update install mysql-server install MySQL Server](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdataanalytics-hadoopecosystem-160723111411/85/BigData-Analytics-with-Hadoop-and-BIRT-6-320.jpg)