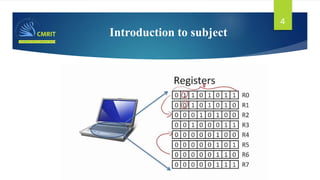
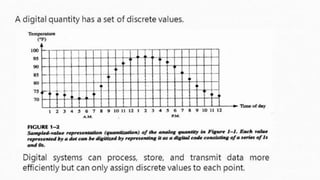
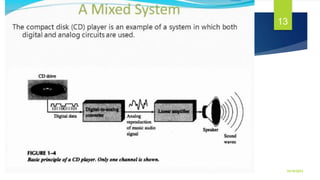
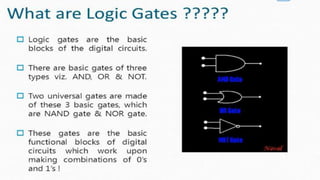
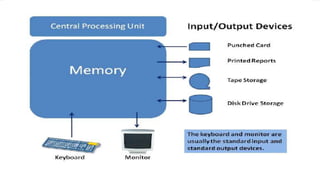
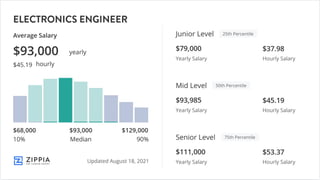
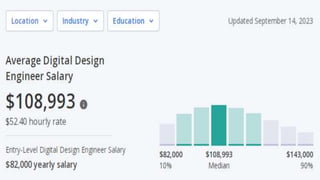
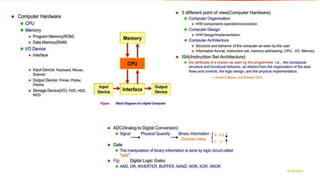
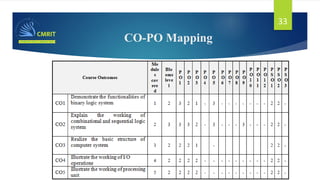
The document outlines the curriculum and expectations for the Digital Design and Computer Organization course, detailing both introductory and advanced topics such as binary logic, VHDL, and the architecture of computer systems. It specifies course objectives, outcomes, assessment plans, and relevant resources, aimed at equipping students with the necessary knowledge and skills for digital system design. Additionally, it highlights the role and responsibilities of digital design engineers along with typical qualifications required for the profession.