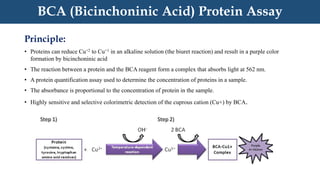
The BCA Protein Assay uses bicinchoninic acid to detect and quantify the amount of protein in a sample. It involves reducing Cu+2 to Cu+1 in an alkaline environment using proteins, which then complexes with BCA to produce a purple color. The absorbance at 562 nm is proportional to the protein concentration in the sample. It is highly sensitive, selective, and simpler than other assays like Lowry, though the color produced is not stable over time.