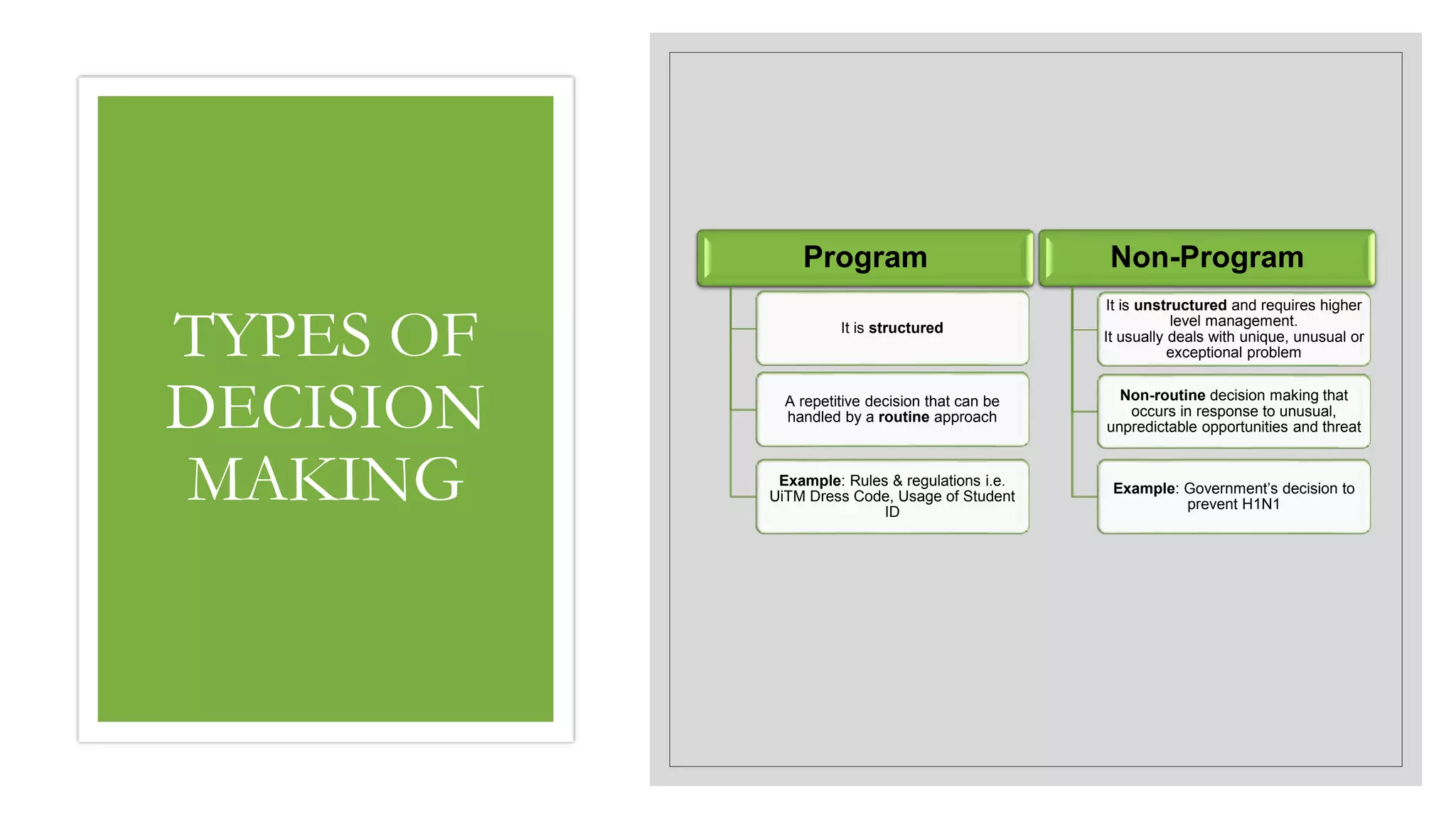
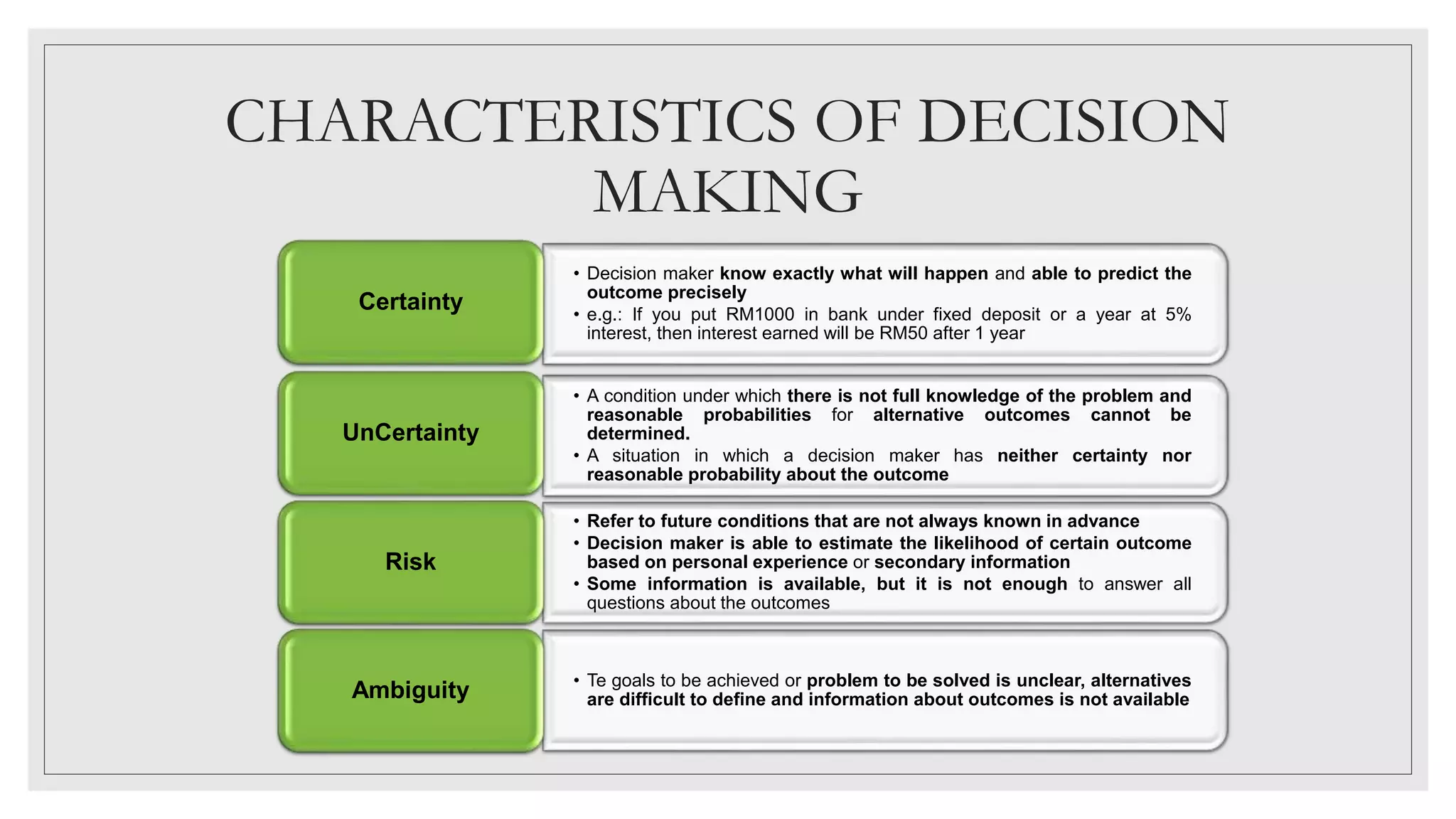
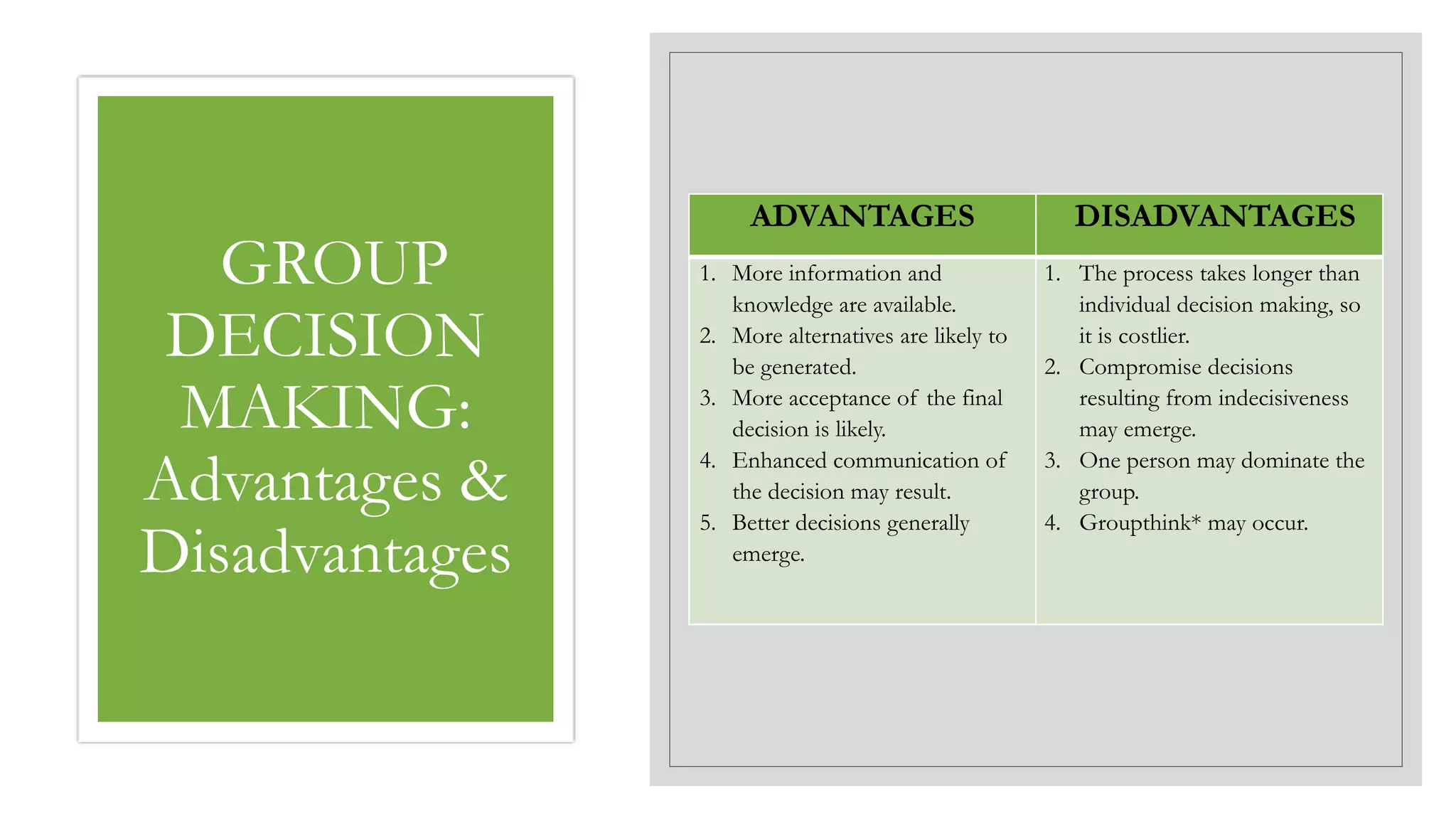
This document discusses decision making. It defines decision making as the process managers use to identify and resolve problems and seize opportunities. There are two types of decisions: programmed decisions which are routine, and non-programmed decisions which are unique and non-routine. The characteristics of decision making include certainty, uncertainty, risk, and ambiguity. The decision making process involves 7 steps: identifying problems and opportunities, setting objectives, generating alternatives, evaluating alternatives, making the decision, implementing strategies, and monitoring results. Group decision making techniques include brainstorming, nominal group technique, and the Delphi technique.