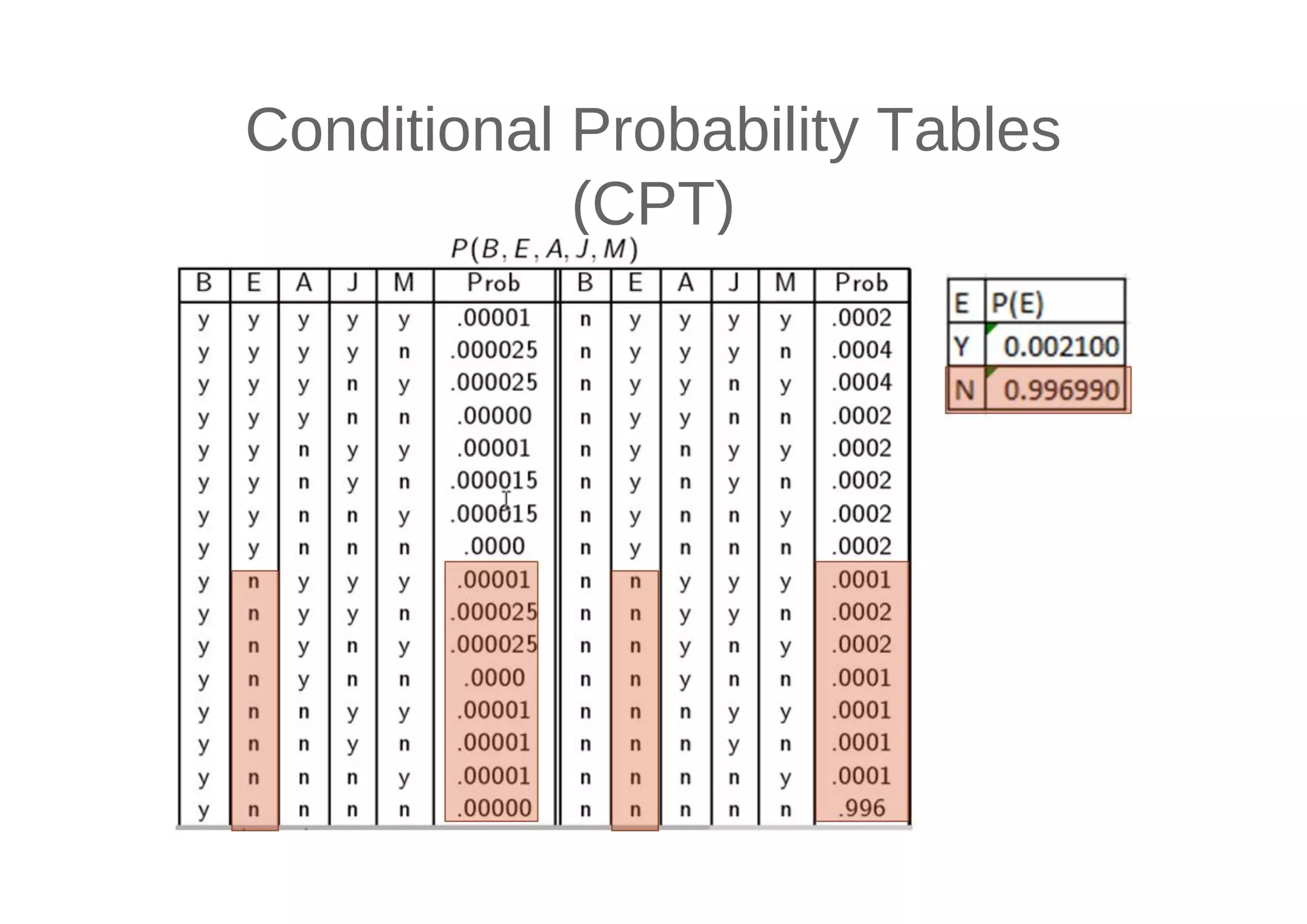
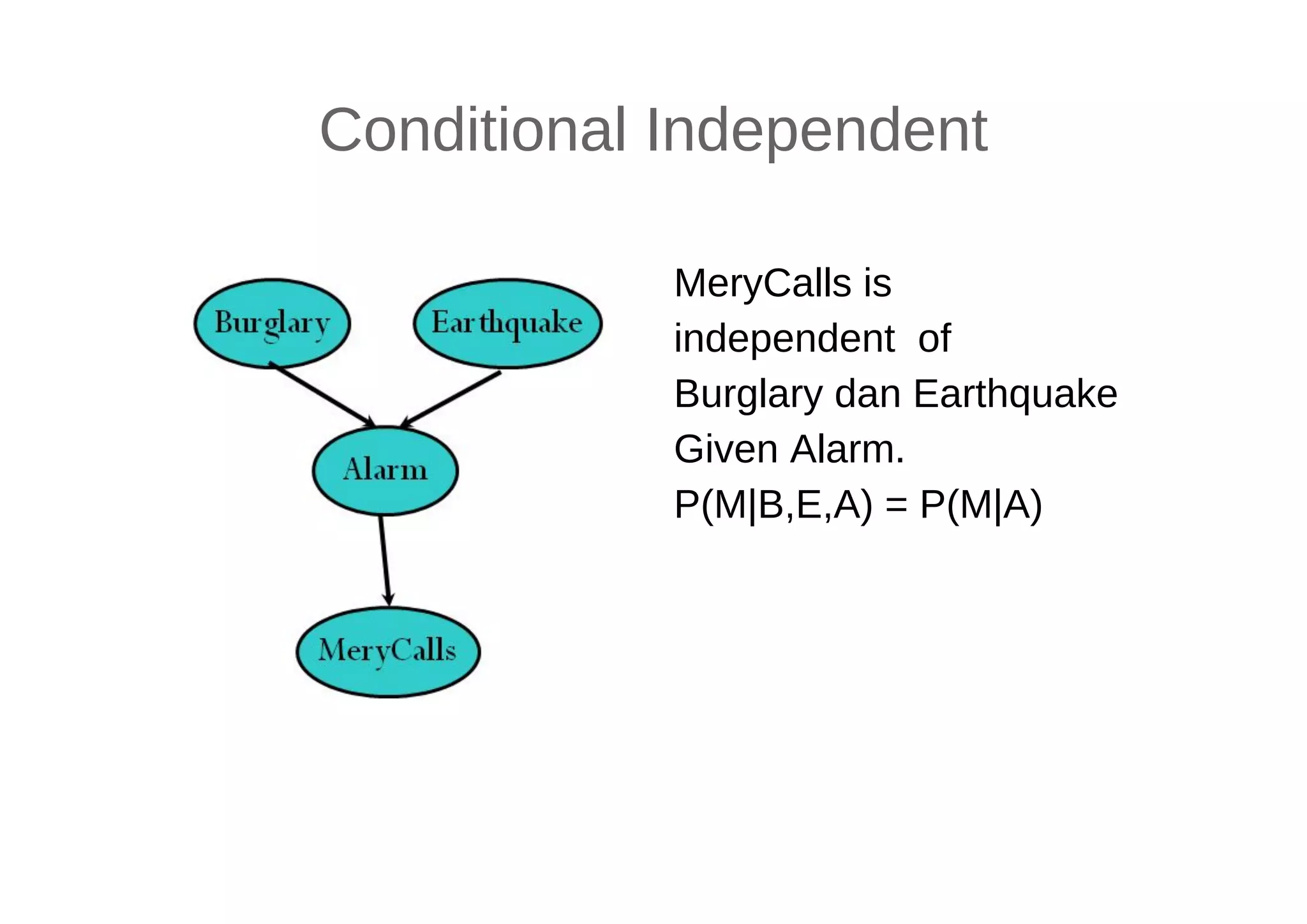
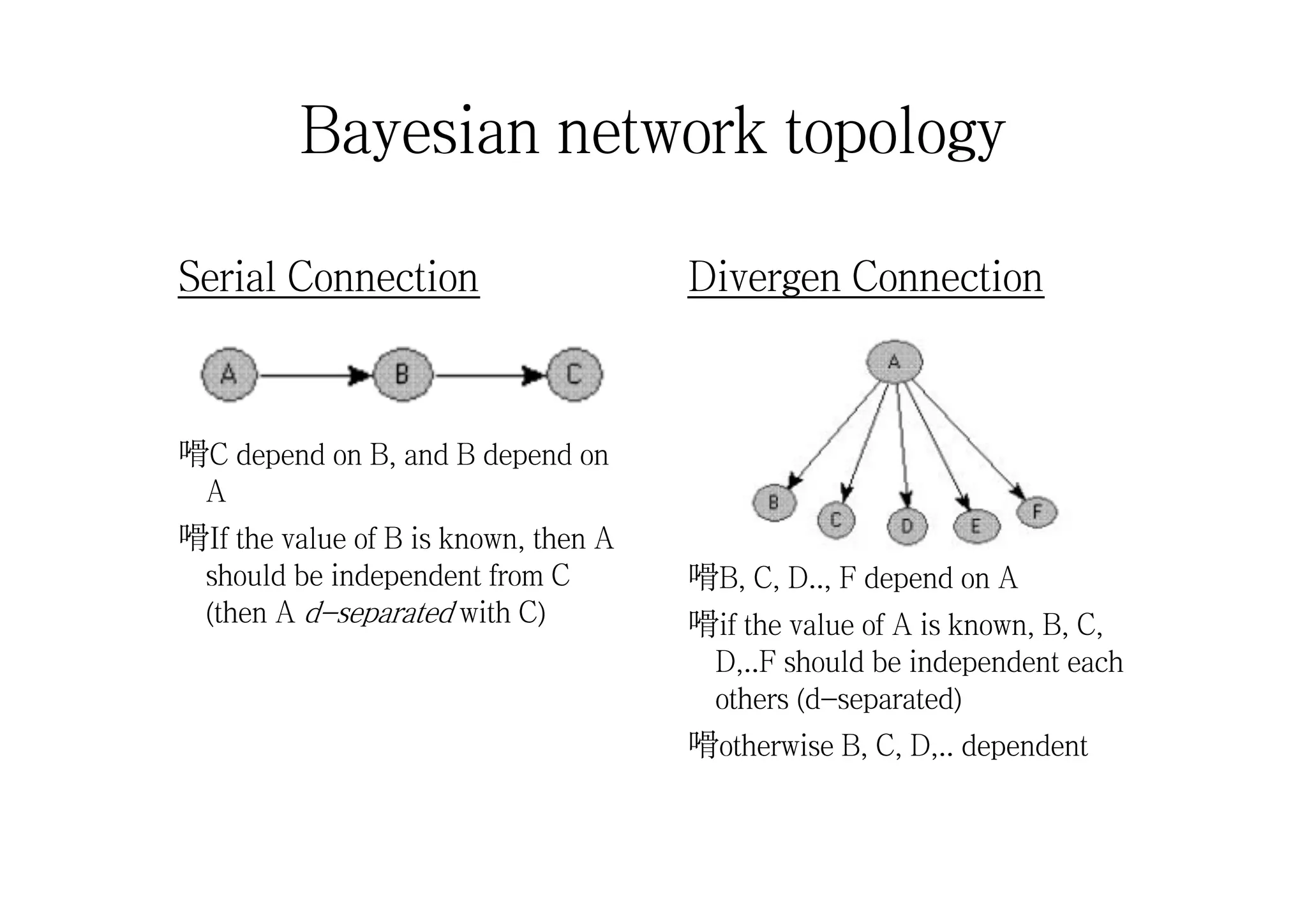
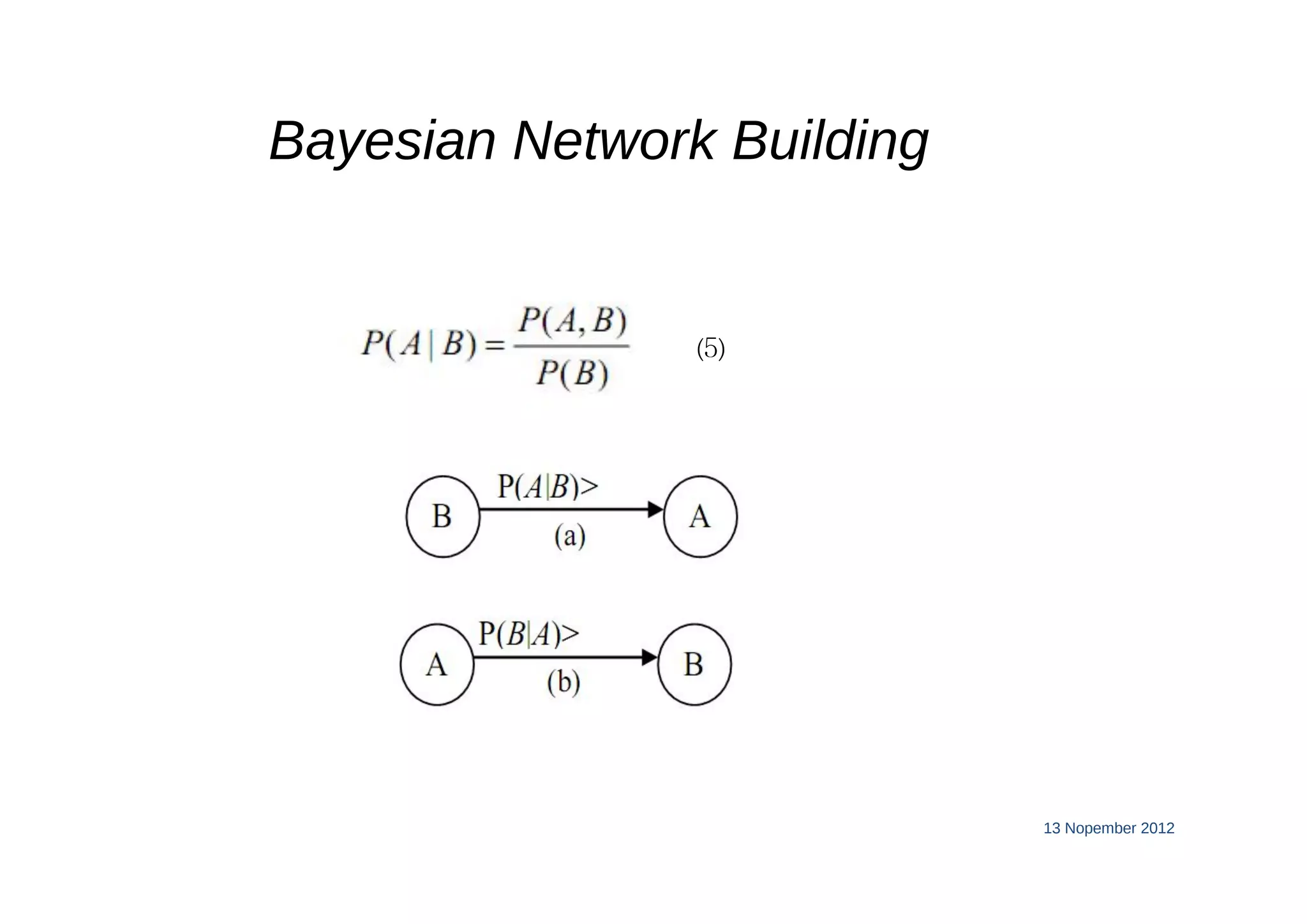
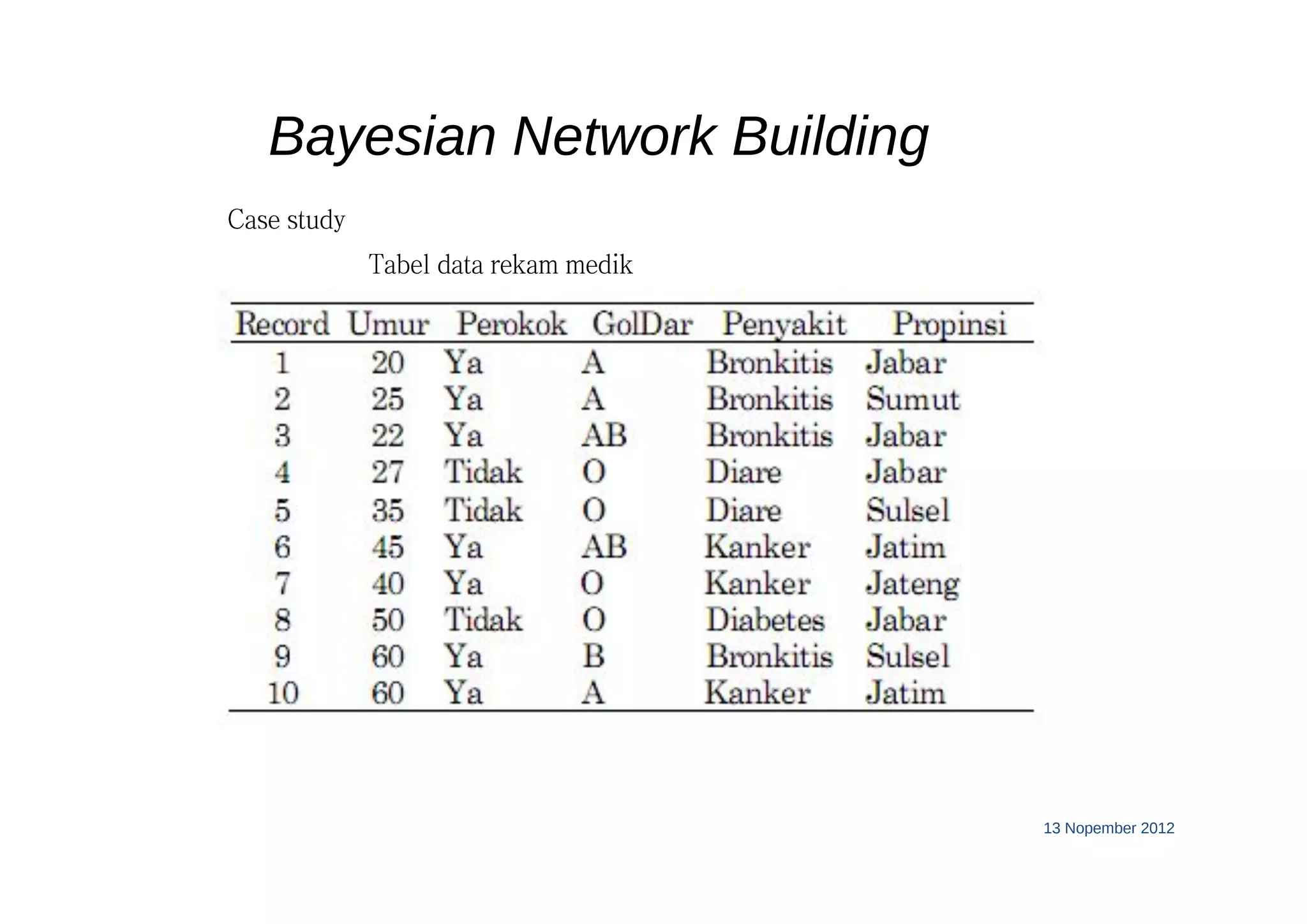
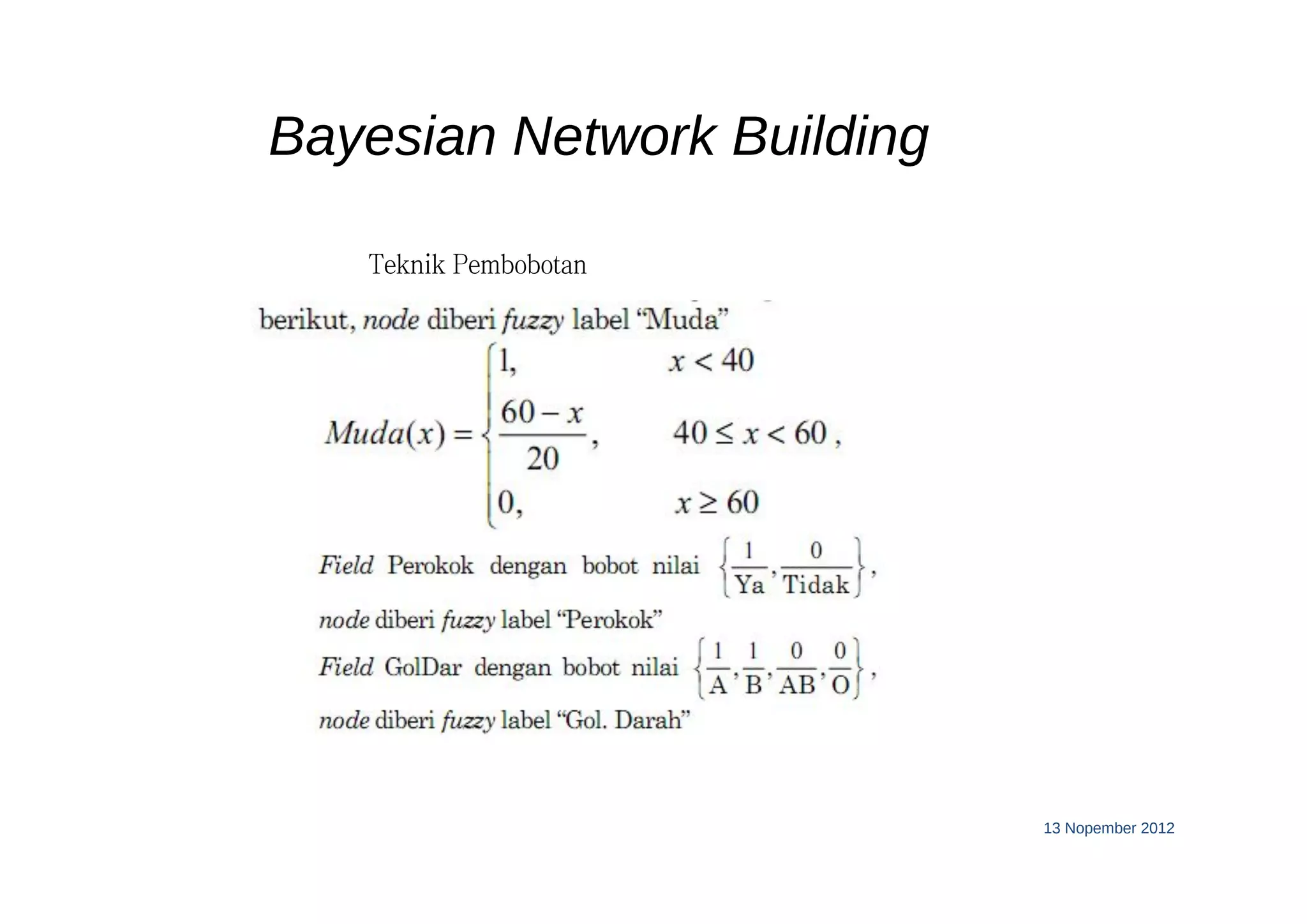
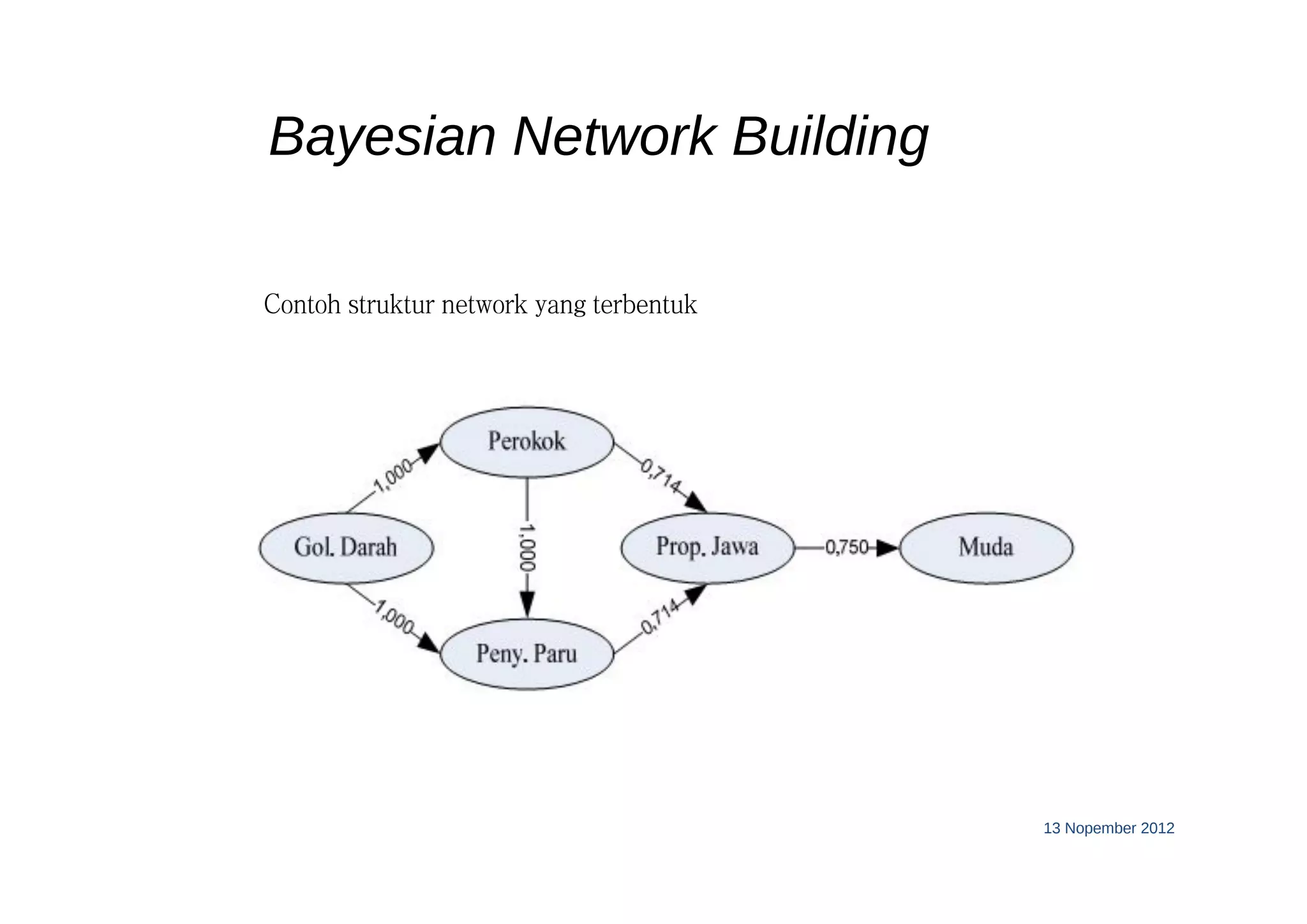
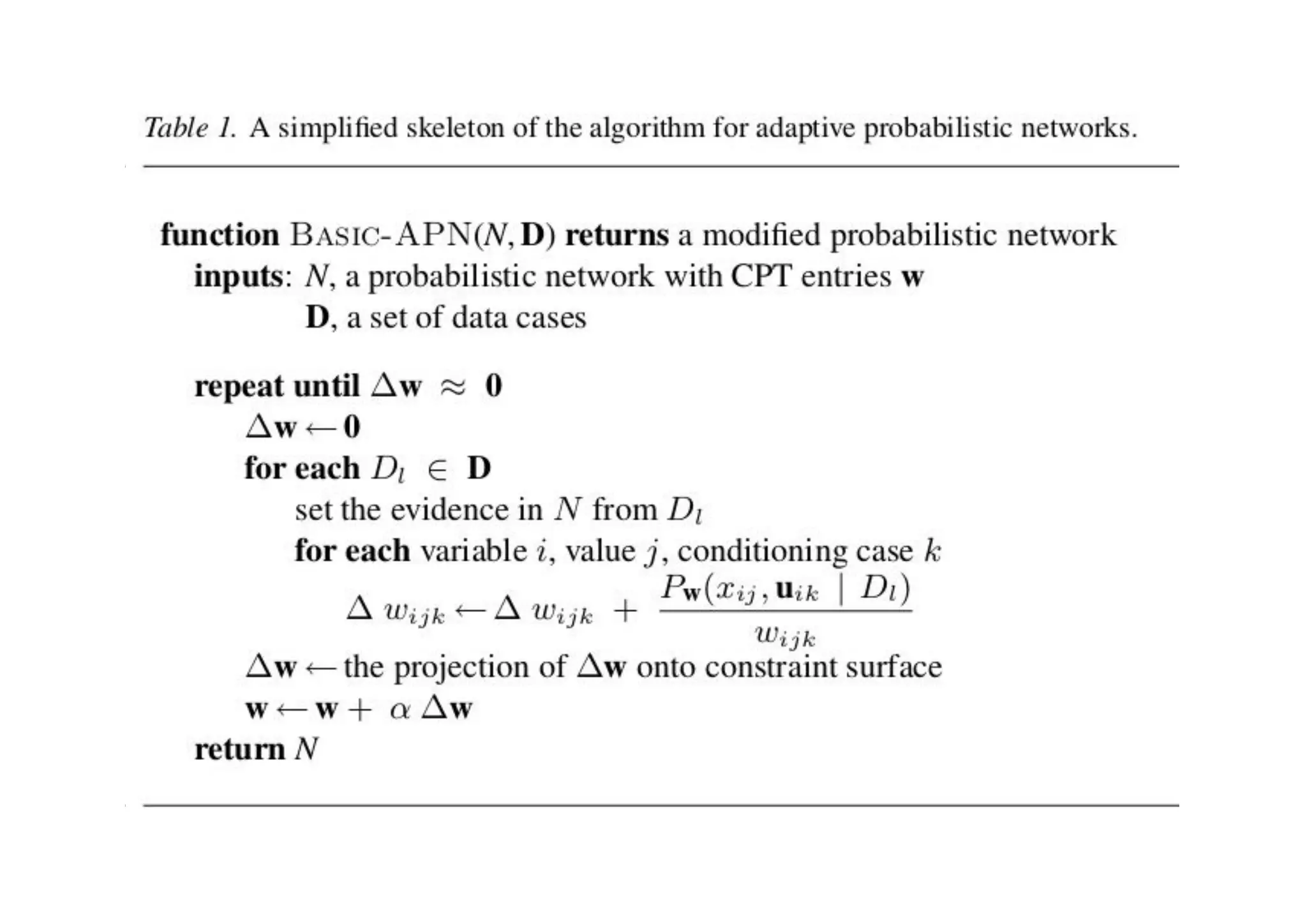
This document discusses machine learning using Bayesian belief networks. It begins by reviewing Bayesian reasoning as a probabilistic approach. It then discusses Bayesian learning as a method used in machine learning that explicitly calculates probabilities for hypotheses. Finally, it provides an example of using Bayes' theorem to calculate probabilities based on prior probabilities and observed data.