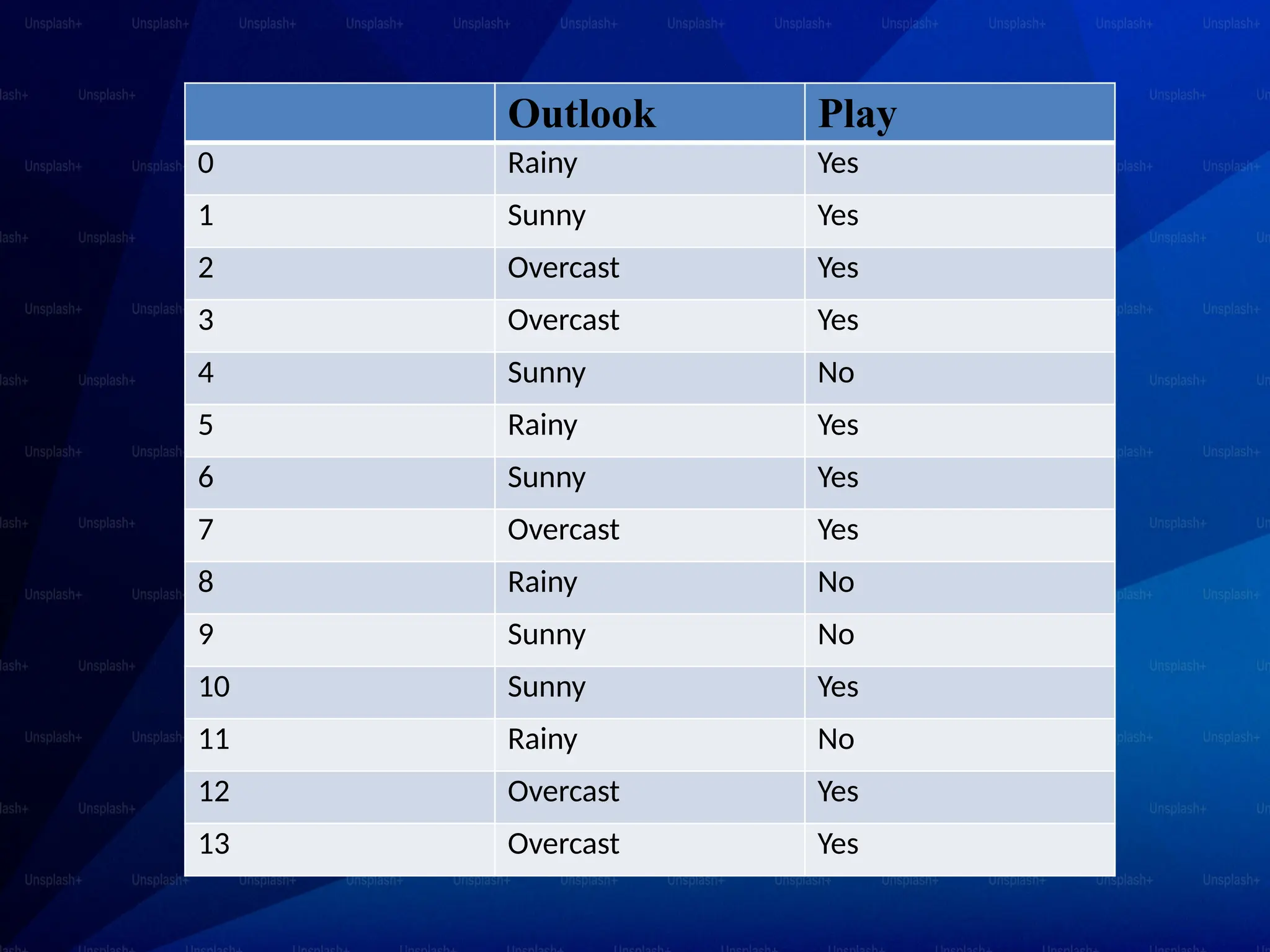
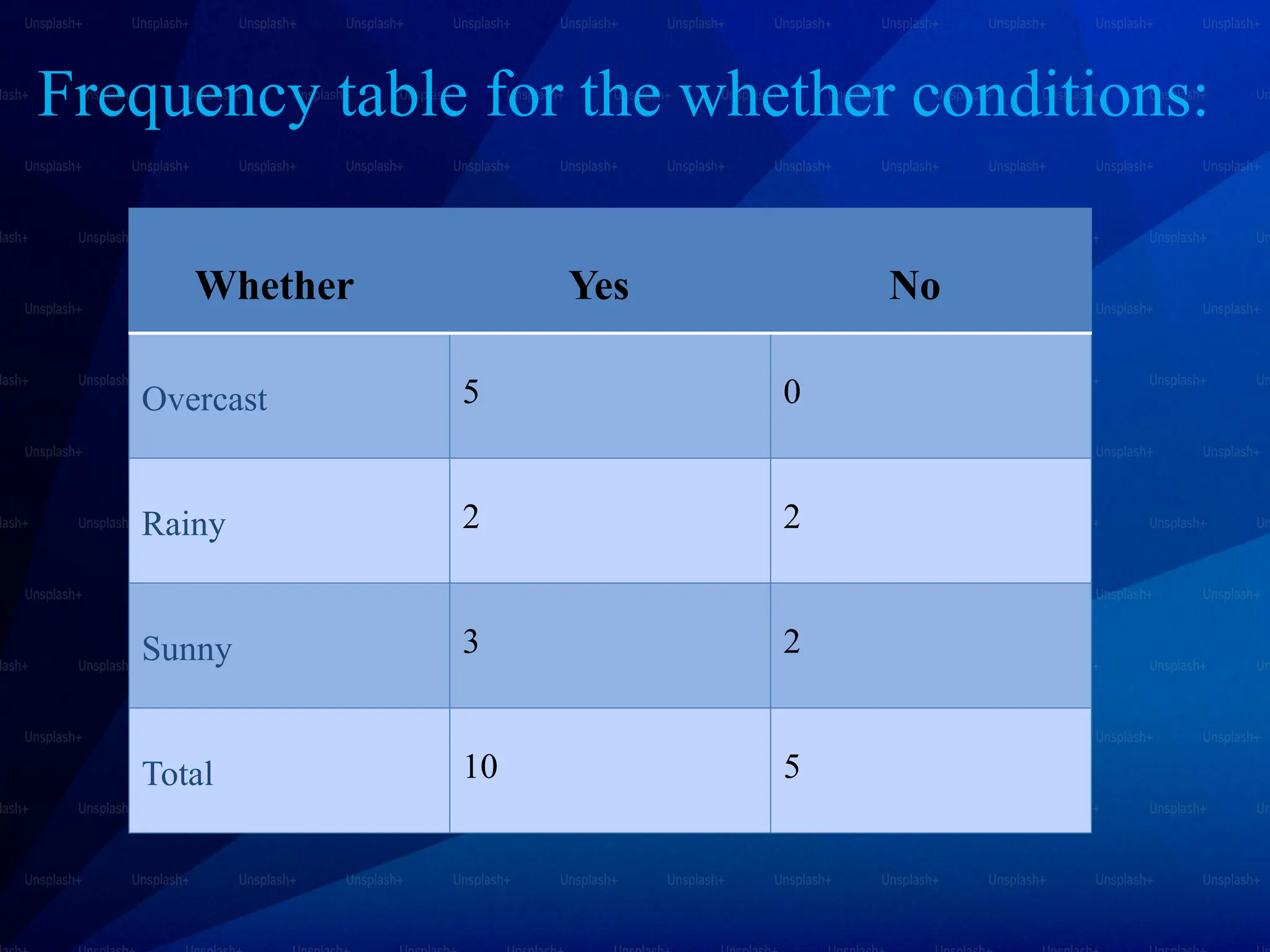
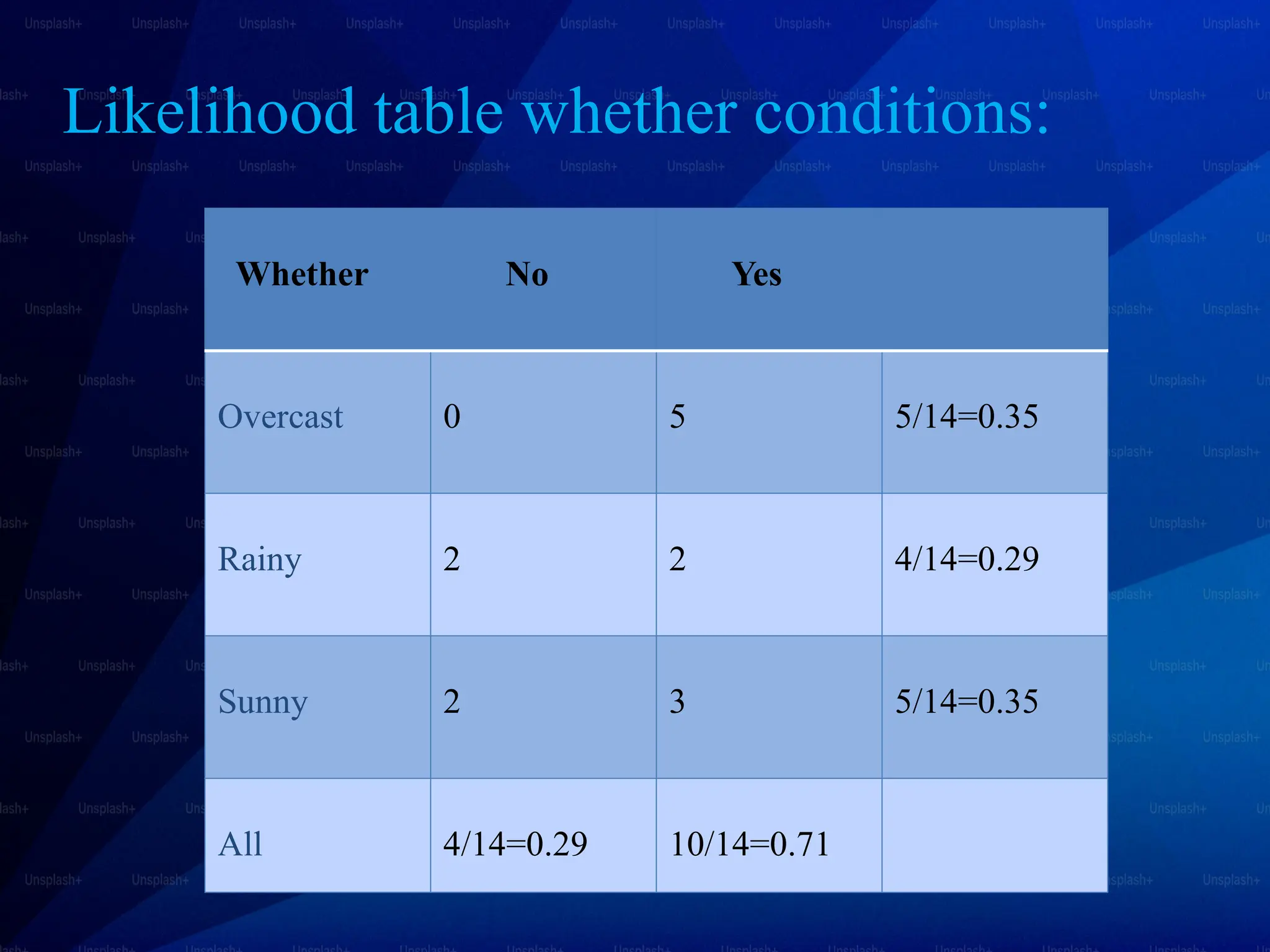
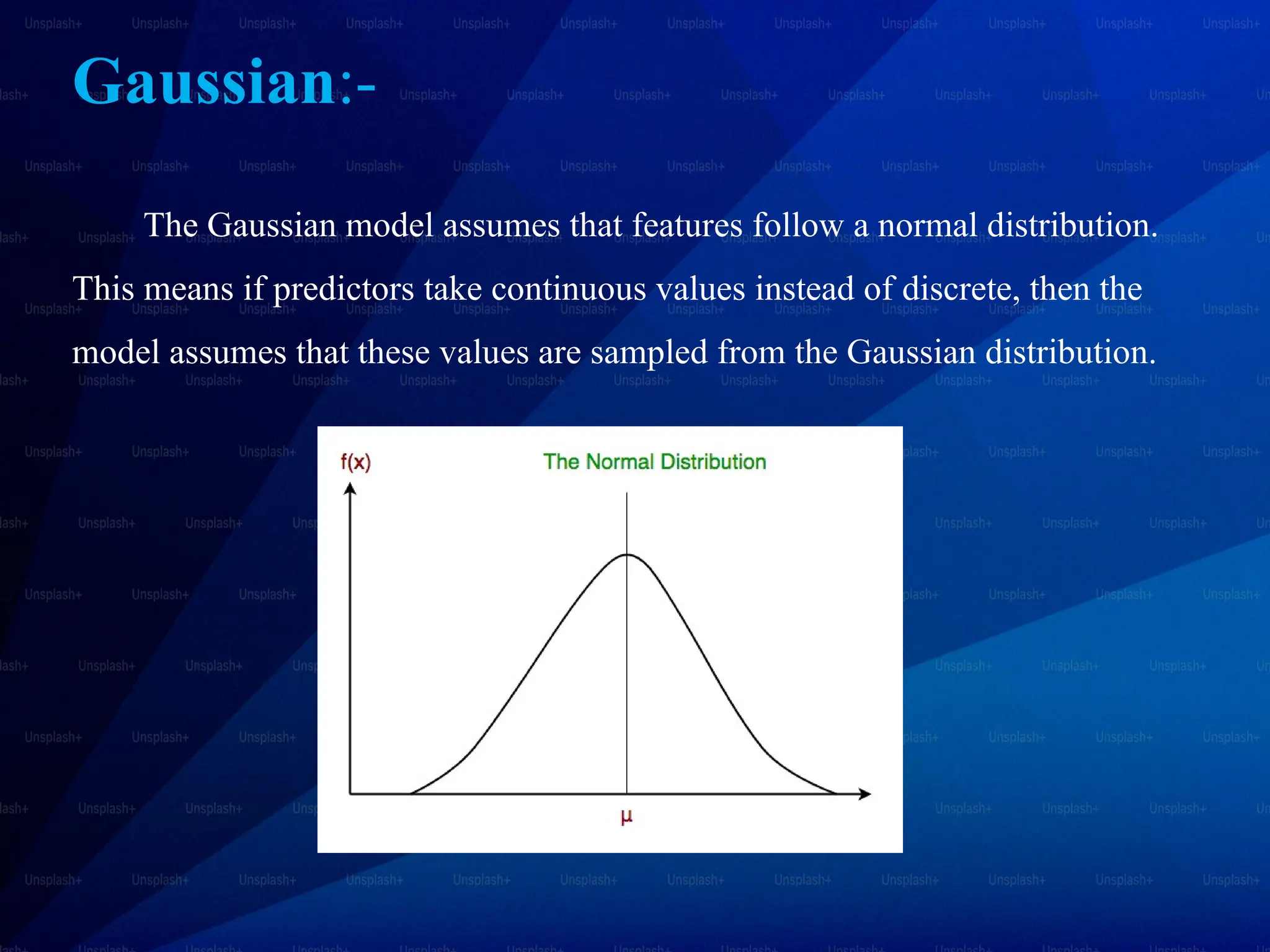
The document discusses Bayes’ theorem and its applications in various fields such as medicine, engineering, and finance. It explains the Naive Bayes classifier, a supervised learning algorithm that utilizes Bayes' theorem for classification tasks, and outlines its types, advantages, and disadvantages. Examples of real-life applications of both Bayes’ theorem and the Naive Bayes classifier include spam filtering, weather forecasting, and medical diagnosis.