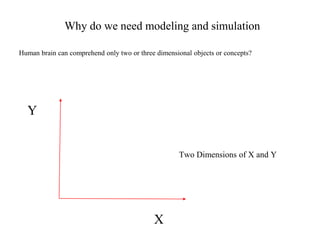
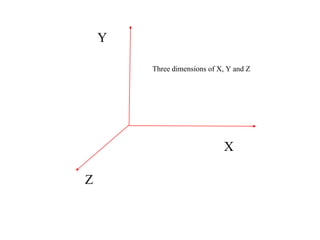
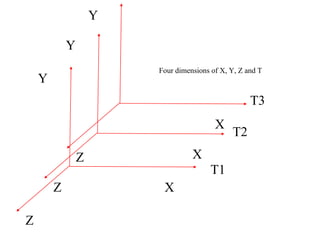
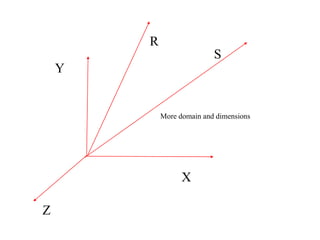
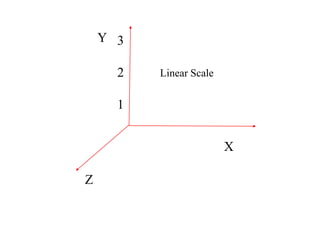
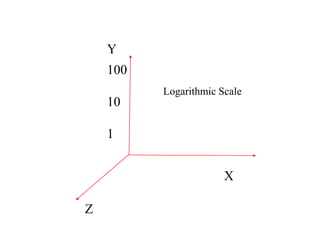
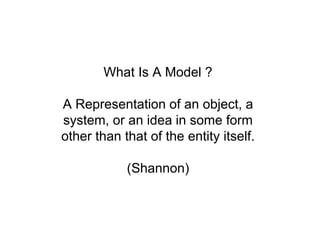
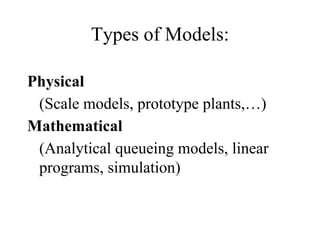
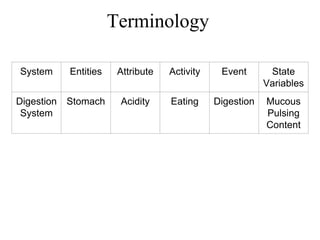
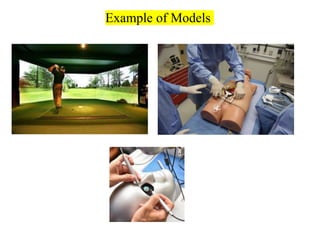
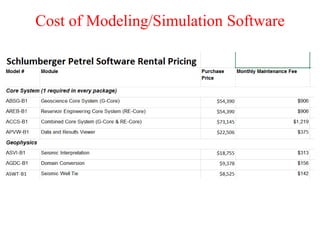
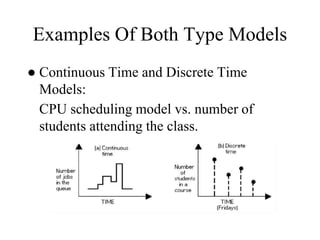
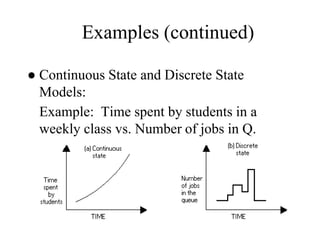
The document provides an overview of modeling and simulation, discussing their importance in representing complex systems and aiding in decision-making. It categorizes models into physical and mathematical types and elaborates on the benefits and risks of simulations, such as flexibility and potential inaccuracies. Various simulation software and classifications of models are also mentioned, highlighting the distinctions between discrete and continuous systems.