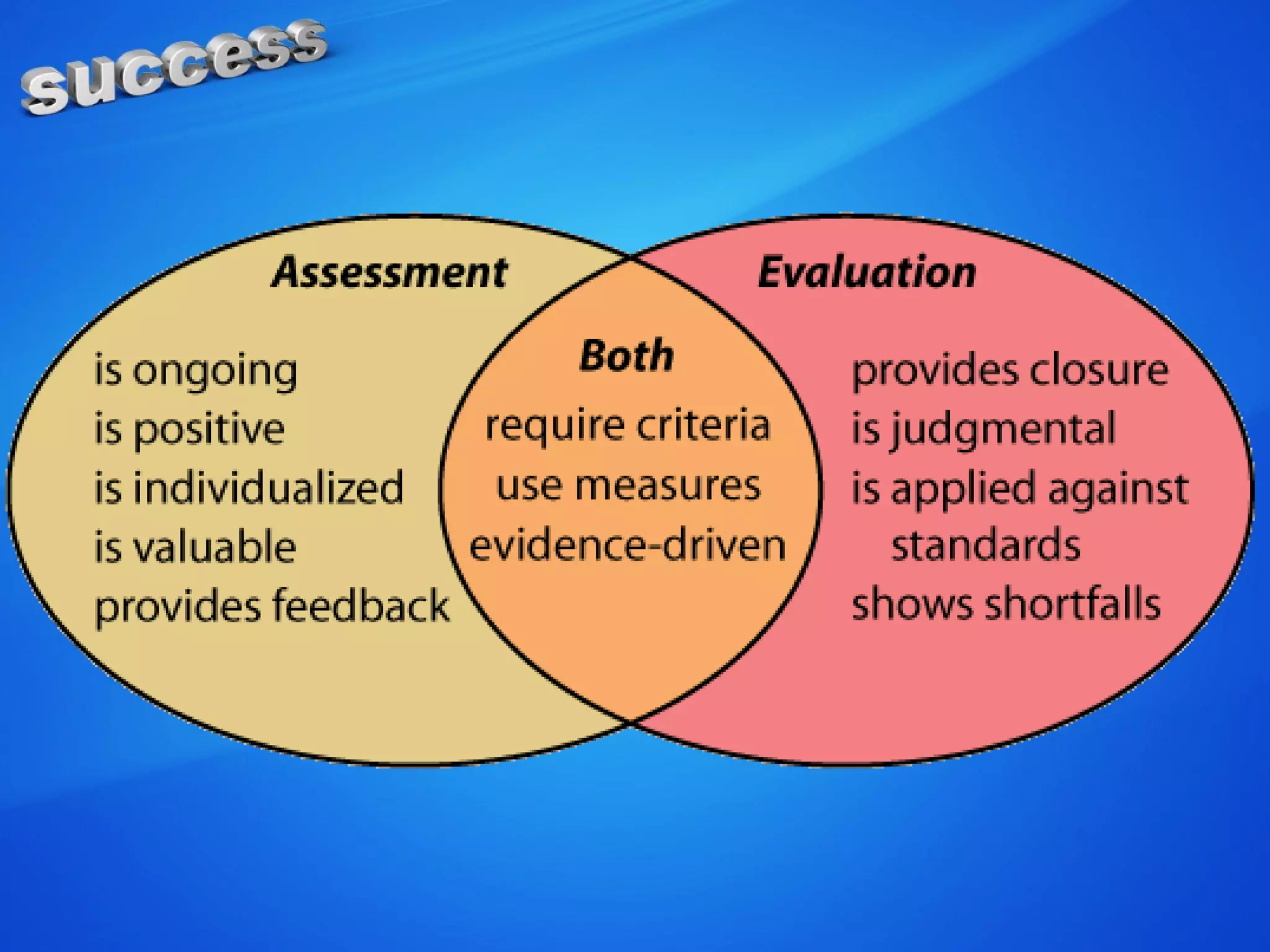
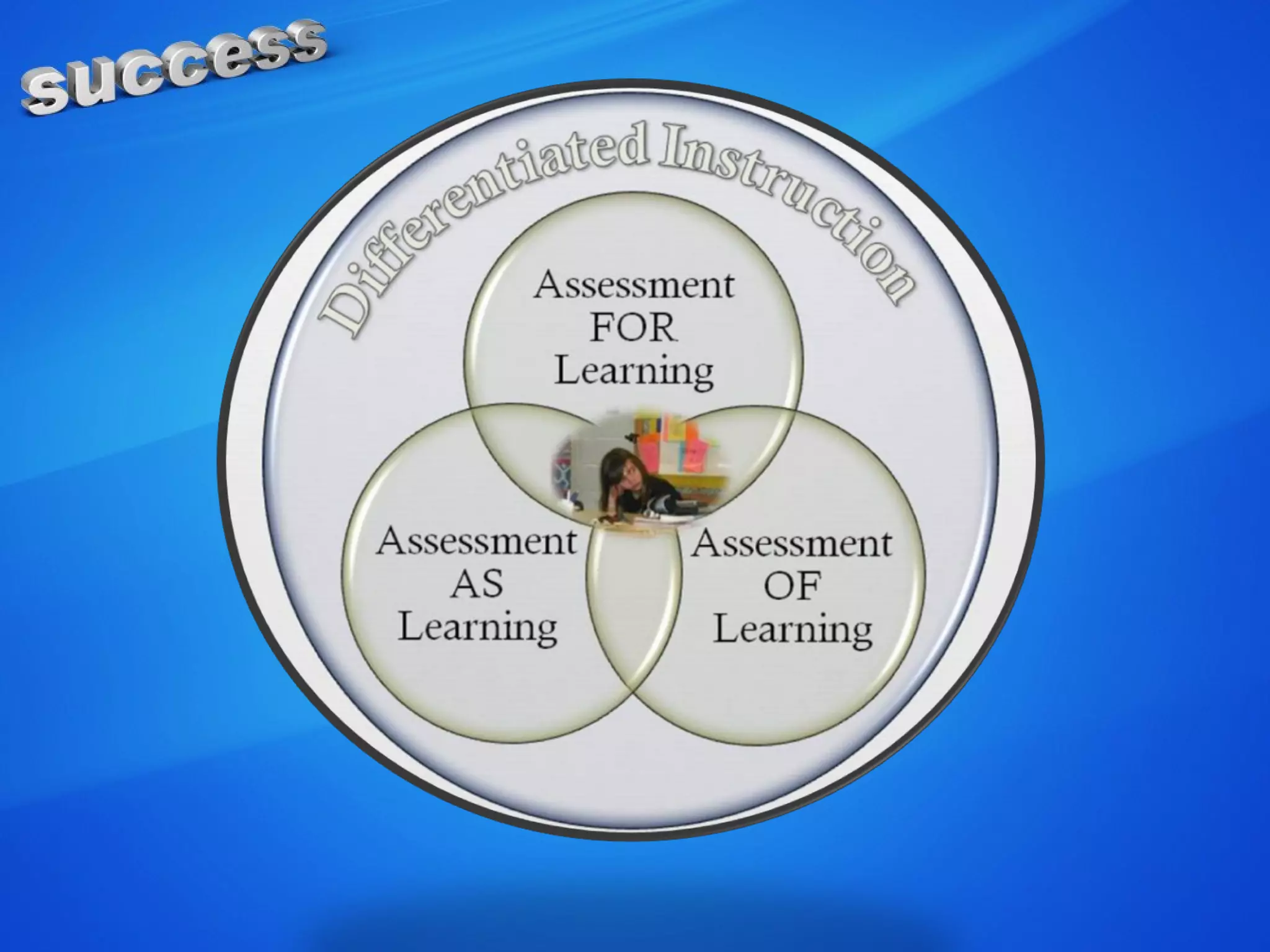
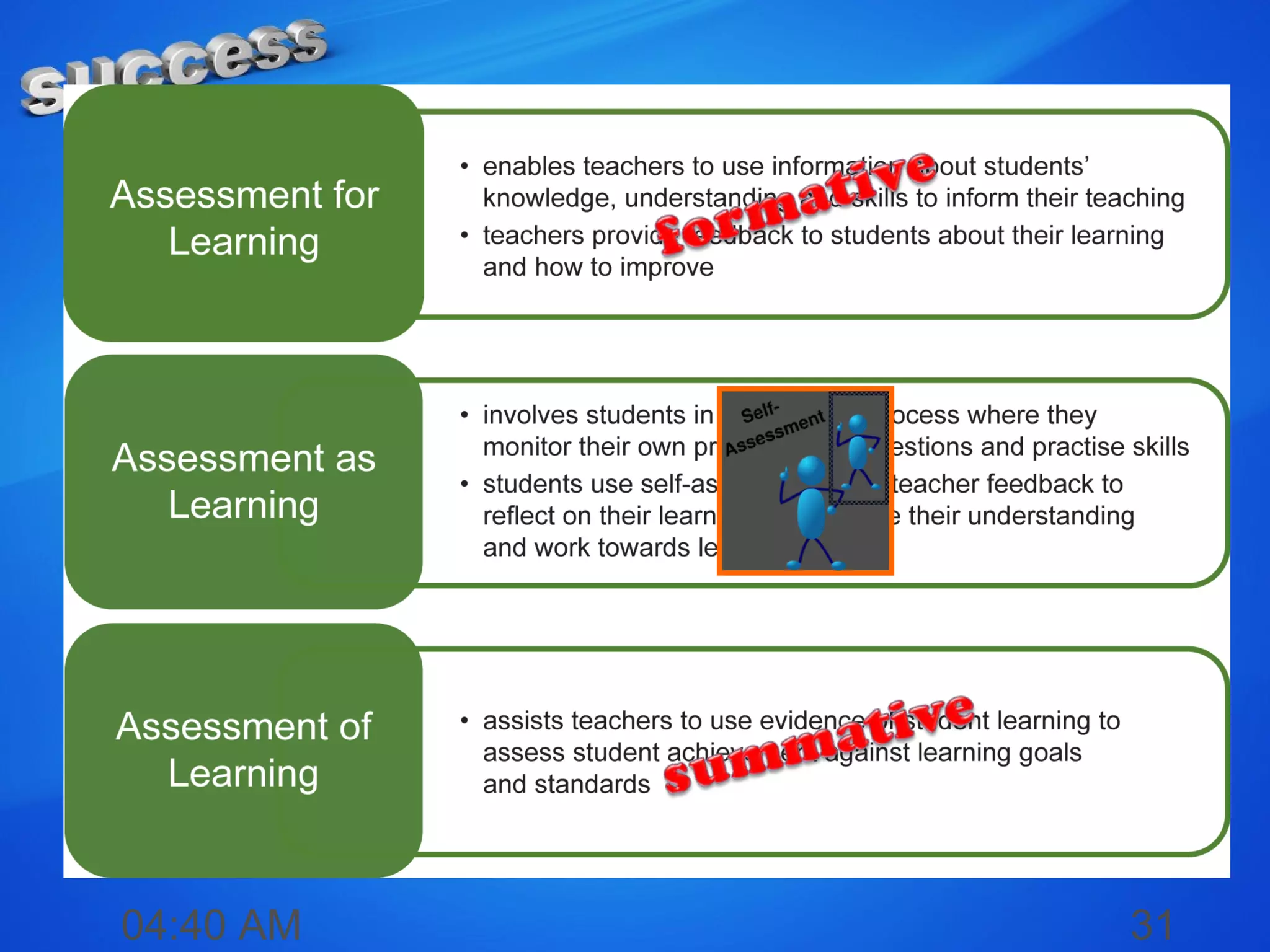
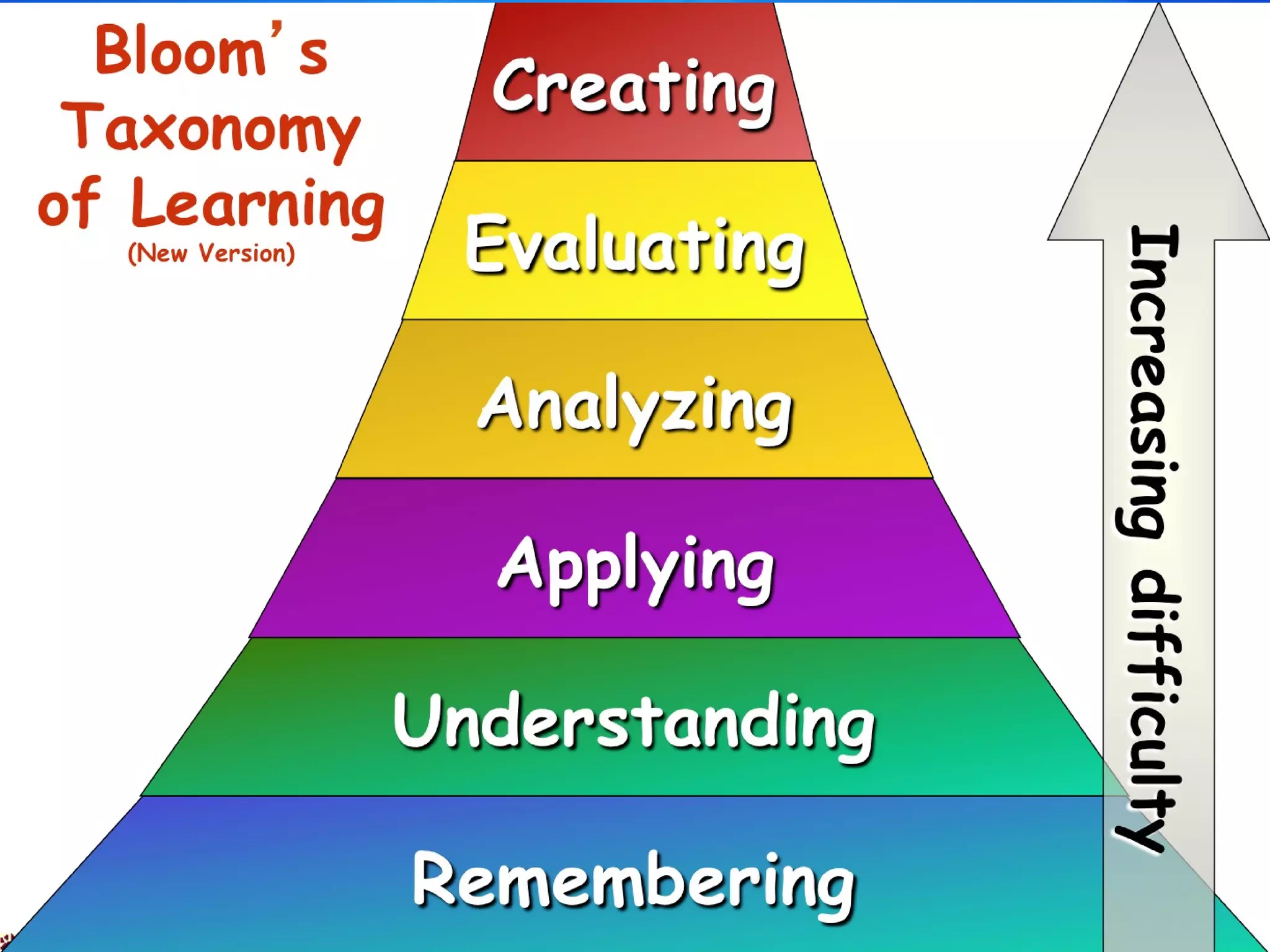
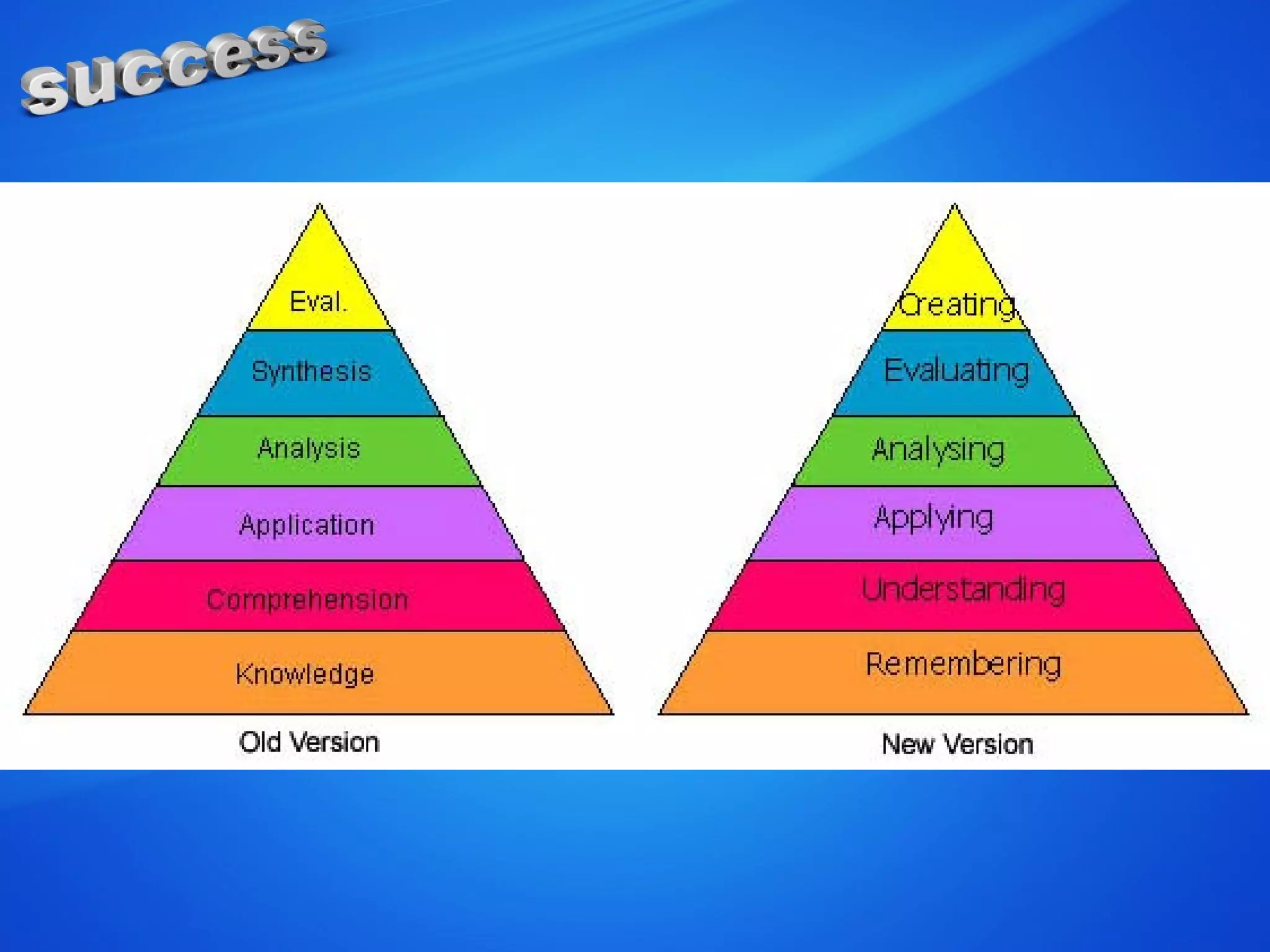
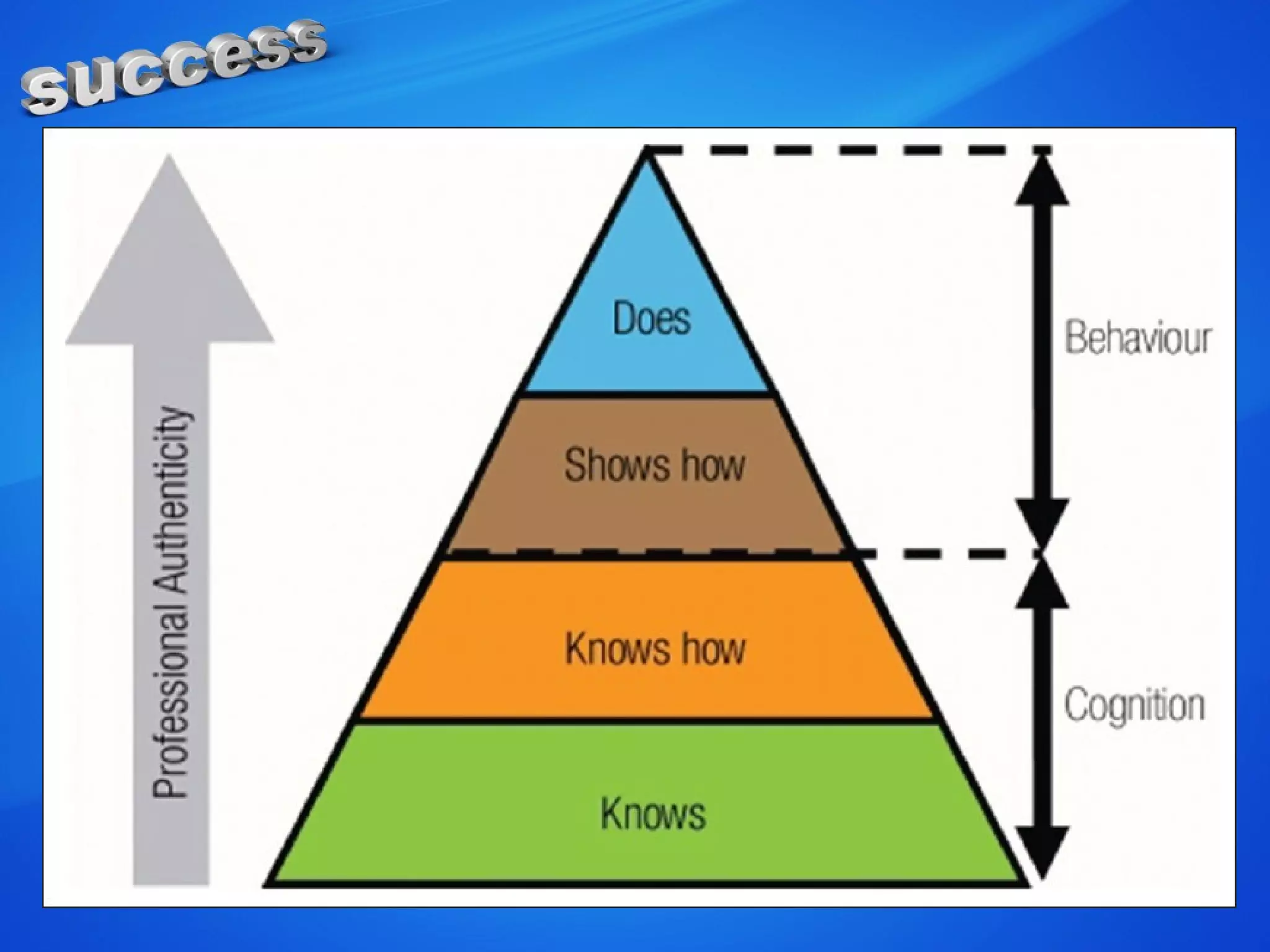
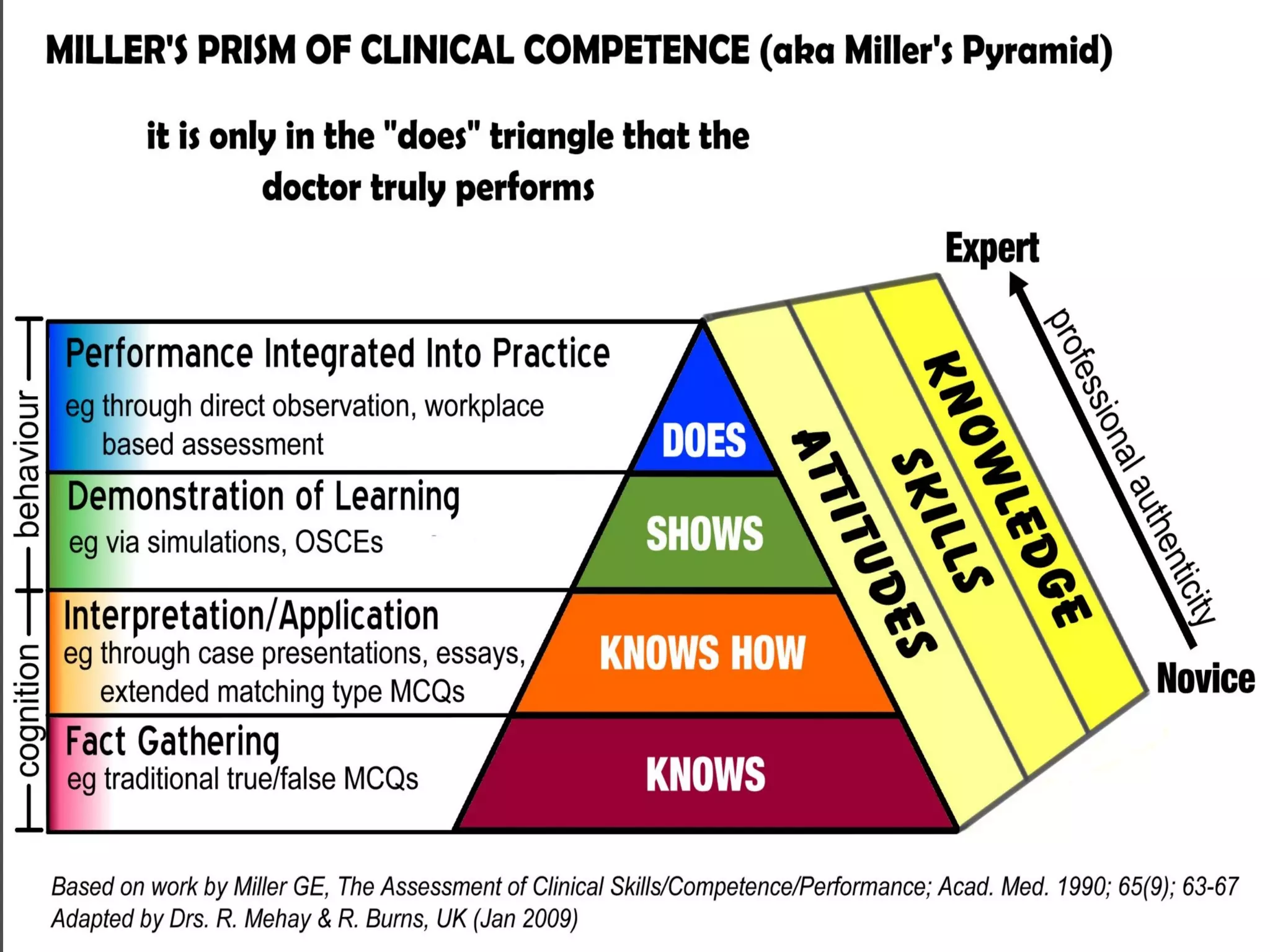
The document discusses the concepts of measurement, assessment, and evaluation in the context of educational attainment, emphasizing their distinct roles. It outlines types of assessments, such as formative, summative, and self-assessment, while highlighting the qualities of good assessments including validity and reliability. Additionally, it addresses the importance of assessing students for feedback, improvement, and maintaining educational quality.