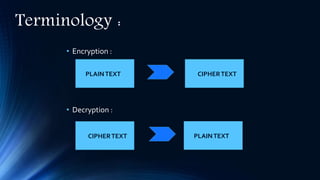
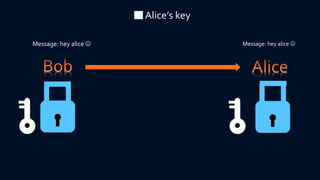
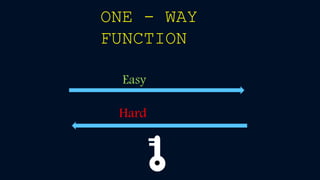
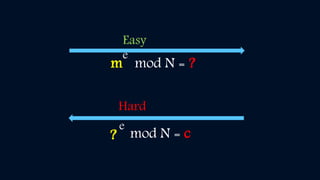
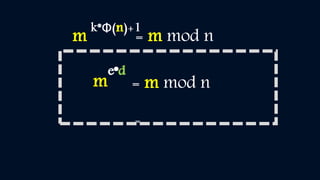
Cryptography involves encryption and decryption of messages. Encryption scrambles a message using an algorithm and key, while decryption restores the original message. There are two main types: private key cryptography uses the same key for encryption and decryption, while public key cryptography uses separate keys - a public key to encrypt and a private key to decrypt. The RSA algorithm is an example of public key cryptography that is widely used for secure communication on the internet. It relies on the fact that multiplying two large prime numbers together is easy, but factoring their product into primes is very difficult.