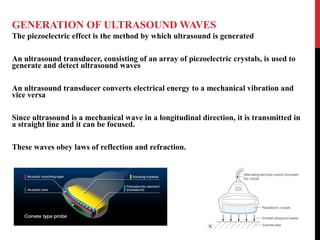
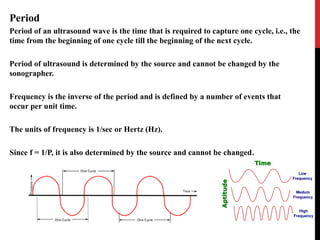
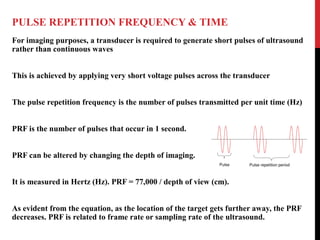
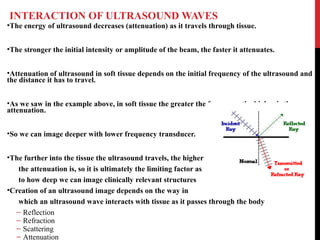
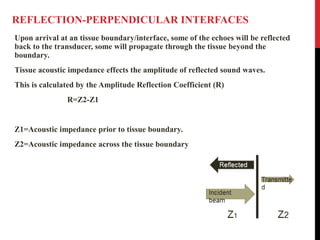
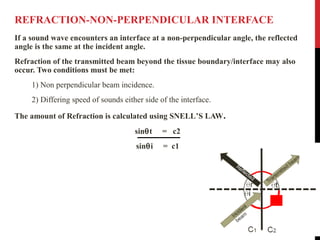
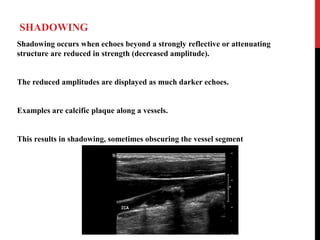
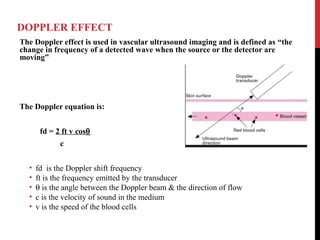
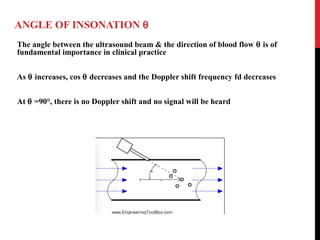
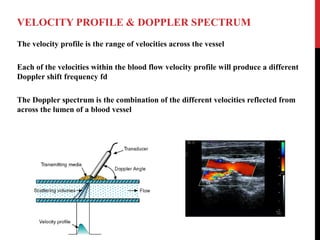
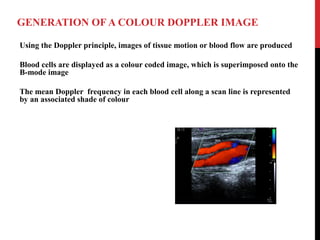
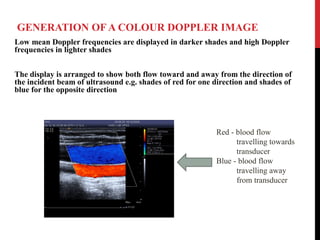
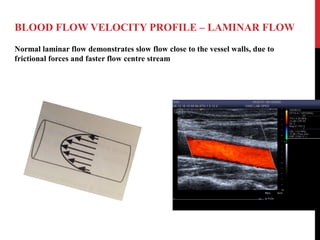
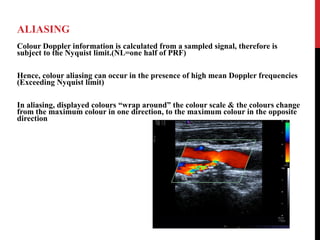
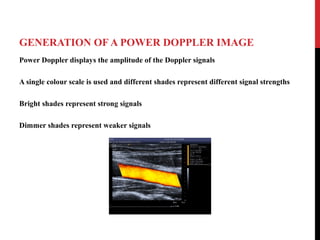
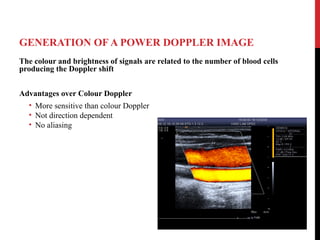
Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to image blood vessels. It combines real-time imaging (B-mode) with Doppler to show anatomy and blood flow. Ultrasound is generated by piezoelectric crystals in the transducer that convert electrical signals to sound waves. Reflected sound waves are converted back to electrical signals to form images. Factors like frequency, amplitude, and wavelength determine image quality and depth of penetration. Ultrasound provides information on vessel structure and blood flow velocity through Doppler modes.