This document provides an introduction and overview of a course on communication electronics. It discusses the following topics:
1. The 5 units that will be covered in the course: electronic communication & analog modulation, analog pulse modulation, digital pulse modulation, mobile telephony systems, and antennas & wireless communication.
2. A basic introduction to communication systems, including their history and key elements such as transmitters, communication mediums, receivers, and noise.
3. A fundamental model of communication systems, outlining the process from the message source to the message destination, and how signals are transmitted and received over a channel.




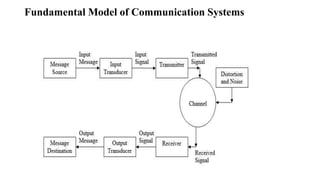

![• Distortion/Noise: External signals/features that affect the signal
• Receiver: Modifies the received signal, undoing the modifications
done by the transmitter
• Output Transducer: Converts message from electrical signal back
into its original form
• Output Message: The message/data/info that has been communicated
• Message Destination: Who/what the message/data/info was intended
for
[adrotate banner=”3″]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/communicationelectronicsppt-200524103311/85/Communication-electronics-ppt-7-320.jpg)
