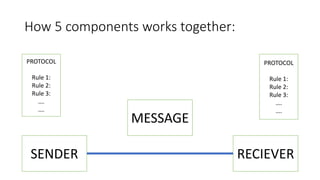
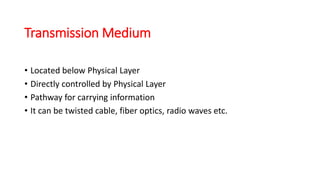
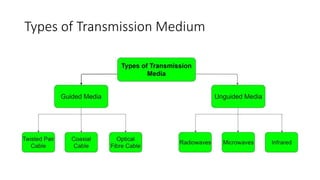
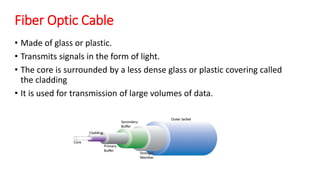
The document explains data communication, defining it as the transfer of data using technology and outlining its types: local and remote. It details the fundamental characteristics of data communication, including delivery, accuracy, and timeliness, along with its 5 key components: message, sender, receiver, transmission media, and protocol. Additionally, it discusses transmission mediums, specifically fiber optic cables, highlighting their advantages such as high bandwidth and immunity to interference.