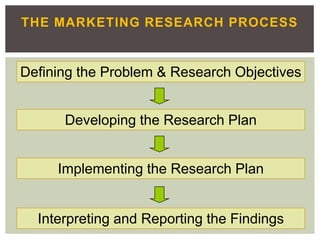
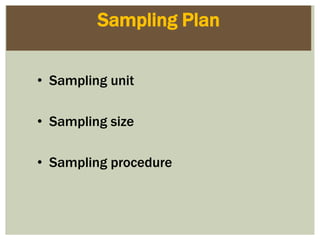
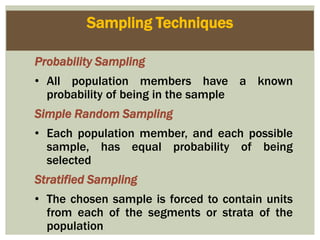
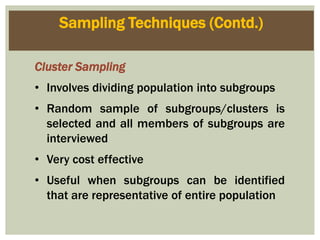
This document defines marketing and marketing management. It discusses that marketing management is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services. The goal is to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational objectives. Marketing management is also defined as choosing target markets and getting, keeping, and growing customers by creating, delivering, and communicating superior customer value. Marketing can involve goods, services, events, people, organizations, ideas and more. The document also outlines the marketing research process including defining problems and objectives, developing a research plan, implementing the plan, interpreting findings, and reporting them.