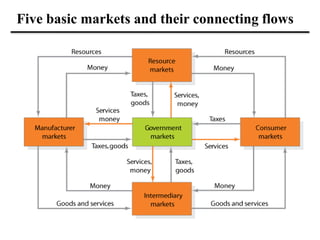
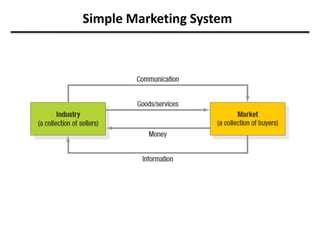
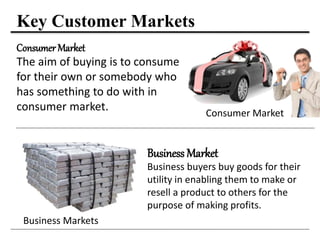
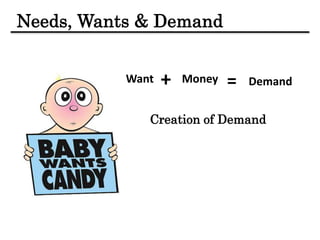
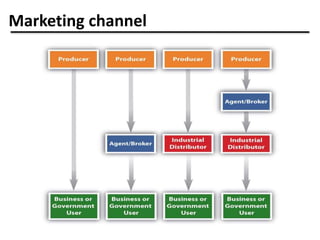
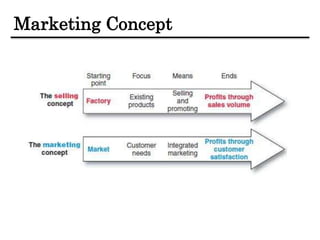
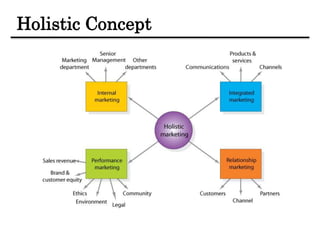
The document discusses the importance and scope of marketing in the 21st century, highlighting its role in financial success and societal impact. It defines marketing and marketing management, outlines fundamental marketing concepts, and examines how these have evolved. Additionally, it details the tasks necessary for successful marketing management, including strategy development, customer connection, and brand building.