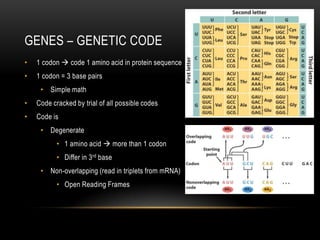
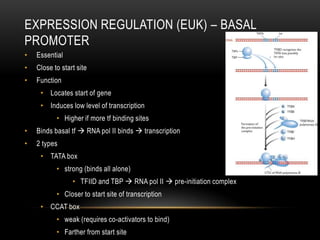
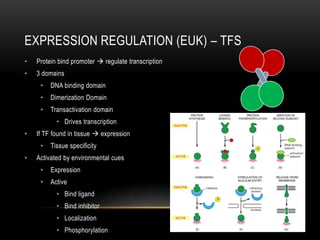
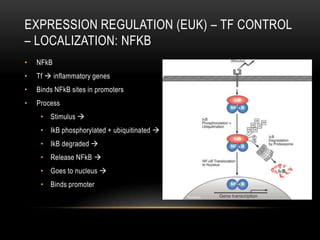
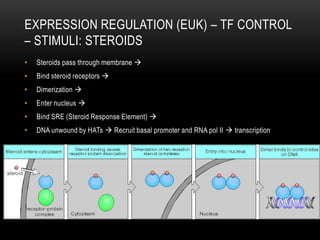
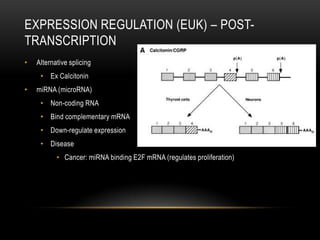
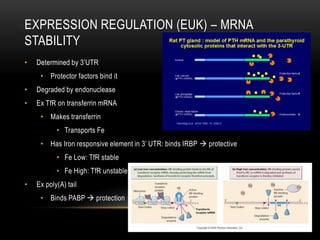
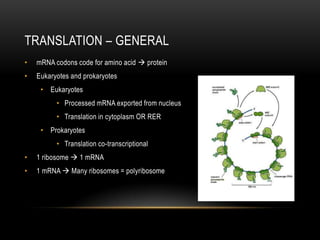
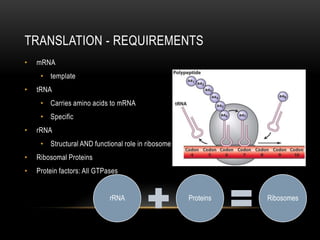
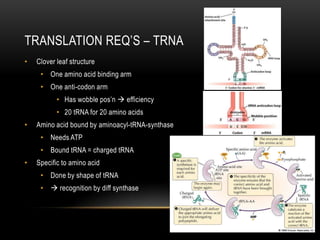
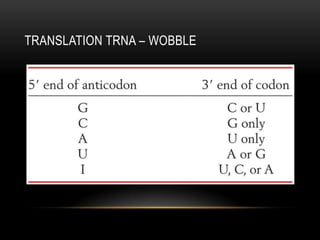
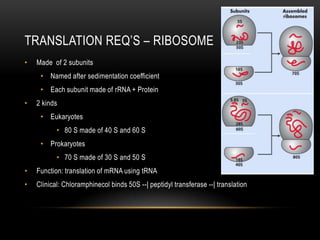
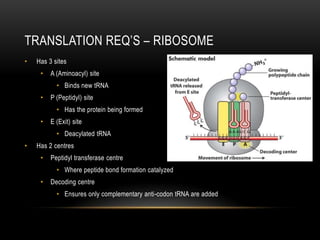
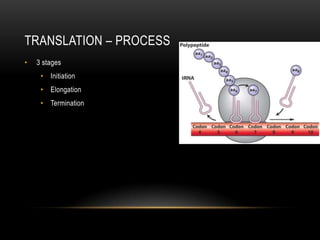
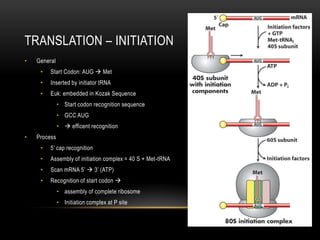
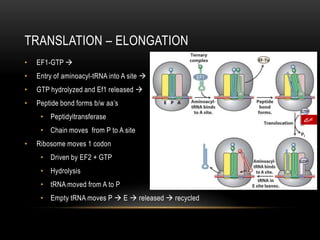
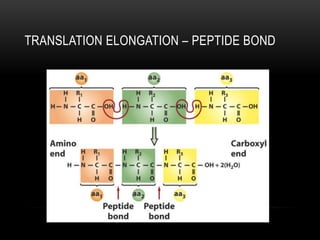
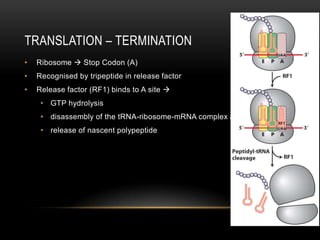
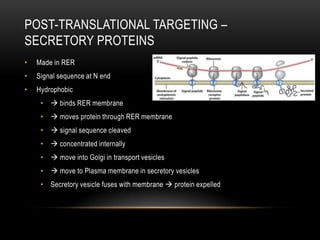
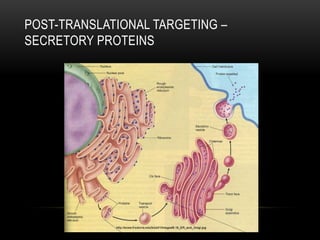
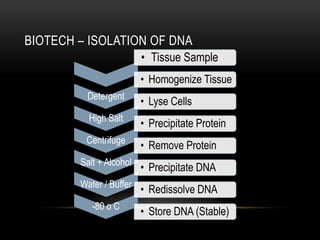
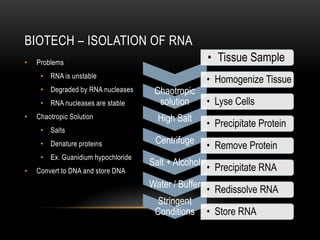
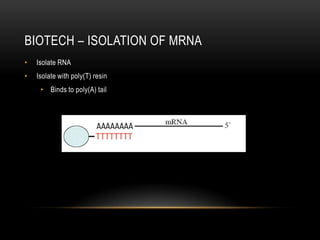
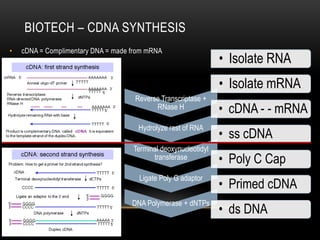
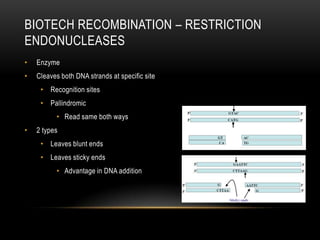
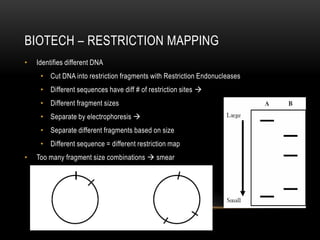
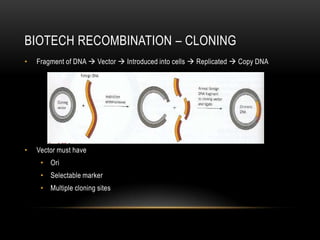
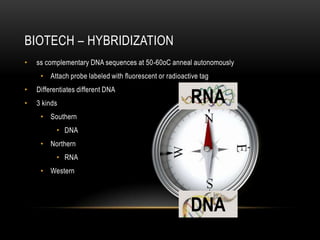
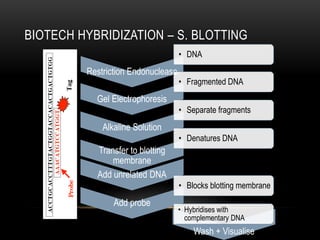
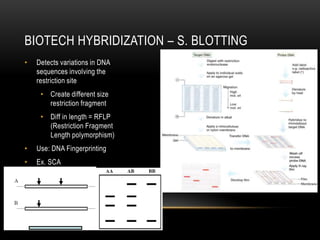
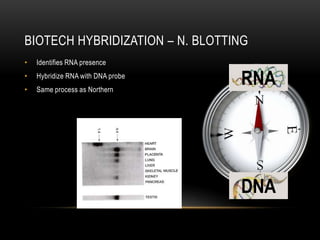
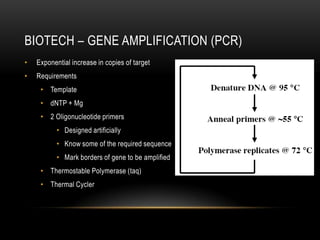
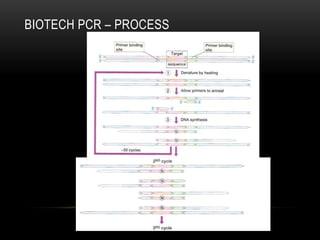
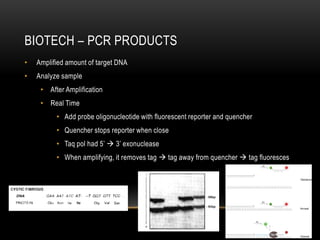
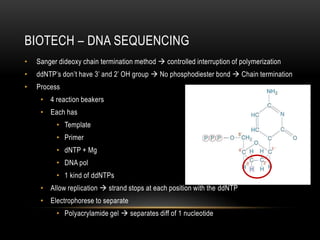
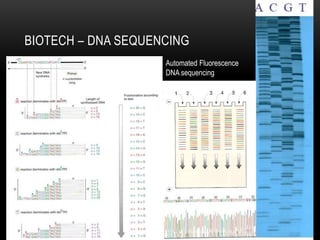
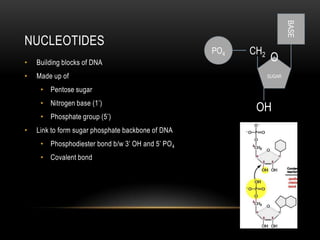
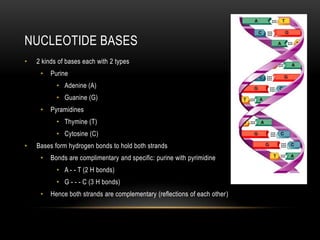
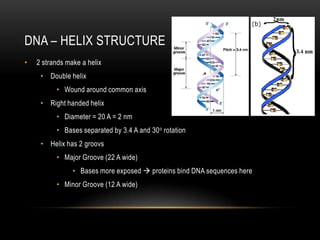
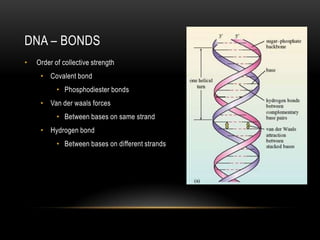
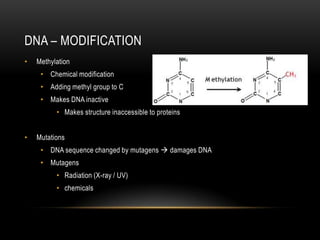
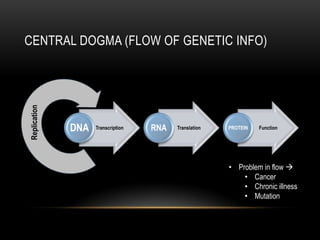
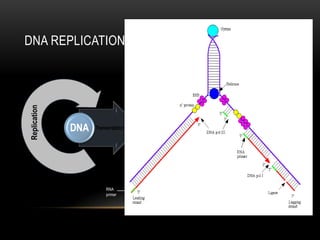
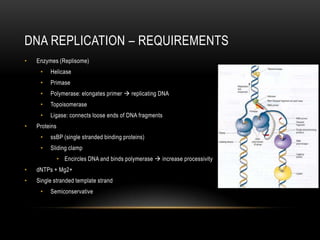
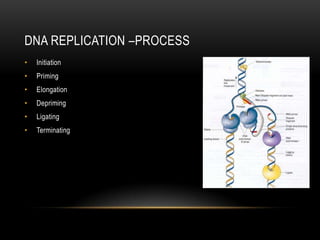
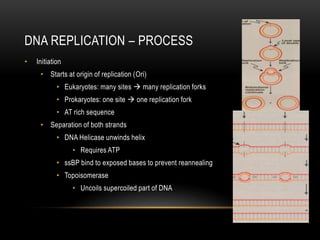
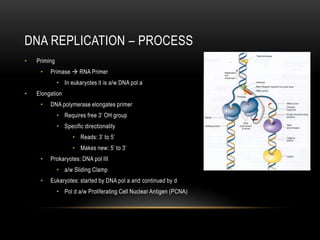
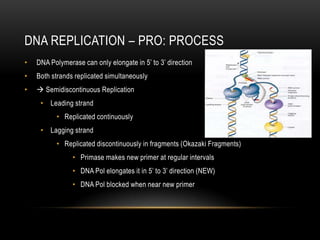
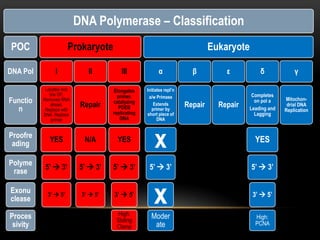
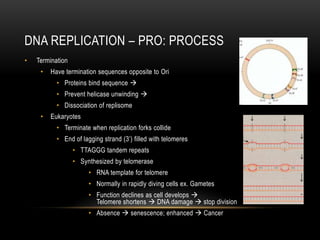
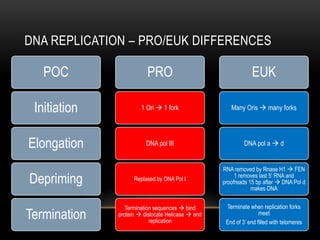
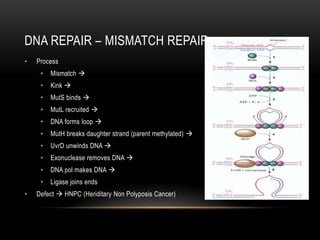
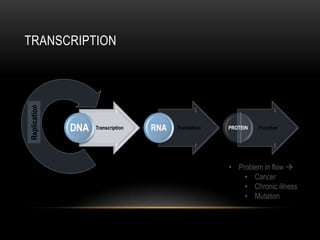
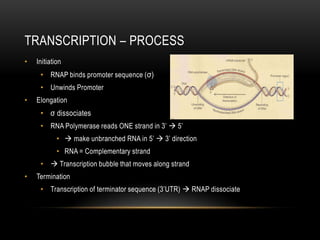
This document provides information about DNA replication, transcription, and repair. It discusses the key components and processes of DNA replication including initiation, priming, elongation, and termination. It describes the central dogma of molecular biology involving the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein. The document also summarizes the main types of DNA repair including mismatch repair, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, nonhomologous end joining, and recombination repair.





















![TRANSCRIPTION - GENES
[+1]
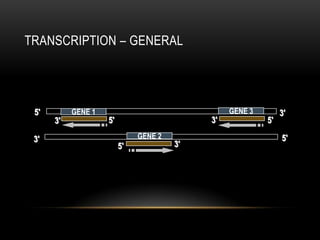
Upstream Downstream
-4-3 -2 P-1 CODING REIGON T
RNA
5' 3'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicgenetics-130315084511-phpapp01/85/Basic-Genetics-43-320.jpg)






![GENES
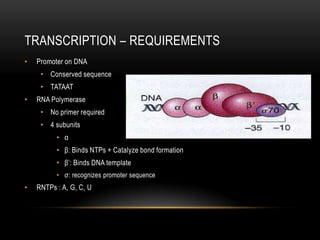
• 1 gene = information for 1 protein
• Has promoter and terminator sequence (consensus sequence)
• Composed of sequence of codons
[+1]
Upstream Downstream
-4-3 -2 P-1 CODING REIGON T
RNA
5' 3'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicgenetics-130315084511-phpapp01/85/Basic-Genetics-59-320.jpg)