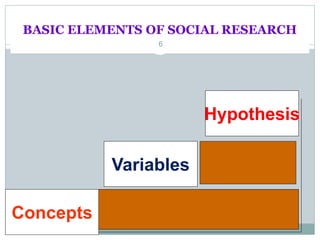
This document provides an overview of the basic elements of social work research, including concepts, variables, hypotheses, and their definitions. It discusses that concepts represent objects, properties, or phenomena; variables take two or more values and can be independent (causes) or dependent (effects); and hypotheses are tentative answers to research questions that need to be tested. The sources of hypotheses are identified as theories, literature, experiences, and prior findings. Characteristics of usable hypotheses are that they must be empirically testable, avoid moral judgments, and be clear and specific concepts.