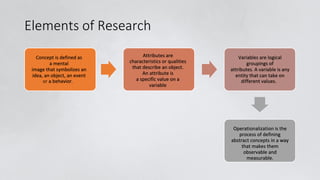
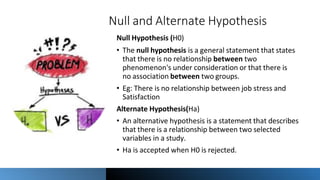
The document outlines the fundamental elements of social work research, focusing on scientific methods, concepts, definitions, assumptions, and hypotheses. Key terms such as variables, operationalization, and types of hypotheses (null and alternate) are defined, alongside the importance of testability and relationships between variables. Additionally, it discusses type 1 and type 2 errors in hypothesis testing and the distinction between theoretical and conceptual frameworks in research.