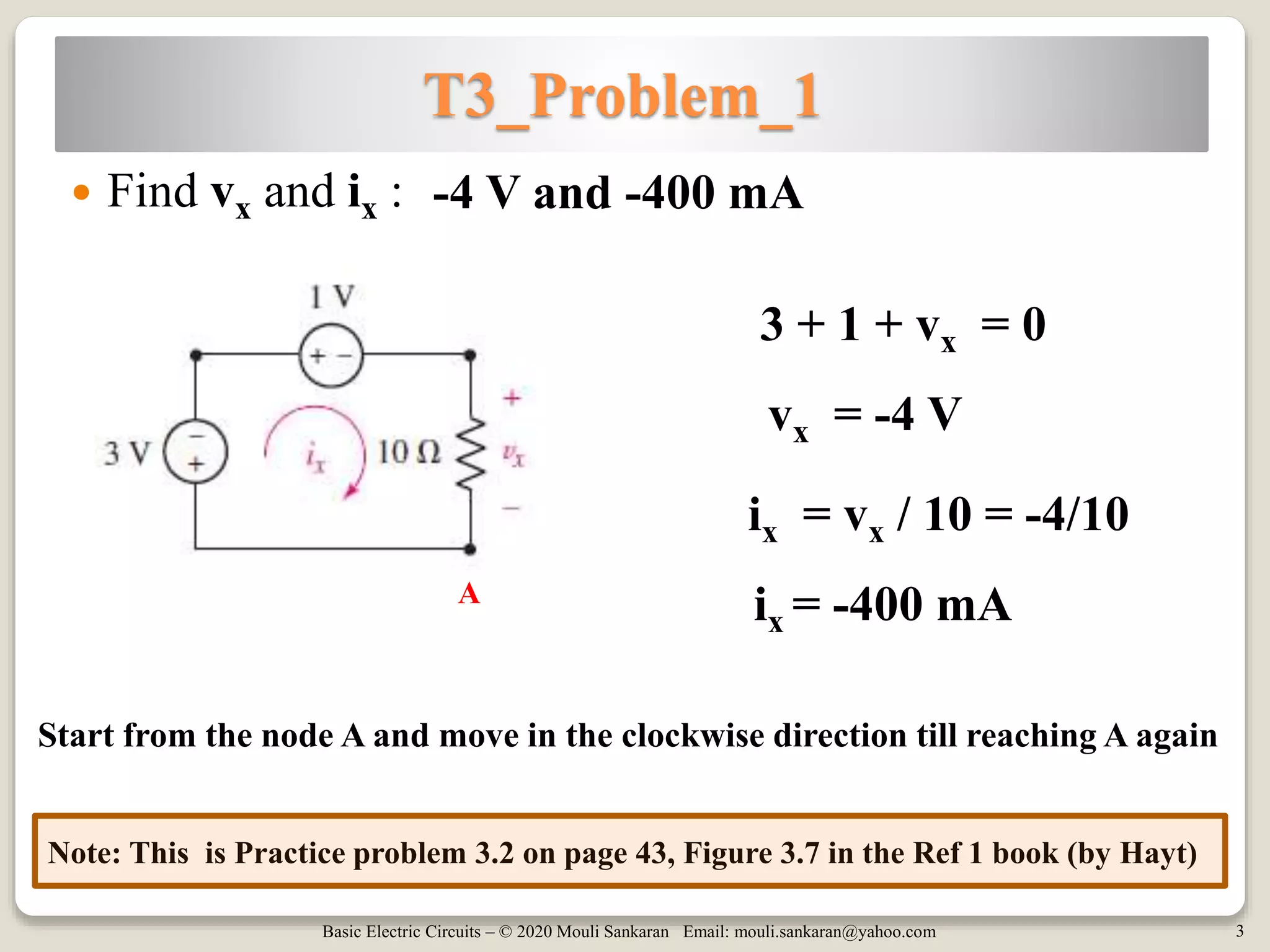
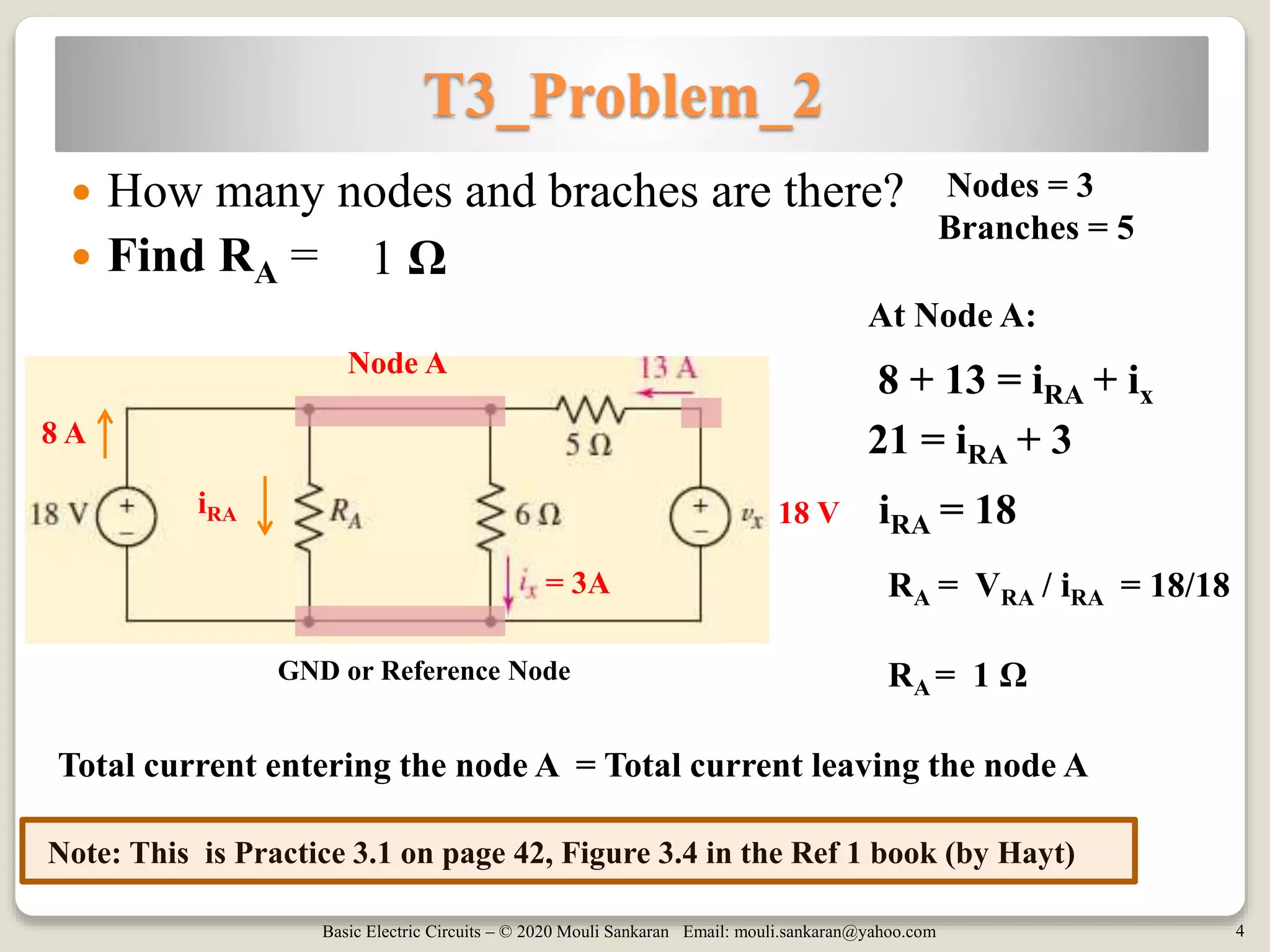
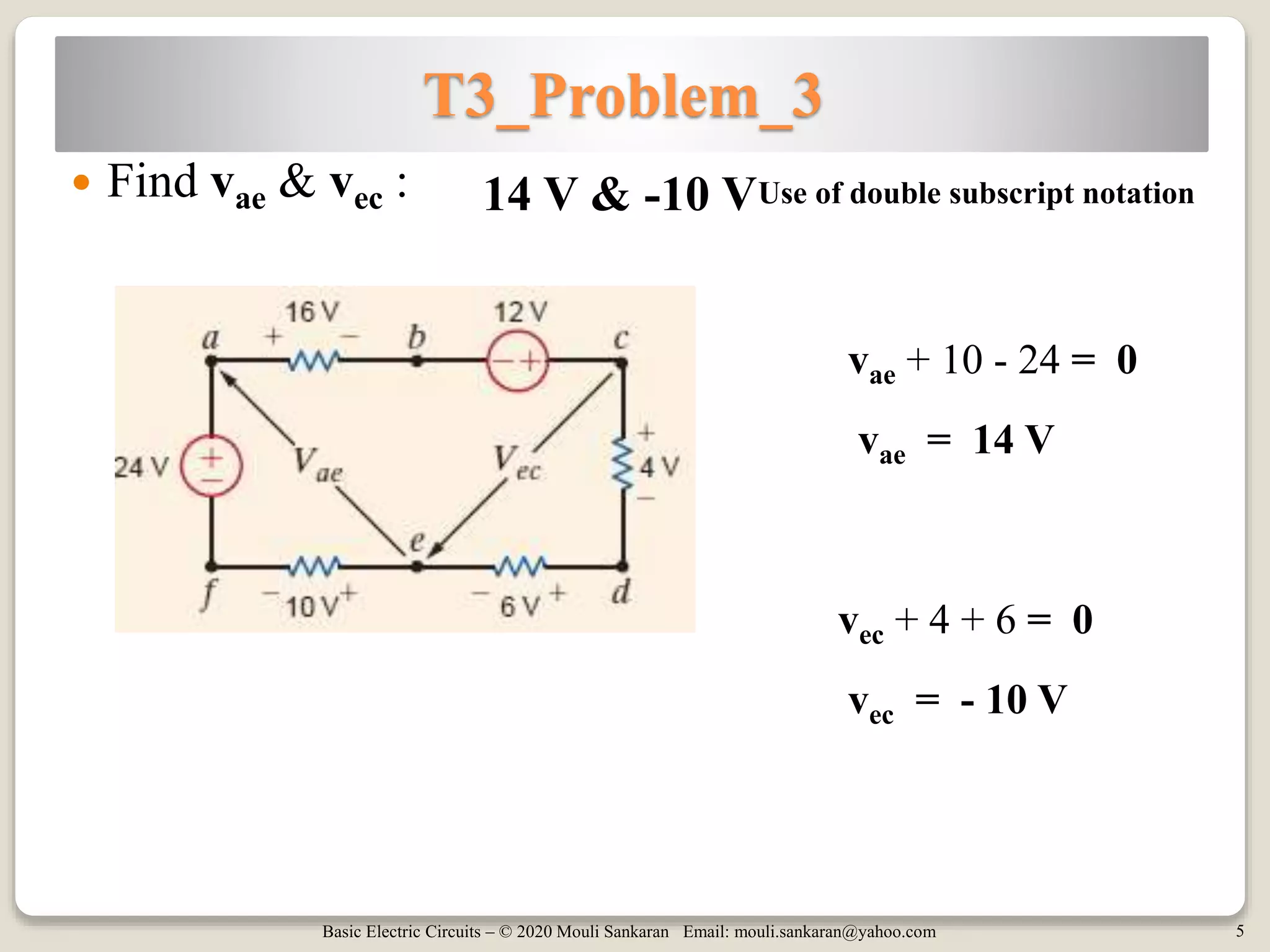
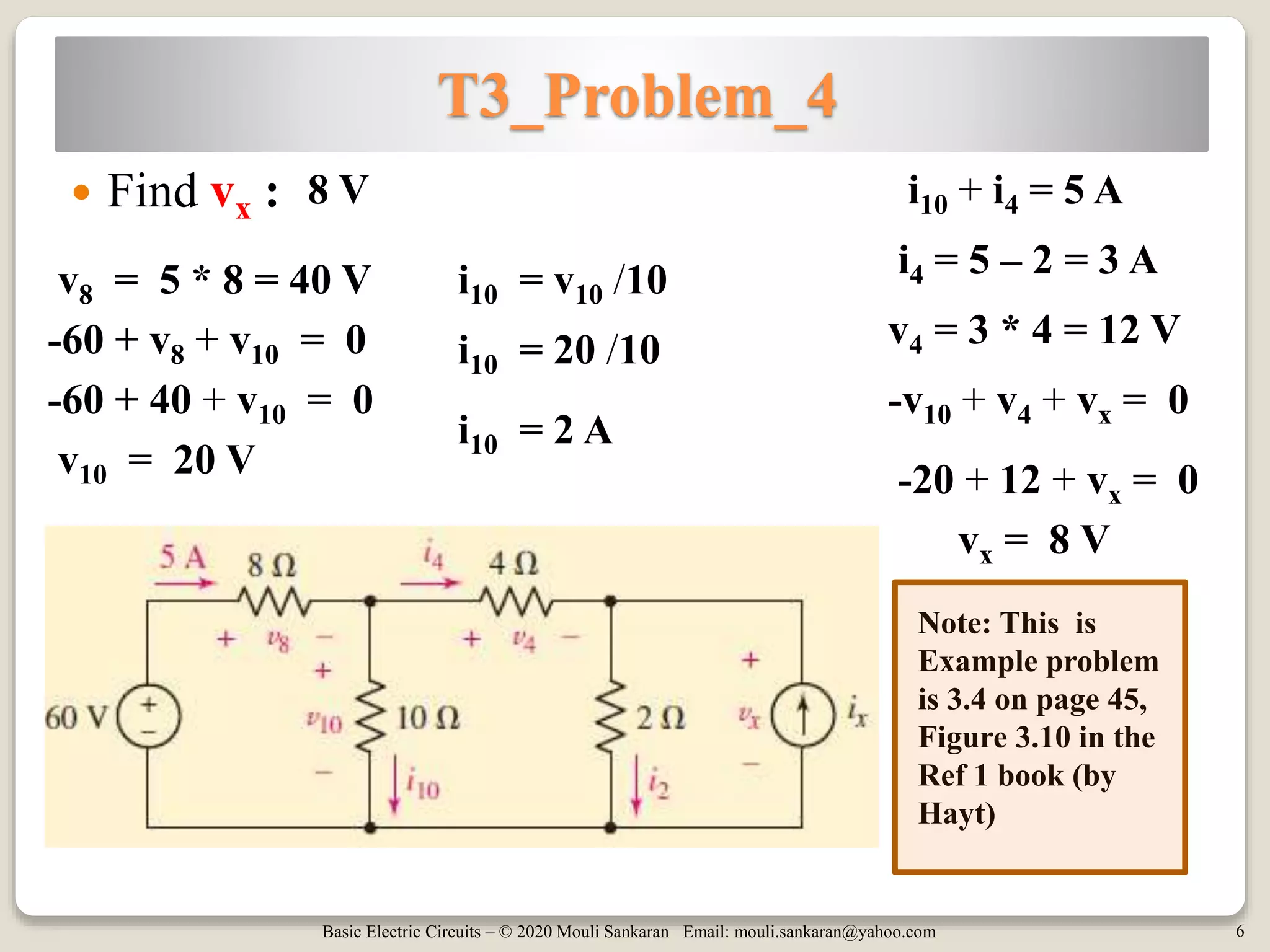
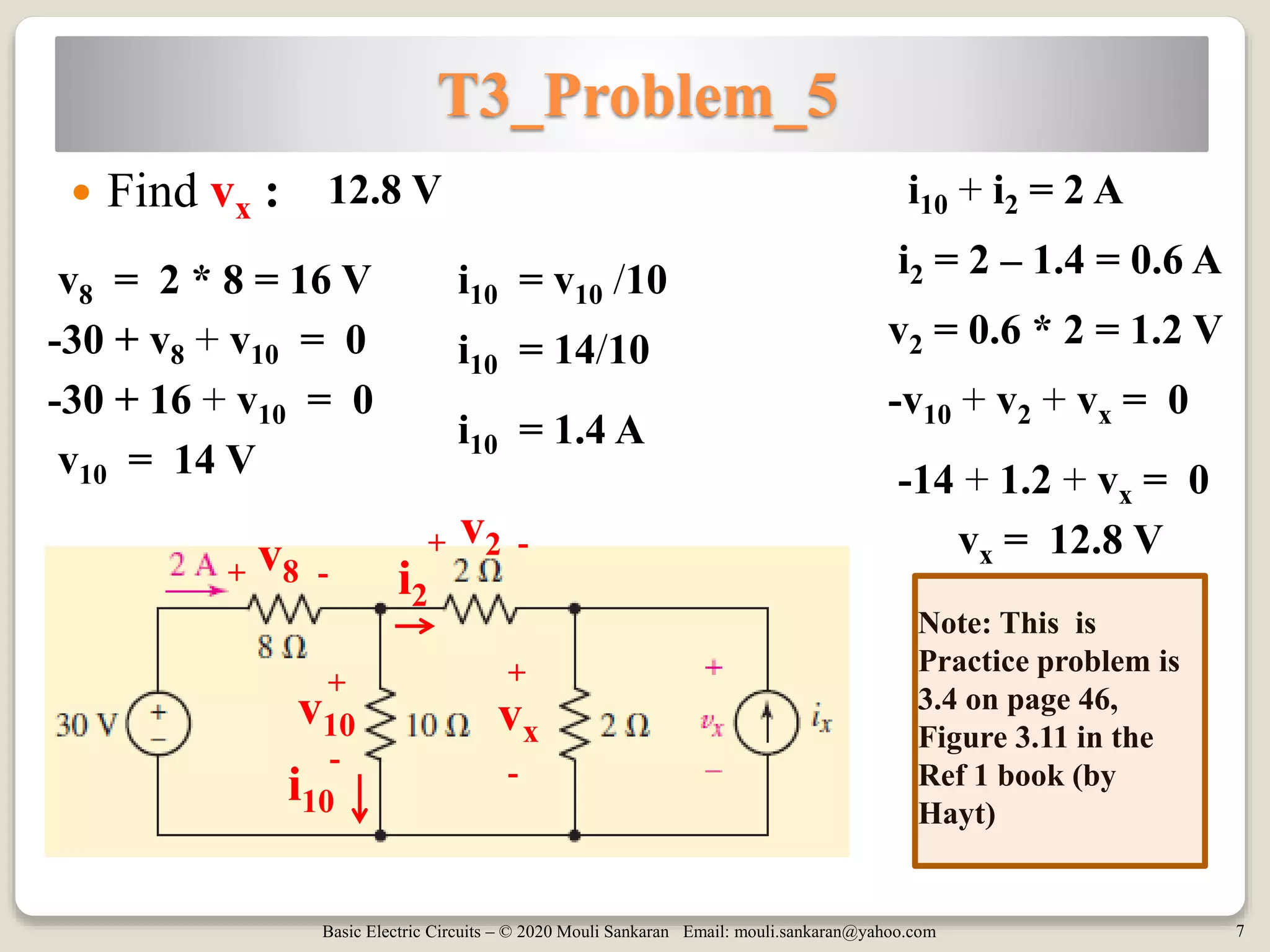
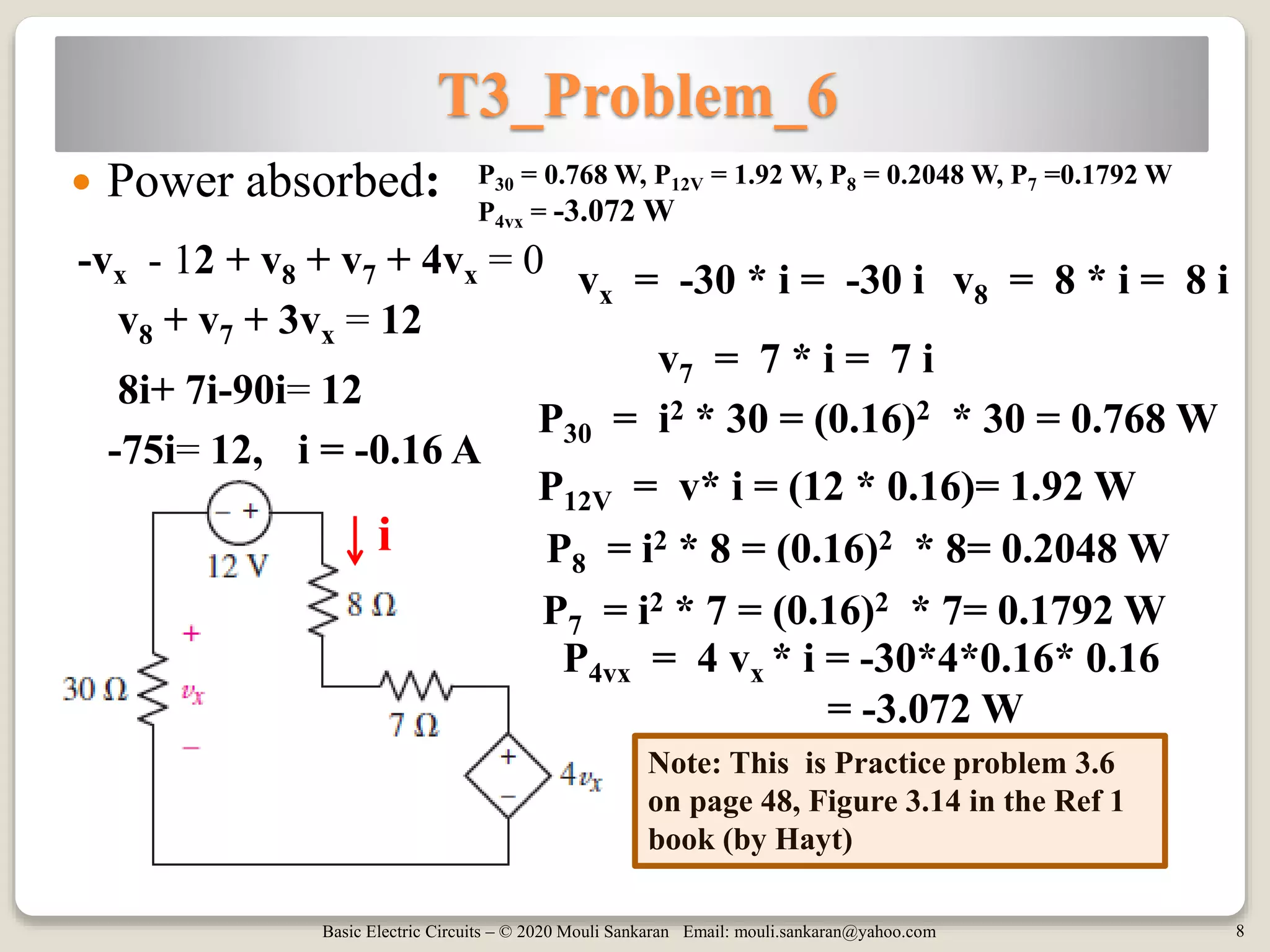
This document contains tutorials and practice problems related to applying Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) to solve for unknown voltages and currents in electric circuits. It includes 6 sample circuit problems where the key steps of writing KCL and KVL equations at nodes and around loops are demonstrated to find values such as the voltage across a resistor (vx), total circuit current (ix), or power dissipated by individual resistors. Diagrams illustrate the node-branch analysis method and solutions are provided for determining variables like resistance (RA) from given voltages and currents.